Last yard delivery focuses on transporting goods from a local distribution center to the final customer, emphasizing speed and accuracy in urban areas. Drop shipping bypasses inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing warehousing costs but potentially increasing delivery times. Explore how these logistics strategies impact your supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
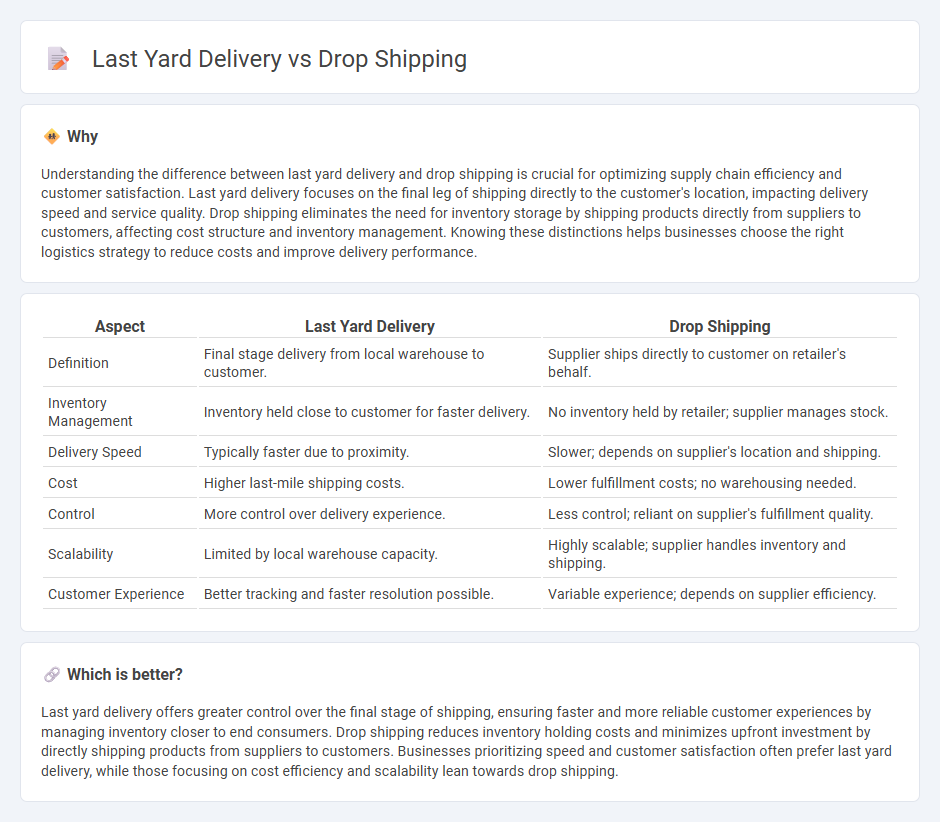
Understanding the difference between last yard delivery and drop shipping is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction. Last yard delivery focuses on the final leg of shipping directly to the customer's location, impacting delivery speed and service quality. Drop shipping eliminates the need for inventory storage by shipping products directly from suppliers to customers, affecting cost structure and inventory management. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses choose the right logistics strategy to reduce costs and improve delivery performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Last Yard Delivery | Drop Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Final stage delivery from local warehouse to customer. | Supplier ships directly to customer on retailer's behalf. |
| Inventory Management | Inventory held close to customer for faster delivery. | No inventory held by retailer; supplier manages stock. |
| Delivery Speed | Typically faster due to proximity. | Slower; depends on supplier's location and shipping. |
| Cost | Higher last-mile shipping costs. | Lower fulfillment costs; no warehousing needed. |
| Control | More control over delivery experience. | Less control; reliant on supplier's fulfillment quality. |
| Scalability | Limited by local warehouse capacity. | Highly scalable; supplier handles inventory and shipping. |
| Customer Experience | Better tracking and faster resolution possible. | Variable experience; depends on supplier efficiency. |
Which is better?
Last yard delivery offers greater control over the final stage of shipping, ensuring faster and more reliable customer experiences by managing inventory closer to end consumers. Drop shipping reduces inventory holding costs and minimizes upfront investment by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers. Businesses prioritizing speed and customer satisfaction often prefer last yard delivery, while those focusing on cost efficiency and scalability lean towards drop shipping.
Connection
Last yard delivery and drop shipping are connected through their focus on optimizing the final stages of the supply chain to enhance customer satisfaction. Last yard delivery handles the transportation of goods from local distribution centers directly to the end consumer, while drop shipping enables retailers to ship products directly from suppliers to customers without holding inventory. This synergy reduces delivery times, lowers logistics costs, and improves efficiency in order fulfillment.
Key Terms
Inventory Ownership
Drop shipping eliminates inventory ownership by transferring product storage and management responsibilities to the supplier, reducing upfront costs and risks for retailers. Last yard delivery maintains retailer control over inventory until the final delivery phase, allowing for better quality assurance and quicker response to customer demands. Explore the key differences in inventory ownership to optimize your supply chain strategy effectively.
Delivery Responsibility
Dropshipping shifts delivery responsibility to the supplier, who manages inventory and ships products directly to customers, minimizing risk for the retailer. Last yard delivery involves the retailer or logistics provider handling the final stage of transport, ensuring control over customer experience and delivery accuracy. Explore these delivery strategies further to determine the best fit for your business model.
Customer Proximity
Drop shipping minimizes inventory holding by shipping products directly from suppliers, often resulting in longer delivery times and less customer proximity. Last yard delivery emphasizes final-mile logistics, ensuring faster, localized delivery and enhanced customer experience through proximity-focused distribution centers. Explore how these strategies impact your supply chain efficiency and customer satisfaction in detail.
Source and External Links
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail business model where the seller accepts orders without keeping inventory, forwarding orders to suppliers who ship directly to customers, allowing sellers to avoid warehousing costs but offering lower profit margins and less control over quality and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping involves an online store partnering with suppliers who handle storage, packaging, and shipping; the retailer markets products, receives orders, forwards them to the supplier, who ships the items directly to customers.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment method where the seller does not own inventory but sells products from a third party who handles production, warehousing, and shipping while the seller focuses on marketing and storefront management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com