Middle mile optimization focuses on streamlining transportation between warehouses and distribution centers to reduce transit times and costs, boosting overall supply chain efficiency. Cross-docking minimizes storage by unloading inbound shipments directly onto outbound vehicles, accelerating delivery and lowering inventory holding expenses. Explore the advantages of these strategies to enhance your logistics operations and improve customer satisfaction.
Why it is important
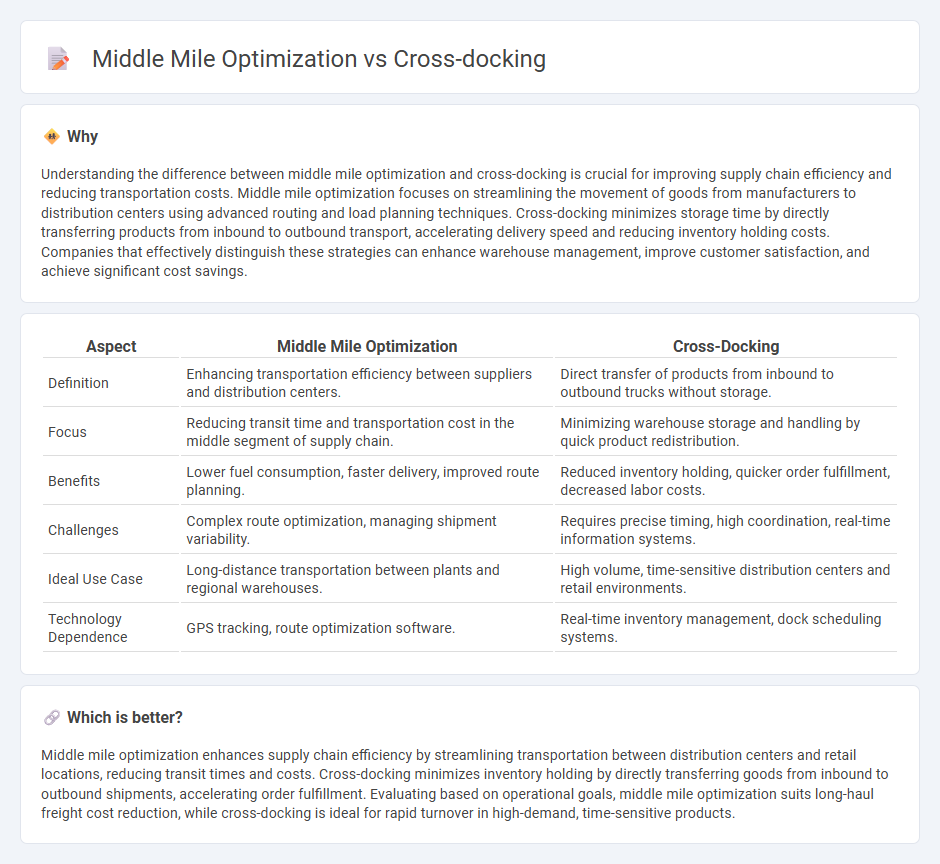
Understanding the difference between middle mile optimization and cross-docking is crucial for improving supply chain efficiency and reducing transportation costs. Middle mile optimization focuses on streamlining the movement of goods from manufacturers to distribution centers using advanced routing and load planning techniques. Cross-docking minimizes storage time by directly transferring products from inbound to outbound transport, accelerating delivery speed and reducing inventory holding costs. Companies that effectively distinguish these strategies can enhance warehouse management, improve customer satisfaction, and achieve significant cost savings.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Middle Mile Optimization | Cross-Docking |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Enhancing transportation efficiency between suppliers and distribution centers. | Direct transfer of products from inbound to outbound trucks without storage. |
| Focus | Reducing transit time and transportation cost in the middle segment of supply chain. | Minimizing warehouse storage and handling by quick product redistribution. |
| Benefits | Lower fuel consumption, faster delivery, improved route planning. | Reduced inventory holding, quicker order fulfillment, decreased labor costs. |
| Challenges | Complex route optimization, managing shipment variability. | Requires precise timing, high coordination, real-time information systems. |
| Ideal Use Case | Long-distance transportation between plants and regional warehouses. | High volume, time-sensitive distribution centers and retail environments. |
| Technology Dependence | GPS tracking, route optimization software. | Real-time inventory management, dock scheduling systems. |
Which is better?
Middle mile optimization enhances supply chain efficiency by streamlining transportation between distribution centers and retail locations, reducing transit times and costs. Cross-docking minimizes inventory holding by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound shipments, accelerating order fulfillment. Evaluating based on operational goals, middle mile optimization suits long-haul freight cost reduction, while cross-docking is ideal for rapid turnover in high-demand, time-sensitive products.
Connection
Middle mile optimization improves the efficiency of goods transportation between warehouses and distribution centers, reducing transit times and costs. Cross-docking facilitates seamless transfers by minimizing storage and handling during the middle mile, accelerating inventory flow. Integrating cross-docking strategies within middle mile logistics enhances supply chain responsiveness and reduces overall operational expenses.
Key Terms
Transshipment
Cross-docking involves the rapid transfer of goods from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage time, optimizing inventory flow and reducing handling costs. Middle mile optimization focuses on improving efficiency and cost-effectiveness during the transport of goods between suppliers, warehouses, and distribution centers, often incorporating transshipment points to consolidate shipments and enhance route efficiency. Explore deeper insights into how transshipment strategies drive operational excellence in supply chain logistics.
Consolidation
Cross-docking streamlines inventory flow by transferring goods directly from inbound to outbound transportation with minimal storage, enhancing consolidation efficiency in supply chains. Middle mile optimization focuses on improving the efficiency of freight movement between suppliers and distribution centers, leveraging consolidation techniques to reduce transportation costs and delivery times. Explore more strategies to maximize consolidation benefits in logistics and supply chain management.
Route Planning
Cross-docking streamlines supply chain operations by unloading incoming shipments directly onto outbound vehicles, minimizing storage time and expediting delivery. Middle mile optimization emphasizes strategic route planning to enhance transportation efficiency between distribution centers and retail locations, reducing fuel consumption and transit times. Explore advanced route planning techniques to unlock greater efficiency in both cross-docking and middle mile logistics.
Source and External Links
Cross Docking: Definition, History, and Process - This webpage provides an overview of cross-docking, including its definition, history, and various methods like continuous, consolidation, and de-consolidation.
What Is Cross-Docking? Definition, Types & Advantages - This article explains cross-docking as a logistics technique that accelerates goods delivery by directly transferring goods from inbound to outbound vehicles, reducing storage needs and costs.
Understanding cross-docking: A comprehensive guide - This guide covers the basics of cross-docking, including its types, such as pre-distribution vs. post-distribution, and specialized forms like retail and e-commerce cross-docking.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com