Middle mile automation focuses on optimizing the transportation and transfer of goods between distribution centers using technologies like autonomous vehicles and advanced routing algorithms. Warehouse automation enhances storage, picking, and packing efficiency through robotics, conveyor systems, and AI-driven inventory management. Explore how these automation strategies revolutionize supply chain efficiency and cost reduction.
Why it is important
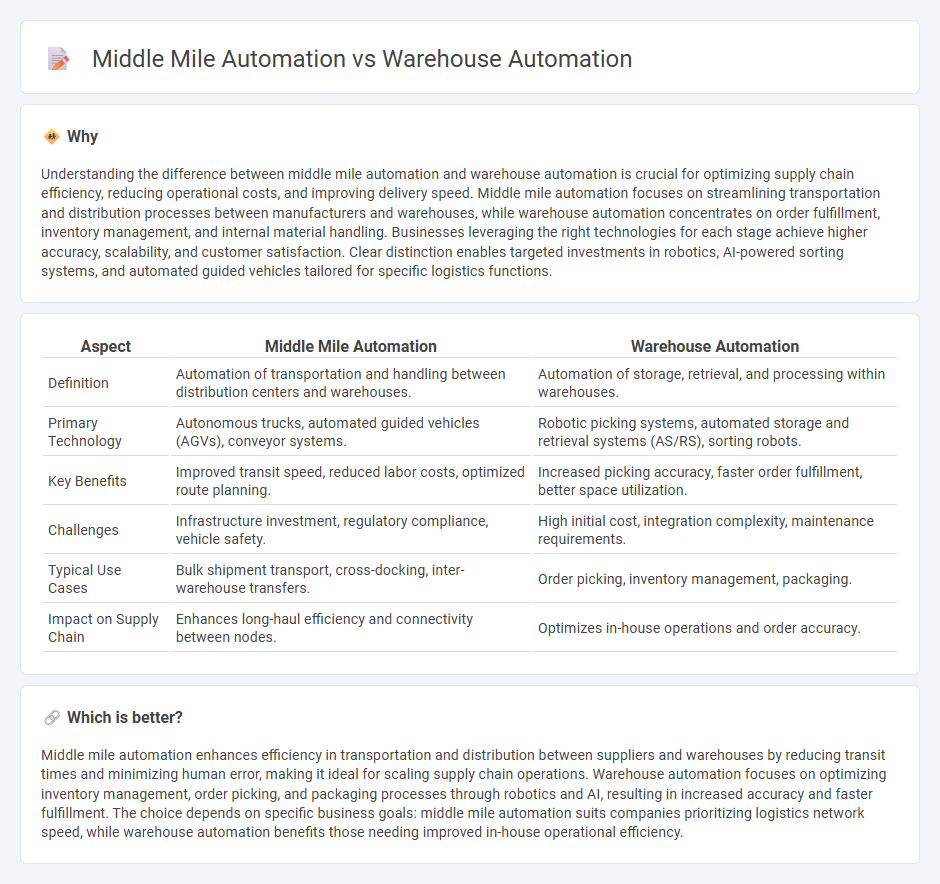
Understanding the difference between middle mile automation and warehouse automation is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency, reducing operational costs, and improving delivery speed. Middle mile automation focuses on streamlining transportation and distribution processes between manufacturers and warehouses, while warehouse automation concentrates on order fulfillment, inventory management, and internal material handling. Businesses leveraging the right technologies for each stage achieve higher accuracy, scalability, and customer satisfaction. Clear distinction enables targeted investments in robotics, AI-powered sorting systems, and automated guided vehicles tailored for specific logistics functions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Middle Mile Automation | Warehouse Automation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automation of transportation and handling between distribution centers and warehouses. | Automation of storage, retrieval, and processing within warehouses. |
| Primary Technology | Autonomous trucks, automated guided vehicles (AGVs), conveyor systems. | Robotic picking systems, automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), sorting robots. |
| Key Benefits | Improved transit speed, reduced labor costs, optimized route planning. | Increased picking accuracy, faster order fulfillment, better space utilization. |
| Challenges | Infrastructure investment, regulatory compliance, vehicle safety. | High initial cost, integration complexity, maintenance requirements. |
| Typical Use Cases | Bulk shipment transport, cross-docking, inter-warehouse transfers. | Order picking, inventory management, packaging. |
| Impact on Supply Chain | Enhances long-haul efficiency and connectivity between nodes. | Optimizes in-house operations and order accuracy. |
Which is better?
Middle mile automation enhances efficiency in transportation and distribution between suppliers and warehouses by reducing transit times and minimizing human error, making it ideal for scaling supply chain operations. Warehouse automation focuses on optimizing inventory management, order picking, and packaging processes through robotics and AI, resulting in increased accuracy and faster fulfillment. The choice depends on specific business goals: middle mile automation suits companies prioritizing logistics network speed, while warehouse automation benefits those needing improved in-house operational efficiency.
Connection
Middle mile automation enhances the efficiency of transporting goods between distribution centers, directly impacting warehouse automation by ensuring timely, accurate inventory flow. Warehouse automation relies on seamless middle mile operations to optimize sorting, storage, and order fulfillment systems using robotics, IoT, and AI-driven software. Integrating these technologies reduces delays, lowers operational costs, and improves supply chain visibility across logistics networks.
Key Terms
**Warehouse Automation:**
Warehouse automation employs robotics, conveyor systems, and AI-driven inventory management to streamline order fulfillment, reduce labor costs, and improve accuracy within the storage facility. Integrating automated picking and packing solutions minimizes human error and accelerates throughput in e-commerce and retail supply chains. Explore how warehouse automation transforms operational efficiency and customer satisfaction in modern logistics.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) play a critical role in warehouse automation by enhancing inventory management, reducing labor costs, and increasing storage density through precise robotic handling of goods. In middle mile automation, AS/RS optimize the flow of products between manufacturing and distribution centers, improving throughput and minimizing errors during sorting and staging processes. Explore how AS/RS technology transforms supply chain efficiency in both warehouse and middle mile operations.
Goods-to-Person (GTP) Technology
Goods-to-Person (GTP) technology revolutionizes warehouse automation by streamlining order fulfillment processes, reducing human error, and enhancing operational efficiency through automated retrieval systems. Middle mile automation, while also increasing throughput, emphasizes the transportation and sorting of goods between warehouses and distribution centers, relying more on autonomous vehicles and conveyor systems. Discover how integrating GTP technology can optimize your supply chain workflow and boost productivity.
Source and External Links
Warehouse Automation Explained: Trends, Types & Best Practices - Warehouse automation automates the movement of inventory into, within, and out of warehouses with minimal human help, and implementation involves steps such as forming an expert committee, collecting critical data, evaluating inventory controls, implementing warehouse management systems (WMS), and defining the type of automation needed based on goals and customer demand.
13 Warehouse Automation Trends in 2025 - Conger Industries - Successfully implementing warehouse automation requires careful preparation including feasibility studies, clear goal setting, budget planning, stakeholder involvement, selecting tailored hardware like ASRS and robots, and software to integrate with existing systems for optimized operations.
Warehouse Automation | SSI SCHAEFER - Warehouse automation uses technologies such as robotics, conveyor belts, automated guided vehicles, and software systems to streamline storage, picking, packing, and shipping processes, increasing efficiency, reducing labor, and improving productivity with key components including Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS).
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com