Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) fractionalization allows investors to own and trade partial shares of a digital asset, increasing liquidity and accessibility without compromising uniqueness. Stock splitting divides a company's existing shares into multiple shares, enhancing affordability and marketability while maintaining total equity. Discover the key differences and financial implications of NFT fractionalization versus stock splitting to optimize your investment strategy.
Why it is important
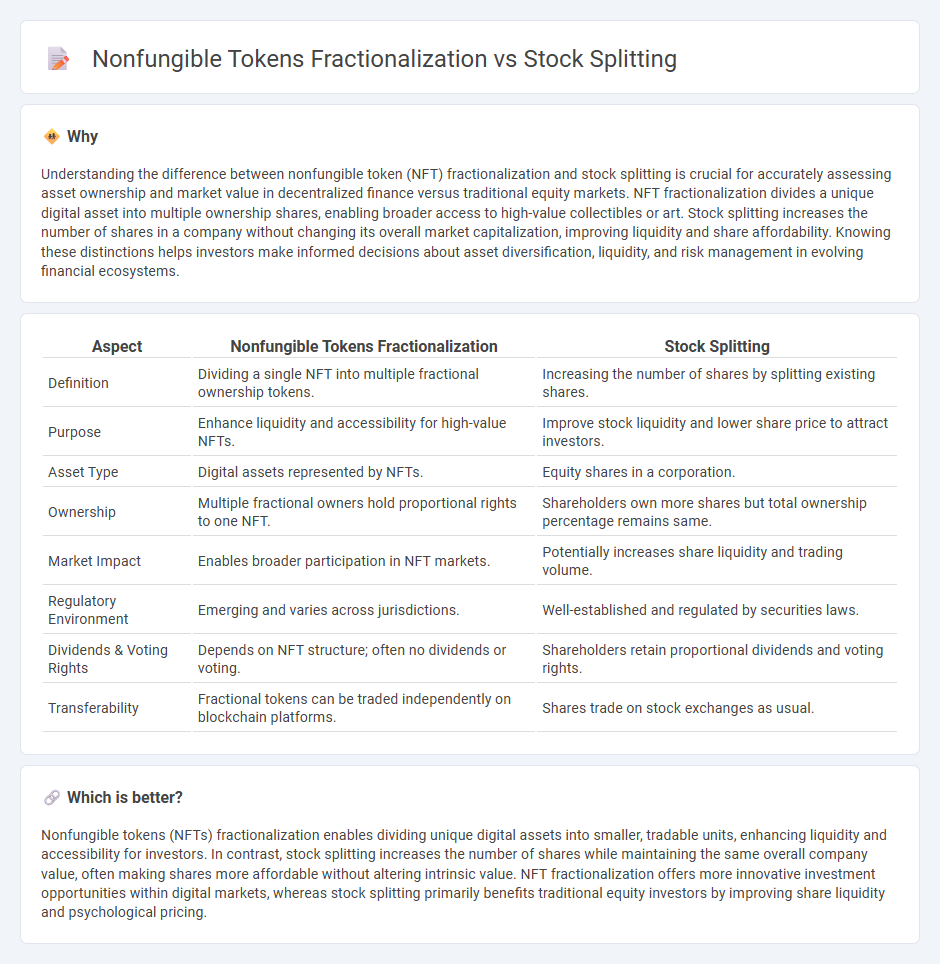
Understanding the difference between nonfungible token (NFT) fractionalization and stock splitting is crucial for accurately assessing asset ownership and market value in decentralized finance versus traditional equity markets. NFT fractionalization divides a unique digital asset into multiple ownership shares, enabling broader access to high-value collectibles or art. Stock splitting increases the number of shares in a company without changing its overall market capitalization, improving liquidity and share affordability. Knowing these distinctions helps investors make informed decisions about asset diversification, liquidity, and risk management in evolving financial ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nonfungible Tokens Fractionalization | Stock Splitting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Dividing a single NFT into multiple fractional ownership tokens. | Increasing the number of shares by splitting existing shares. |
| Purpose | Enhance liquidity and accessibility for high-value NFTs. | Improve stock liquidity and lower share price to attract investors. |
| Asset Type | Digital assets represented by NFTs. | Equity shares in a corporation. |
| Ownership | Multiple fractional owners hold proportional rights to one NFT. | Shareholders own more shares but total ownership percentage remains same. |
| Market Impact | Enables broader participation in NFT markets. | Potentially increases share liquidity and trading volume. |
| Regulatory Environment | Emerging and varies across jurisdictions. | Well-established and regulated by securities laws. |
| Dividends & Voting Rights | Depends on NFT structure; often no dividends or voting. | Shareholders retain proportional dividends and voting rights. |
| Transferability | Fractional tokens can be traded independently on blockchain platforms. | Shares trade on stock exchanges as usual. |
Which is better?
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) fractionalization enables dividing unique digital assets into smaller, tradable units, enhancing liquidity and accessibility for investors. In contrast, stock splitting increases the number of shares while maintaining the same overall company value, often making shares more affordable without altering intrinsic value. NFT fractionalization offers more innovative investment opportunities within digital markets, whereas stock splitting primarily benefits traditional equity investors by improving share liquidity and psychological pricing.
Connection
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) fractionalization and stock splitting both involve dividing an asset into smaller, more affordable units to increase liquidity and accessibility for investors. Fractionalizing NFTs allows multiple owners to hold shares of a unique digital asset, similar to how stock splits increase the number of shares outstanding to lower the price per share without altering the company's market capitalization. Both mechanisms enhance market participation by enabling more investors to acquire partial ownership of valuable assets.
Key Terms
Shares Outstanding
Stock splitting increases the number of shares outstanding by dividing existing shares into smaller units, maintaining the total market capitalization while improving liquidity and accessibility for investors. Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) fractionalization breaks a single NFT into multiple fractional ownerships without changing the total number of overall units but enabling partial investment and trading. Explore how these mechanisms impact market dynamics and investor participation by learning more about shares outstanding and digital asset division.
Ownership Fraction
Stock splitting increases the number of shares while maintaining the same ownership percentage, enabling greater liquidity without altering control stakes. Nonfungible token (NFT) fractionalization divides a unique digital asset into smaller ownership fractions, allowing multiple investors to hold partial rights simultaneously. Explore the differences in ownership structures and investment potentials between these methods to understand their impact on asset management.
Liquidity
Stock splitting increases liquidity by dividing existing shares into smaller units, making them more affordable and accessible to a broader range of investors without altering the company's market capitalization. Nonfungible tokens (NFTs) fractionalization enhances liquidity by allowing multiple investors to own portions of a high-value digital asset, enabling easier trading and investment diversification within the blockchain ecosystem. Explore the detailed mechanisms and implications of both processes to deepen your understanding of liquidity management in traditional and digital asset markets.
Source and External Links
What is a Stock Split and How Does it Work? - Vision Retirement - A stock split increases the number of outstanding shares by issuing additional shares to current shareholders, lowering the stock price but keeping overall value the same, and involves key dates like announcement, record, and effective dates.
Stock Split | Investor.gov - A stock split raises the number of shares outstanding without diluting shareholder equity, often to make shares more affordable, e.g., a 2-for-1 split doubles shares but halves the price per share.
Stock split - Wikipedia - Stock splits increase share liquidity by lowering the stock price and increasing the number of shares held, with common ratios like 2-for-1 or 3-for-1, and may signal management confidence or attract small investors.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com