Dynamic routing leverages real-time data and advanced algorithms to optimize delivery paths, reducing transit times and fuel consumption. Autonomous vehicle routing integrates self-driving technology with navigation systems to enable efficient, driverless logistics operations. Explore how these innovations transform supply chain efficiency and reduce operational costs.
Why it is important
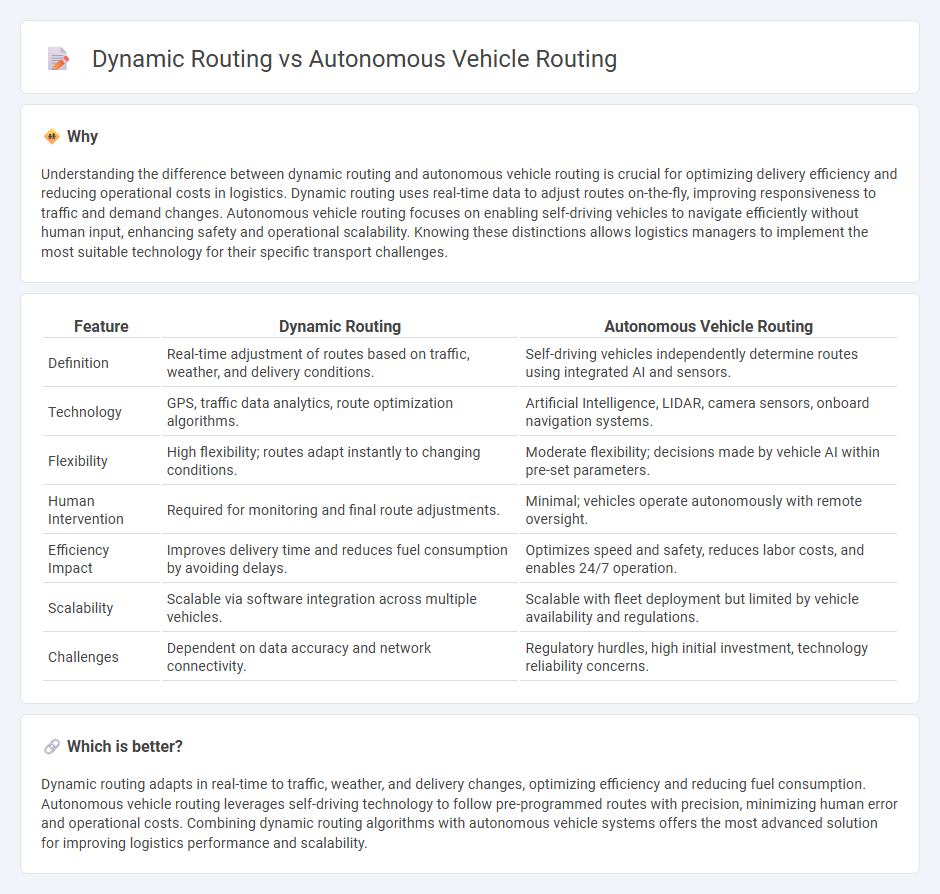
Understanding the difference between dynamic routing and autonomous vehicle routing is crucial for optimizing delivery efficiency and reducing operational costs in logistics. Dynamic routing uses real-time data to adjust routes on-the-fly, improving responsiveness to traffic and demand changes. Autonomous vehicle routing focuses on enabling self-driving vehicles to navigate efficiently without human input, enhancing safety and operational scalability. Knowing these distinctions allows logistics managers to implement the most suitable technology for their specific transport challenges.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Dynamic Routing | Autonomous Vehicle Routing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Real-time adjustment of routes based on traffic, weather, and delivery conditions. | Self-driving vehicles independently determine routes using integrated AI and sensors. |
| Technology | GPS, traffic data analytics, route optimization algorithms. | Artificial Intelligence, LIDAR, camera sensors, onboard navigation systems. |
| Flexibility | High flexibility; routes adapt instantly to changing conditions. | Moderate flexibility; decisions made by vehicle AI within pre-set parameters. |
| Human Intervention | Required for monitoring and final route adjustments. | Minimal; vehicles operate autonomously with remote oversight. |
| Efficiency Impact | Improves delivery time and reduces fuel consumption by avoiding delays. | Optimizes speed and safety, reduces labor costs, and enables 24/7 operation. |
| Scalability | Scalable via software integration across multiple vehicles. | Scalable with fleet deployment but limited by vehicle availability and regulations. |
| Challenges | Dependent on data accuracy and network connectivity. | Regulatory hurdles, high initial investment, technology reliability concerns. |
Which is better?
Dynamic routing adapts in real-time to traffic, weather, and delivery changes, optimizing efficiency and reducing fuel consumption. Autonomous vehicle routing leverages self-driving technology to follow pre-programmed routes with precision, minimizing human error and operational costs. Combining dynamic routing algorithms with autonomous vehicle systems offers the most advanced solution for improving logistics performance and scalability.
Connection
Dynamic routing leverages real-time data to optimize delivery paths, enhancing efficiency in logistics operations. Autonomous vehicle routing incorporates these dynamic algorithms to enable self-driving vehicles to adjust routes on the fly, responding to traffic, weather, and delivery demands. Integrating dynamic routing with autonomous systems reduces operational costs, improves delivery speed, and increases overall supply chain reliability.
Key Terms
**Autonomous Vehicle Routing:**
Autonomous vehicle routing leverages real-time data, advanced AI algorithms, and sensor inputs to optimize navigation paths for self-driving cars, improving safety and efficiency. It prioritizes adaptive decision-making in complex environments, integrating vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communication to reduce traffic congestion and travel time. Explore the latest breakthroughs in autonomous vehicle routing technologies and their impact on urban mobility.
Sensor Integration
Autonomous vehicle routing leverages real-time sensor integration, including LiDAR, radar, and cameras, to create highly accurate, adaptive navigation paths, whereas dynamic routing primarily relies on external data such as traffic updates without direct sensor input. Sensor integration enhances autonomous vehicles' ability to perceive their environment, detect obstacles, and optimize routes instantly, leading to improved safety and efficiency. Explore how cutting-edge sensor technologies revolutionize autonomous vehicle routing for a deeper understanding.
Path Planning Algorithms
Autonomous vehicle routing relies heavily on advanced path planning algorithms such as A* and Dijkstra's algorithm to compute optimal routes considering vehicle dynamics and environmental constraints, enabling precise navigation without human input. Dynamic routing algorithms continuously update routes in real-time based on traffic conditions, accidents, or road closures, leveraging adaptive methods like Reinforcement Learning and Genetic Algorithms to optimize travel efficiency. Explore our detailed analysis to understand how these path planning algorithms shape the future of intelligent transportation systems.
Source and External Links
Routing for an Optimized Autonomous Drive | Inframix - Presents a specialized vehicle routing algorithm that prioritizes road segments cleared for autonomous driving to minimize manual driving and optimize autonomous route choice under varying conditions like weather or incidents.
Routing Autonomous Vehicles in Congested Transportation Networks - Analyzes routing and rebalancing of shared autonomous vehicle fleets in congested networks, showing coordinated routing can prevent increased congestion and proposing efficient algorithms for congestion-aware, system-wide vehicle management.
Routing autonomous vehicles in congested transportation networks - Explores structural properties, performance limits, and real-time routing/rebalancing algorithms for autonomous mobility-on-demand systems, focusing on congestion effects and feasibility of solutions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com