Cold chain management ensures the temperature-controlled supply of perishable goods from origin to destination, maintaining product integrity and compliance with safety standards. Customs brokerage facilitates the smooth clearance of shipments across international borders by managing documentation, duties, and regulatory requirements. Explore the critical differences and integrations between cold chain management and customs brokerage to optimize your global logistics strategy.
Why it is important
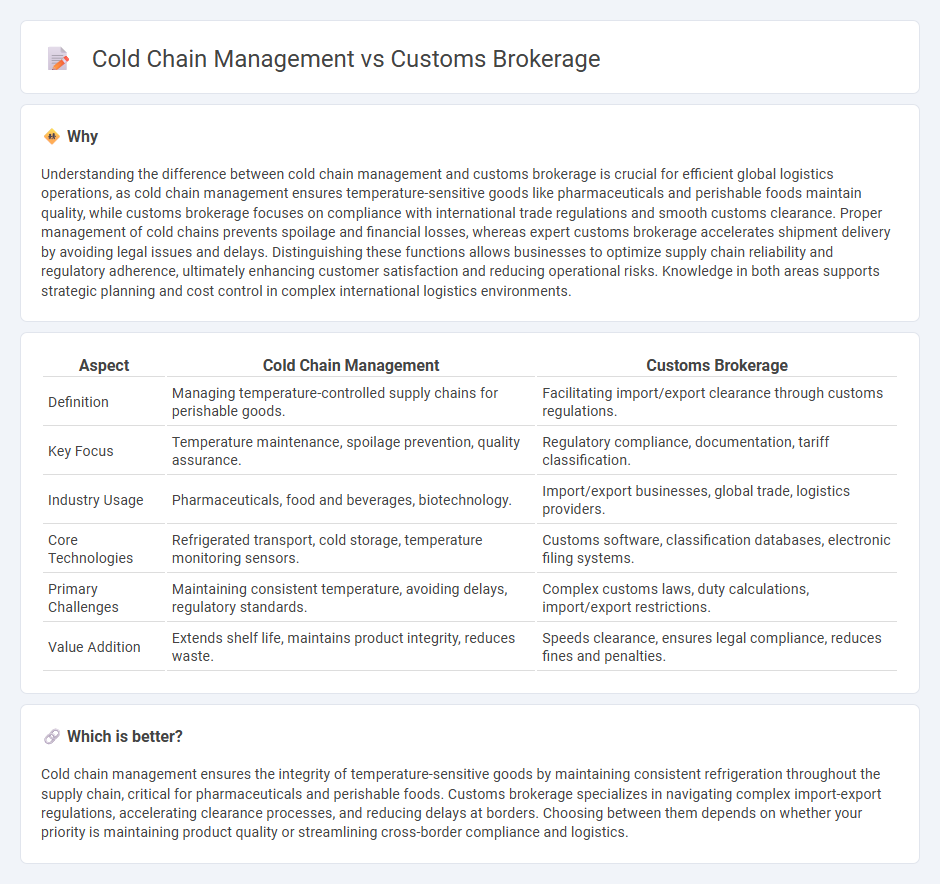
Understanding the difference between cold chain management and customs brokerage is crucial for efficient global logistics operations, as cold chain management ensures temperature-sensitive goods like pharmaceuticals and perishable foods maintain quality, while customs brokerage focuses on compliance with international trade regulations and smooth customs clearance. Proper management of cold chains prevents spoilage and financial losses, whereas expert customs brokerage accelerates shipment delivery by avoiding legal issues and delays. Distinguishing these functions allows businesses to optimize supply chain reliability and regulatory adherence, ultimately enhancing customer satisfaction and reducing operational risks. Knowledge in both areas supports strategic planning and cost control in complex international logistics environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Cold Chain Management | Customs Brokerage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Managing temperature-controlled supply chains for perishable goods. | Facilitating import/export clearance through customs regulations. |
| Key Focus | Temperature maintenance, spoilage prevention, quality assurance. | Regulatory compliance, documentation, tariff classification. |
| Industry Usage | Pharmaceuticals, food and beverages, biotechnology. | Import/export businesses, global trade, logistics providers. |
| Core Technologies | Refrigerated transport, cold storage, temperature monitoring sensors. | Customs software, classification databases, electronic filing systems. |
| Primary Challenges | Maintaining consistent temperature, avoiding delays, regulatory standards. | Complex customs laws, duty calculations, import/export restrictions. |
| Value Addition | Extends shelf life, maintains product integrity, reduces waste. | Speeds clearance, ensures legal compliance, reduces fines and penalties. |
Which is better?
Cold chain management ensures the integrity of temperature-sensitive goods by maintaining consistent refrigeration throughout the supply chain, critical for pharmaceuticals and perishable foods. Customs brokerage specializes in navigating complex import-export regulations, accelerating clearance processes, and reducing delays at borders. Choosing between them depends on whether your priority is maintaining product quality or streamlining cross-border compliance and logistics.
Connection
Cold chain management ensures temperature-controlled environments for perishable goods during transportation, which is critical for regulatory compliance and product integrity. Customs brokerage facilitates the smooth clearance of these temperature-sensitive shipments by handling documentation, tariffs, and inspections efficiently. Integration of cold chain logistics with customs brokerage minimizes delays and maintains product quality throughout cross-border supply chains.
Key Terms
Customs Brokerage:
Customs brokerage involves the expert handling of import and export documentation to ensure compliance with international trade regulations, minimizing delays and avoiding costly penalties. Licensed customs brokers facilitate communication between importers, exporters, and government authorities, streamlining the clearance process for goods across borders. Explore detailed insights on how customs brokerage boosts efficiency in global supply chains.
Tariff Classification
Tariff classification plays a crucial role in customs brokerage by ensuring accurate identification and categorization of goods for duty calculation and compliance with international trade regulations. In cold chain management, tariff classification helps optimize the handling and storage requirements for perishable goods, maintaining product integrity through temperature-controlled logistics. Explore the intricacies of tariff classification in both domains to enhance operational efficiency and regulatory compliance.
Import/Export Compliance
Customs brokerage ensures the timely clearance of goods by managing documentation, tariffs, and compliance with import/export regulations, minimizing delays and penalties. Cold chain management maintains temperature-sensitive products within prescribed conditions during transportation and storage, ensuring product integrity and regulatory adherence in sectors like pharmaceuticals and food. Explore in-depth strategies to optimize import/export compliance through integrated customs and cold chain solutions.
Source and External Links
Becoming a Customs Broker | U.S. Customs and Border Protection - Customs brokers are licensed individuals or businesses who assist importers and exporters in meeting federal requirements by submitting necessary documentation and payments to U.S. Customs and Border Protection on their behalf, requiring expertise in customs procedures, classification, valuation, and duties for imported goods.
Customs Broker Definition | UPS Supply Chain Solutions - A customs broker is a licensed intermediary that helps importers and exporters understand regulatory requirements, obtains clearances, and submits paperwork and payments to customs authorities, facilitating the customs clearance process.
What is Customs Brokerage | Farrow - Customs brokerage firms manage the complex and ever-changing rules of international trade, ensuring compliance with customs regulations to expedite shipments across borders and allowing clients to focus on their core business activities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com