Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics enhances operational efficiency by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing and shipment tracking, reducing human error and accelerating workflows. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) facilitates seamless data exchange between supply chain partners through standardized electronic formats, ensuring accurate and timely communication of orders, invoices, and shipment details. Discover how integrating RPA and EDI can transform logistics operations and boost supply chain performance.
Why it is important
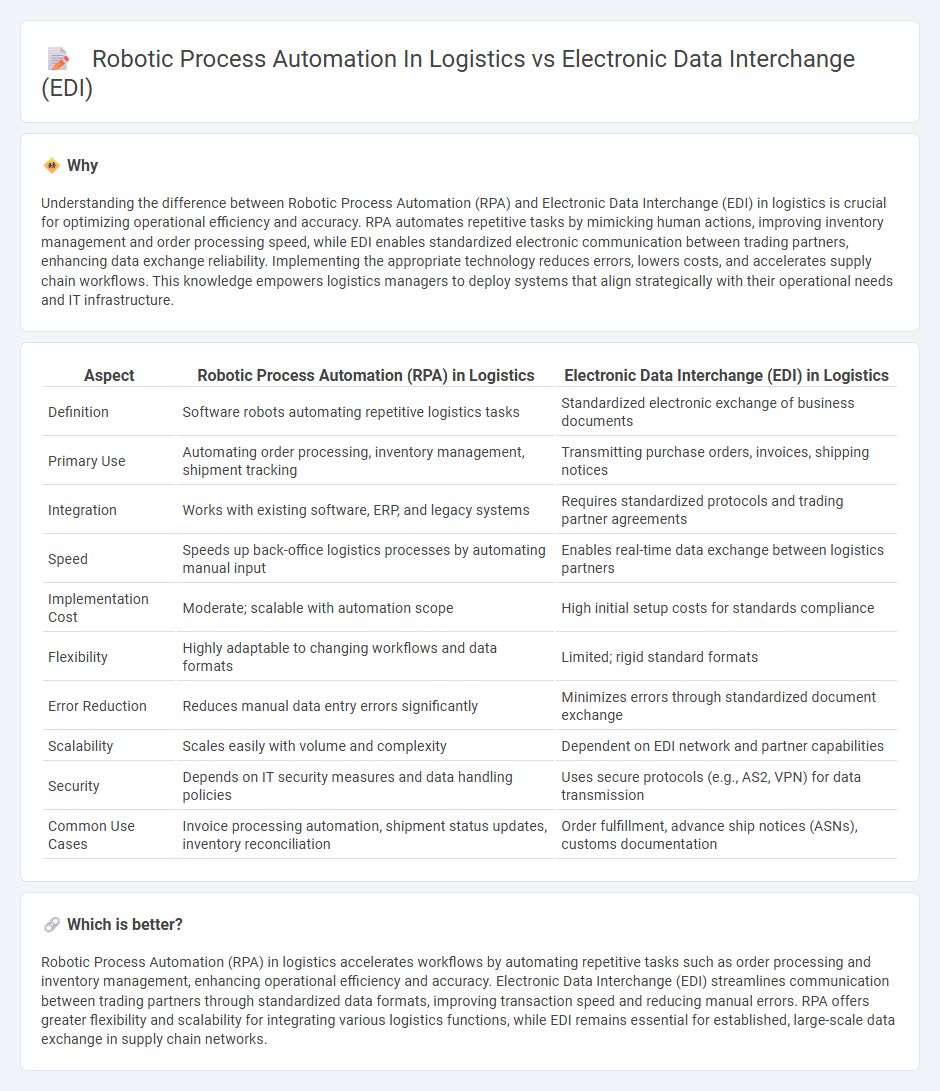
Understanding the difference between Robotic Process Automation (RPA) and Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in logistics is crucial for optimizing operational efficiency and accuracy. RPA automates repetitive tasks by mimicking human actions, improving inventory management and order processing speed, while EDI enables standardized electronic communication between trading partners, enhancing data exchange reliability. Implementing the appropriate technology reduces errors, lowers costs, and accelerates supply chain workflows. This knowledge empowers logistics managers to deploy systems that align strategically with their operational needs and IT infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in Logistics | Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) in Logistics |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Software robots automating repetitive logistics tasks | Standardized electronic exchange of business documents |
| Primary Use | Automating order processing, inventory management, shipment tracking | Transmitting purchase orders, invoices, shipping notices |
| Integration | Works with existing software, ERP, and legacy systems | Requires standardized protocols and trading partner agreements |
| Speed | Speeds up back-office logistics processes by automating manual input | Enables real-time data exchange between logistics partners |
| Implementation Cost | Moderate; scalable with automation scope | High initial setup costs for standards compliance |
| Flexibility | Highly adaptable to changing workflows and data formats | Limited; rigid standard formats |
| Error Reduction | Reduces manual data entry errors significantly | Minimizes errors through standardized document exchange |
| Scalability | Scales easily with volume and complexity | Dependent on EDI network and partner capabilities |
| Security | Depends on IT security measures and data handling policies | Uses secure protocols (e.g., AS2, VPN) for data transmission |
| Common Use Cases | Invoice processing automation, shipment status updates, inventory reconciliation | Order fulfillment, advance ship notices (ASNs), customs documentation |
Which is better?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) in logistics accelerates workflows by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing and inventory management, enhancing operational efficiency and accuracy. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) streamlines communication between trading partners through standardized data formats, improving transaction speed and reducing manual errors. RPA offers greater flexibility and scalability for integrating various logistics functions, while EDI remains essential for established, large-scale data exchange in supply chain networks.
Connection
