Hyper-local delivery focuses on the rapid transportation of goods within a limited geographic area, ensuring faster delivery times and enhanced customer satisfaction. Drop-shipping, by contrast, eliminates the need for inventory holding by directly shipping products from suppliers to customers, reducing upfront costs and storage requirements. Explore the key differences and benefits to determine the best logistics strategy for your business.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between hyper-local delivery and drop-shipping ensures businesses optimize supply chain efficiency and cost management. Hyper-local delivery enables rapid order fulfillment within a limited geographic area, enhancing customer satisfaction through faster delivery times. Drop-shipping allows retailers to sell products without holding inventory, reducing overhead but increasing reliance on suppliers' fulfillment efficiency. Mastering these models empowers companies to tailor logistics strategies for improved operational performance and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
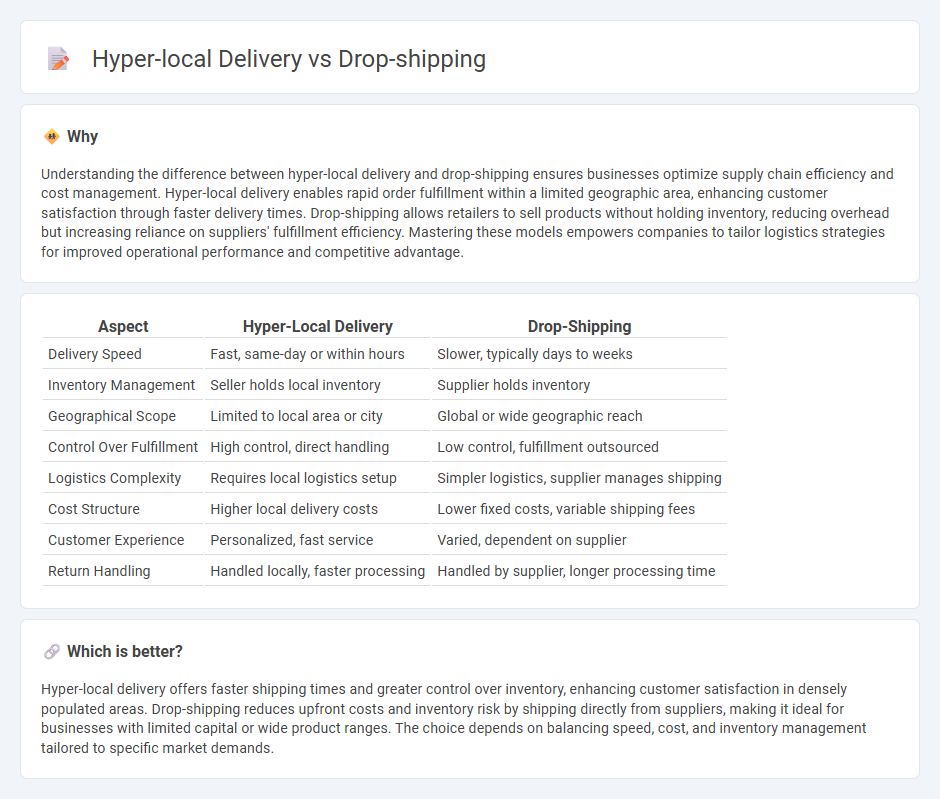
| Aspect | Hyper-Local Delivery | Drop-Shipping |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Speed | Fast, same-day or within hours | Slower, typically days to weeks |
| Inventory Management | Seller holds local inventory | Supplier holds inventory |
| Geographical Scope | Limited to local area or city | Global or wide geographic reach |
| Control Over Fulfillment | High control, direct handling | Low control, fulfillment outsourced |
| Logistics Complexity | Requires local logistics setup | Simpler logistics, supplier manages shipping |
| Cost Structure | Higher local delivery costs | Lower fixed costs, variable shipping fees |
| Customer Experience | Personalized, fast service | Varied, dependent on supplier |
| Return Handling | Handled locally, faster processing | Handled by supplier, longer processing time |
Which is better?
Hyper-local delivery offers faster shipping times and greater control over inventory, enhancing customer satisfaction in densely populated areas. Drop-shipping reduces upfront costs and inventory risk by shipping directly from suppliers, making it ideal for businesses with limited capital or wide product ranges. The choice depends on balancing speed, cost, and inventory management tailored to specific market demands.
Connection
Hyper-local delivery and drop-shipping are interconnected through their focus on minimizing inventory held by retailers while enabling fast fulfillment to end customers. Hyper-local delivery leverages local warehouses or stores to quickly dispatch goods within a confined geographic area, complementing drop-shipping's direct shipment model from suppliers to consumers without intermediary stock. This synergy enhances supply chain efficiency, reduces delivery times, and lowers last-mile shipping costs in the logistics sector.
Key Terms
Inventory ownership
Drop-shipping eliminates inventory ownership by having suppliers directly ship products to customers, reducing storage costs and risks for retailers. Hyper-local delivery requires businesses to maintain and own inventory within a localized area, enabling faster fulfillment and better control over stock quality. Explore the differences in inventory management to choose the best model for your business needs.
Delivery radius
Drop-shipping typically operates with a broad delivery radius, often nationwide or international, leveraging third-party suppliers to ship products directly to customers without holding inventory. Hyper-local delivery concentrates on a limited delivery radius, usually within a few miles, emphasizing speed and convenience by sourcing products from nearby stores or warehouses. Explore the advantages and logistics of each model to determine which delivery radius strategy suits your business needs.
Fulfillment speed
Drop-shipping relies on third-party suppliers to ship products directly to customers, often resulting in longer fulfillment times due to geographic distance and inventory dependencies. Hyper-local delivery emphasizes ultra-fast fulfillment by sourcing products from nearby stores or warehouses, typically enabling same-day or next-day delivery. Explore how these fulfillment speed differences impact customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail business model where the seller accepts customer orders without keeping stock, instead transferring orders to a third party (manufacturer, wholesaler, or fulfillment house) who ships directly to the customer, allowing minimal investment and overhead but with less control over product quality and shipping.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping involves partnering with suppliers who store and ship products; the seller creates an online store to sell these products, forwards orders to suppliers after customer purchases, and the suppliers ship directly to customers, facilitating low upfront costs and automated order management.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a fulfillment model in which the merchant sets up an online store, markets products they don't stock, and upon receiving customer orders, purchases inventory from a third party who handles the shipping directly to customers, allowing retailers to avoid inventory management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com