Empty miles reduction focuses on minimizing distance traveled without cargo, thereby enhancing fuel efficiency and reducing operational costs. Collaborative transportation leverages shared freight capacity among multiple carriers to optimize route utilization and decrease overall emissions. Explore techniques and technologies driving these innovative logistics strategies for improved supply chain sustainability.
Why it is important
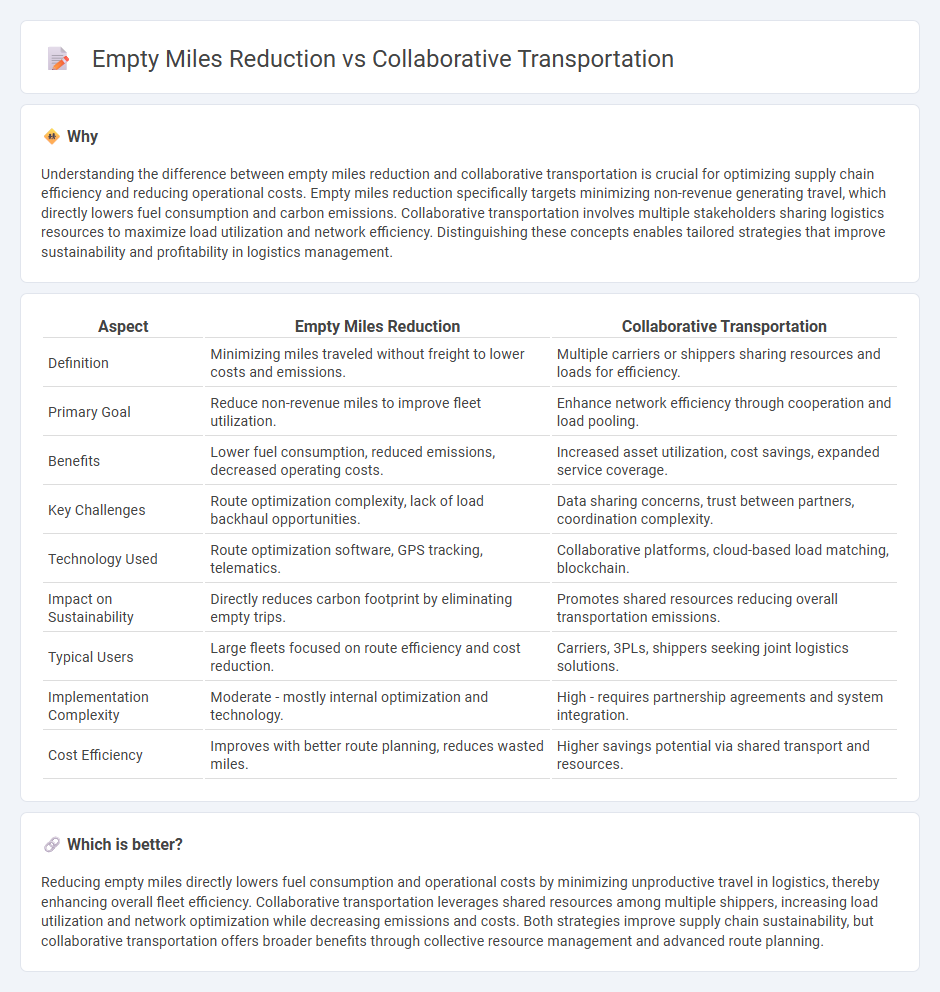
Understanding the difference between empty miles reduction and collaborative transportation is crucial for optimizing supply chain efficiency and reducing operational costs. Empty miles reduction specifically targets minimizing non-revenue generating travel, which directly lowers fuel consumption and carbon emissions. Collaborative transportation involves multiple stakeholders sharing logistics resources to maximize load utilization and network efficiency. Distinguishing these concepts enables tailored strategies that improve sustainability and profitability in logistics management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Empty Miles Reduction | Collaborative Transportation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Minimizing miles traveled without freight to lower costs and emissions. | Multiple carriers or shippers sharing resources and loads for efficiency. |
| Primary Goal | Reduce non-revenue miles to improve fleet utilization. | Enhance network efficiency through cooperation and load pooling. |
| Benefits | Lower fuel consumption, reduced emissions, decreased operating costs. | Increased asset utilization, cost savings, expanded service coverage. |
| Key Challenges | Route optimization complexity, lack of load backhaul opportunities. | Data sharing concerns, trust between partners, coordination complexity. |
| Technology Used | Route optimization software, GPS tracking, telematics. | Collaborative platforms, cloud-based load matching, blockchain. |
| Impact on Sustainability | Directly reduces carbon footprint by eliminating empty trips. | Promotes shared resources reducing overall transportation emissions. |
| Typical Users | Large fleets focused on route efficiency and cost reduction. | Carriers, 3PLs, shippers seeking joint logistics solutions. |
| Implementation Complexity | Moderate - mostly internal optimization and technology. | High - requires partnership agreements and system integration. |
| Cost Efficiency | Improves with better route planning, reduces wasted miles. | Higher savings potential via shared transport and resources. |
Which is better?
Reducing empty miles directly lowers fuel consumption and operational costs by minimizing unproductive travel in logistics, thereby enhancing overall fleet efficiency. Collaborative transportation leverages shared resources among multiple shippers, increasing load utilization and network optimization while decreasing emissions and costs. Both strategies improve supply chain sustainability, but collaborative transportation offers broader benefits through collective resource management and advanced route planning.
Connection
