Ghost warehousing streamlines inventory management by utilizing unbranded storage spaces that retailers can access on-demand, reducing overhead costs and improving flexibility. The hub-and-spoke model centralizes distribution through a primary hub, optimizing transportation routes and enabling faster delivery to satellite locations. Explore the advantages and challenges of these logistics strategies to find the best fit for your supply chain needs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost warehousing and the hub-and-spoke model is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and cost management. Ghost warehousing involves outsourcing storage without physical possession, reducing overhead but potentially limiting control and responsiveness. The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in a main hub with distribution to satellite locations, enhancing delivery speed and inventory accuracy. This knowledge enables businesses to select the appropriate strategy for inventory control, scalability, and customer satisfaction.
Comparison Table
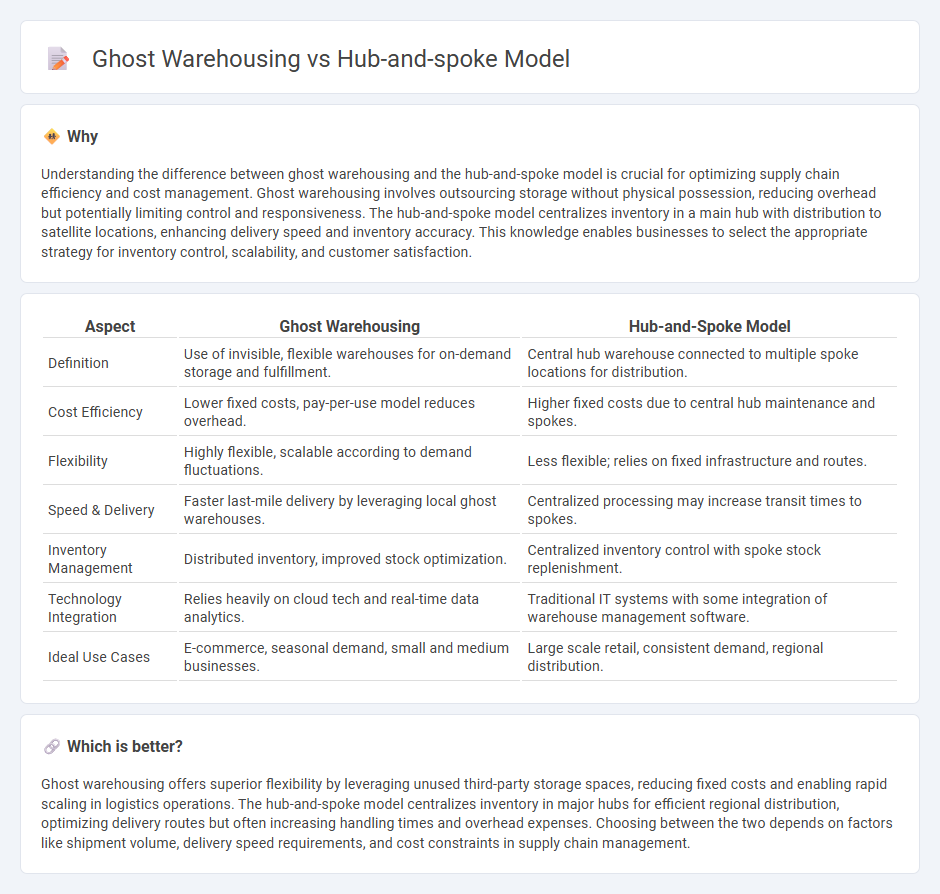
| Aspect | Ghost Warehousing | Hub-and-Spoke Model |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of invisible, flexible warehouses for on-demand storage and fulfillment. | Central hub warehouse connected to multiple spoke locations for distribution. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower fixed costs, pay-per-use model reduces overhead. | Higher fixed costs due to central hub maintenance and spokes. |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, scalable according to demand fluctuations. | Less flexible; relies on fixed infrastructure and routes. |
| Speed & Delivery | Faster last-mile delivery by leveraging local ghost warehouses. | Centralized processing may increase transit times to spokes. |
| Inventory Management | Distributed inventory, improved stock optimization. | Centralized inventory control with spoke stock replenishment. |
| Technology Integration | Relies heavily on cloud tech and real-time data analytics. | Traditional IT systems with some integration of warehouse management software. |
| Ideal Use Cases | E-commerce, seasonal demand, small and medium businesses. | Large scale retail, consistent demand, regional distribution. |
Which is better?
Ghost warehousing offers superior flexibility by leveraging unused third-party storage spaces, reducing fixed costs and enabling rapid scaling in logistics operations. The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in major hubs for efficient regional distribution, optimizing delivery routes but often increasing handling times and overhead expenses. Choosing between the two depends on factors like shipment volume, delivery speed requirements, and cost constraints in supply chain management.
Connection
Ghost warehousing enhances the hub-and-spoke model by optimizing inventory distribution and reducing delivery times through invisible, flexible storage locations near key hubs. This integration allows for real-time demand responsiveness and lowers operational costs by minimizing excess warehouse space. Leveraging ghost warehouses within the hub-and-spoke network streamlines last-mile delivery efficiency and improves overall supply chain agility.
Key Terms
### Hub-and-Spoke Model
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes inventory in a main hub, enabling efficient distribution to multiple spoke locations, reducing overall transportation costs and improving delivery speed. This system optimizes stock management by consolidating goods in a strategic hub, minimizing inventory holding at peripheral spokes while maintaining service levels. Explore the advantages and application strategies of the hub-and-spoke model to enhance your supply chain efficiency.
Centralized Distribution
The hub-and-spoke model centralizes distribution through a single hub where inventory is stored and then dispatched to spokes, optimizing delivery routes and reducing transportation costs. Ghost warehousing involves strategically located, unseen inventory storage points that enable rapid fulfillment without the typical overhead of traditional warehouses. Explore the advantages and operational differences between these centralized distribution strategies to enhance supply chain efficiency.
Spoke Nodes
Spoke nodes in a hub-and-spoke model serve as centralized distribution points that streamline logistics by consolidating inventory closer to demand centers, improving delivery speed and reducing transportation costs. In contrast, ghost warehousing assigns inventory to virtual or unstaffed locations, which may limit real-time inventory access but enhances flexibility and scalability in managing spoke nodes. Explore the distinct advantages of spoke node strategies in optimizing supply chain performance to make informed decisions.
Source and External Links
What is a Hub-and-Spoke Network: 9 Tips, Benefits & Limitations - The hub-and-spoke model is a centralized network structure where a central hub organization coordinates with several partner spokes, streamlining communication, decision-making, and resource allocation.
Spoke-hub distribution paradigm - Wikipedia - The hub-and-spoke system organizes routes or connections by linking spokes (outlying points) to a central hub; it was pioneered in commercial aviation by Delta Air Lines in 1955 to optimize transport topology.
Hub-spoke network topology in Azure - Azure Architecture Center - In cloud networking, the hub-spoke topology connects multiple spokes to a central hub for shared services, workload isolation, and centralized security control, commonly used in Azure environments.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com