Milk run delivery streamlines transportation by consolidating multiple shipments into a single route, reducing fuel costs and improving delivery efficiency. Decentralized distribution disperses inventory across various local warehouses, enhancing responsiveness and minimizing lead times to customers. Explore how these logistics strategies can optimize your supply chain performance.
Why it is important
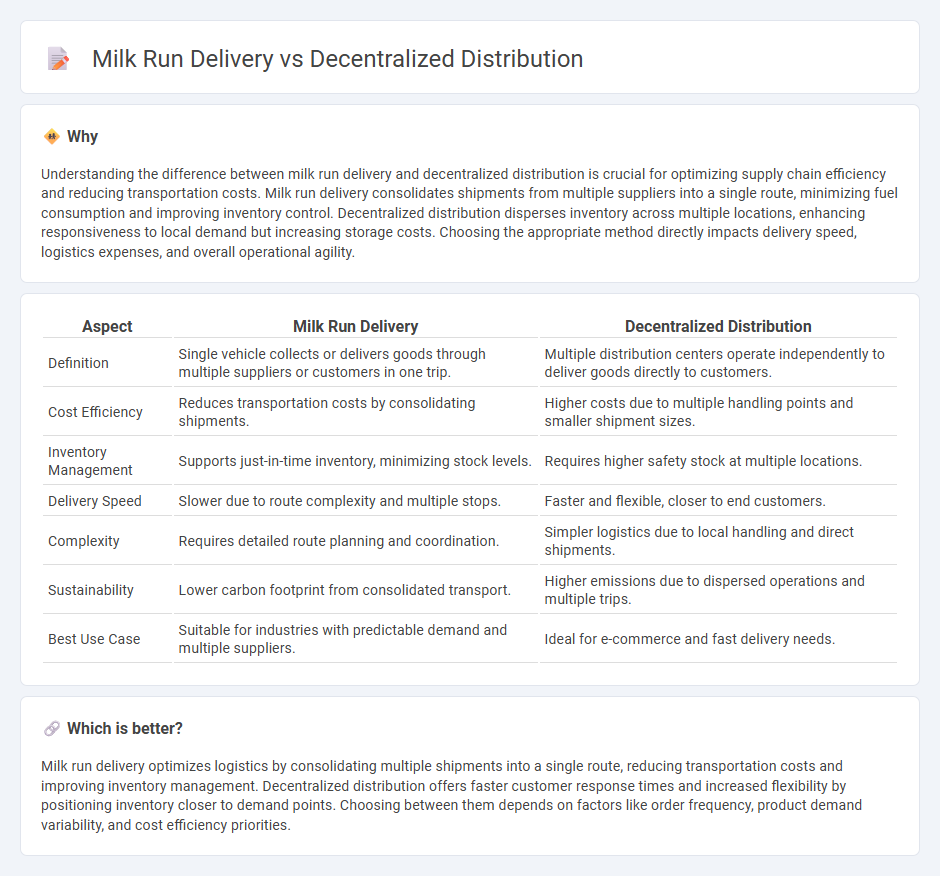
Understanding the difference between milk run delivery and decentralized distribution is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Milk run delivery consolidates shipments from multiple suppliers into a single route, minimizing fuel consumption and improving inventory control. Decentralized distribution disperses inventory across multiple locations, enhancing responsiveness to local demand but increasing storage costs. Choosing the appropriate method directly impacts delivery speed, logistics expenses, and overall operational agility.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Milk Run Delivery | Decentralized Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Single vehicle collects or delivers goods through multiple suppliers or customers in one trip. | Multiple distribution centers operate independently to deliver goods directly to customers. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduces transportation costs by consolidating shipments. | Higher costs due to multiple handling points and smaller shipment sizes. |
| Inventory Management | Supports just-in-time inventory, minimizing stock levels. | Requires higher safety stock at multiple locations. |
| Delivery Speed | Slower due to route complexity and multiple stops. | Faster and flexible, closer to end customers. |
| Complexity | Requires detailed route planning and coordination. | Simpler logistics due to local handling and direct shipments. |
| Sustainability | Lower carbon footprint from consolidated transport. | Higher emissions due to dispersed operations and multiple trips. |
| Best Use Case | Suitable for industries with predictable demand and multiple suppliers. | Ideal for e-commerce and fast delivery needs. |
Which is better?
Milk run delivery optimizes logistics by consolidating multiple shipments into a single route, reducing transportation costs and improving inventory management. Decentralized distribution offers faster customer response times and increased flexibility by positioning inventory closer to demand points. Choosing between them depends on factors like order frequency, product demand variability, and cost efficiency priorities.
Connection
Milk run delivery optimizes logistics by consolidating multiple shipments into a single route, reducing transportation costs and improving efficiency. Decentralized distribution complements this method by positioning inventory closer to end customers, enabling frequent, smaller deliveries that maintain product freshness and responsiveness. Together, they enhance supply chain agility and reduce lead times in logistics operations.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Decentralized distribution reduces inventory holding costs by placing stock closer to demand points, enabling faster replenishment and minimizing stockouts. Milk run delivery optimizes inventory by consolidating shipments into a single route, improving supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation expenses. Explore the advantages of each method to enhance your inventory management strategy.
Route Optimization
Decentralized distribution and milk run delivery differ significantly in route optimization strategies; decentralized distribution employs multiple direct routes from several warehouses to customers, enhancing flexibility and reducing transportation time. Milk run delivery optimizes routes by combining multiple shipments into a single loop, minimizing travel distance and improving load efficiency. Explore detailed comparisons and case studies on route optimization for both methods to enhance your logistics strategy.
Distribution Nodes
Decentralized distribution leverages multiple distribution nodes strategically placed closer to end consumers, reducing transportation distances and enhancing delivery speed. Milk run delivery consolidates shipments from these nodes, optimizing routes and lowering overall logistics costs through scheduled, repetitive supply pickups. Explore detailed comparisons to optimize your supply chain strategy effectively.
Source and External Links
Centralized vs. Decentralized Distribution Network: Which is More Efficient for FMCG Supply Chains? - Decentralized distribution involves multiple distribution centers serving specific regions, enabling faster lead times, lower risk of disruptions, and greater flexibility to adapt to local market demands, as exemplified by companies like Coca-Cola and Walmart.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Centralized and Decentralized Distribution? - Decentralized distribution spreads warehouses across regions closer to consumers, improves delivery speed and customer service, allows local decision-making, but may incur higher downstream shipping costs and longer transport times for distant areas.
Centralized vs. Decentralized Logistics: Which One is Right For Your Business? - Decentralized logistics disperses operations across multiple autonomous centers tailored to local market conditions, improving flexibility, responsiveness, and capability to meet diverse regional demand while simplifying management through unified platforms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com