Empty miles reduction and collaborative transportation are closely connected through the optimization of freight routes and shared carrier capacities, which minimizes unnecessary vehicle travel without cargo. By leveraging collaborative platforms, multiple shippers coordinate shipments to fill trucks more efficiently, directly reducing empty miles and lowering transportation costs. Enhanced data sharing and route planning technologies enable real-time load matching, significantly improving operational efficiency across supply chains.
Key Terms
Freight Consolidation
Collaborative transportation leverages shared freight capacity across multiple shippers to maximize load efficiency, while empty miles reduction targets minimizing trips without cargo, directly cutting operational costs and emissions. Freight consolidation plays a crucial role by combining partial shipments into full loads, enhancing vehicle utilization and reducing both empty miles and overall transportation spend. Explore advanced freight consolidation strategies to optimize your supply chain and boost sustainability.
Backhauling
Backhauling in collaborative transportation significantly reduces empty miles by strategically combining outbound and return shipments, maximizing truck utilization and cutting operational costs. Leveraging digital platforms for load matching enhances coordination among carriers, promoting sustainability through lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions. Discover more about how backhauling optimizes transport efficiency and benefits logistics networks.
Load Matching
Collaborative transportation leverages shared logistics platforms to optimize load matching, significantly reducing empty miles by connecting carriers with complementary shipments. Load matching algorithms enhance route efficiency, decrease fuel consumption, and lower transportation costs by minimizing unproductive travel distances. Explore the latest strategies in load matching technology to maximize empty miles reduction and improve supply chain sustainability.
Source and External Links
What is collaborative transport in logistics and how can it ... - Collaborative transportation in logistics involves sharing resources like vehicles and routes among different companies, resulting in lower transportation costs, optimized vehicle load capacity, increased sustainability by reducing CO2 emissions, agile demand adaptation, and more efficient use of technology like TMS software.
A fresh new take on collaborative transport mgmt - Collaborative transportation management is a strategy synchronizing transportation activities between carriers, shippers, and other stakeholders through real-time data sharing, integrated processes, and technology to cut costs, improve service levels, and reduce environmental impact.
Collaborative Logistics: The Who, What, Why and How -- ... - Collaborative logistics refers to competitors or suppliers working together through a neutral third party to optimize load utilization and service common customers, generating significant cost savings and improved service levels through complex software coordination.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com