Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics streamlines repetitive tasks such as order processing, shipment tracking, and invoice management, enhancing operational efficiency beyond traditional Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) that focus primarily on inventory control and warehouse operations. While WMS optimizes physical storage and material handling, RPA integrates seamlessly with various enterprise systems to automate end-to-end workflows, reducing errors and labor costs. Explore the transformative impact of RPA on logistics workflows and how it complements WMS capabilities.
Why it is important
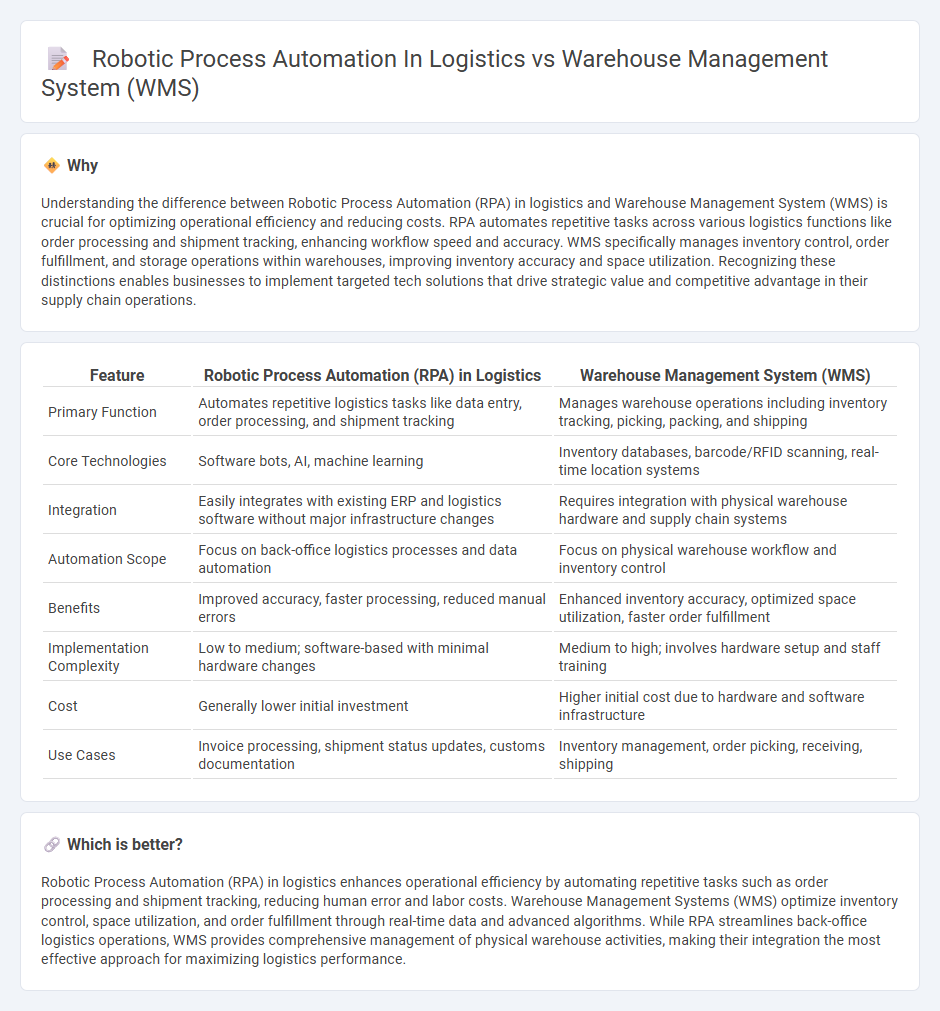
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics and Warehouse Management System (WMS) is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and reducing costs. RPA automates repetitive tasks across various logistics functions like order processing and shipment tracking, enhancing workflow speed and accuracy. WMS specifically manages inventory control, order fulfillment, and storage operations within warehouses, improving inventory accuracy and space utilization. Recognizing these distinctions enables businesses to implement targeted tech solutions that drive strategic value and competitive advantage in their supply chain operations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Warehouse Management System (WMS) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Automates repetitive logistics tasks like data entry, order processing, and shipment tracking | Manages warehouse operations including inventory tracking, picking, packing, and shipping |
| Core Technologies | Software bots, AI, machine learning | Inventory databases, barcode/RFID scanning, real-time location systems |
| Integration | Easily integrates with existing ERP and logistics software without major infrastructure changes | Requires integration with physical warehouse hardware and supply chain systems |
| Automation Scope | Focus on back-office logistics processes and data automation | Focus on physical warehouse workflow and inventory control |
| Benefits | Improved accuracy, faster processing, reduced manual errors | Enhanced inventory accuracy, optimized space utilization, faster order fulfillment |
| Implementation Complexity | Low to medium; software-based with minimal hardware changes | Medium to high; involves hardware setup and staff training |
| Cost | Generally lower initial investment | Higher initial cost due to hardware and software infrastructure |
| Use Cases | Invoice processing, shipment status updates, customs documentation | Inventory management, order picking, receiving, shipping |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing and shipment tracking, reducing human error and labor costs. Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) optimize inventory control, space utilization, and order fulfillment through real-time data and advanced algorithms. While RPA streamlines back-office logistics operations, WMS provides comprehensive management of physical warehouse activities, making their integration the most effective approach for maximizing logistics performance.
Connection
Robotic process automation (RPA) enhances logistics and warehouse management systems (WMS) by streamlining repetitive tasks such as inventory tracking, order processing, and shipment scheduling. The integration of RPA with WMS improves operational efficiency, reduces human errors, and accelerates data handling, leading to optimized supply chain workflows. Automation technologies enable real-time inventory visibility and faster decision-making, significantly boosting warehouse productivity and accuracy.
Key Terms
Inventory Control (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) provide real-time inventory tracking, precise stock level management, and streamlined order fulfillment to enhance accuracy and reduce discrepancies. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics automates repetitive tasks such as data entry and shipment processing, but it does not directly control physical inventory like a WMS. Discover how integrating WMS with RPA can revolutionize inventory control efficiency in your supply chain.
Order Fulfillment (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) streamline order fulfillment by optimizing inventory tracking, picking processes, and real-time shipment status updates, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in logistics operations. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) complements WMS by automating repetitive tasks such as data entry and order processing, reducing errors but lacking direct inventory control capabilities. Explore how integrating WMS and RPA technologies can revolutionize your order fulfillment strategy for improved productivity and customer satisfaction.
Workflow Automation (RPA)
Warehouse Management System (WMS) streamlines inventory tracking, order fulfillment, and real-time data management within warehouses, boosting operational efficiency. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances logistics by automating repetitive workflows such as data entry, shipment scheduling, and invoicing across multiple systems without manual intervention. Explore how combining WMS and RPA can revolutionize logistics workflow automation for greater accuracy and productivity.
Source and External Links
What is a WMS? | Warehouse Management System - Extensiv - A Warehouse Management System (WMS) is software that manages all daily warehouse operations including labor management, pick efficiency, real-time inventory tracking, shipping, order fulfillment, and reporting to optimize productivity and profit margins.
What is WMS (Warehouse Management System)? - Oracle - A WMS provides visibility into inventory and supply chain fulfillment, maximizing labor and space utilization by coordinating resources and material flows, and supports dynamic omnichannel fulfillment with real-time data accessible via internet-connected devices.
Warehouse management system - Wikipedia - A WMS is a set of policies and processes, usually supported by software, that organize warehouse operations to improve efficiency by tracking inventory arrival/departure, optimizing space, coordinating tasks, and enhancing order delivery and returns management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com