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) streamlines logistics operations by automating repetitive tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and shipment tracking. Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) facilitates seamless communication between supply chain partners, enabling the automated exchange of transaction data like purchase orders and invoices. Integrating RPA with EDI enhances data accuracy, reduces manual errors, and accelerates logistics workflows for improved operational efficiency.
Key Terms
Data Integration
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) facilitates standardized data integration by enabling the automated transfer of structured business documents between logistics partners, ensuring accuracy and compliance across supply chain systems. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances data integration by automating repetitive tasks, such as data entry and validation, allowing seamless interaction between disparate legacy systems without requiring complex coding. Explore detailed comparisons and case studies to better understand the impact of EDI and RPA on logistics data integration.
Process Automation
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) streamlines logistics by enabling the automated exchange of standardized business documents, reducing manual data entry and errors in supply chain transactions. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances process automation by mimicking human actions to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks across various systems without changing existing infrastructure. Explore the key differences and applications of EDI and RPA in logistics process automation to optimize your operations.
Transaction Speed
Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) enables standardized, high-volume transaction processing in logistics with consistent speed, facilitating seamless communication between trading partners. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) enhances transaction speed by automating manual data entry and exception handling, accelerating processes without altering the underlying communication protocols. Explore how integrating EDI and RPA can optimize transaction speed and efficiency in your logistics operations.
Source and External Links
Electronic data interchange - Wikipedia - Electronic data interchange (EDI) is the computer-to-computer transfer of standardized business documents like purchase orders and invoices, replacing traditional paper communication to enable automated data exchange without human intervention, based on agreed technical standards such as X12 and EDIFACT.
What is Electronic Data Interchange (EDI)? - TechTarget - EDI is the standardized electronic data transfer between computer systems of businesses, allowing automated exchange of documents like orders and invoices without human processing, often using the internet or other networks and relying on mutual adherence to EDI standards for message formatting.
What is EDI (Electronic Data Interchange)? | EDI Basics - Electronic Data Interchange enables direct computer-to-computer exchange of business documents in a standard digital format, eliminating paper and manual handling to reduce errors and speed up processing of common documents like purchase orders, advance ship notices, and invoices between trading partners.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com