Climate-linked derivatives offer investors financial instruments designed to hedge risks associated with climate change impacts, such as extreme weather or carbon pricing fluctuations. Green loans provide direct financing for projects with positive environmental benefits, often featuring lower interest rates tied to sustainability performance metrics. Explore the distinct roles and advantages of these innovative finance tools in advancing sustainable investment strategies.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between climate-linked derivatives and green loans is crucial for financial risk management and sustainable investment strategies. Climate-linked derivatives hedge against climate-related financial risks by tying contract values to environmental indicators, while green loans provide capital specifically for environmentally beneficial projects with predefined green criteria. Accurate knowledge enables investors and institutions to optimize portfolio performance, ensure regulatory compliance, and promote environmental responsibility. Distinguishing these instruments supports transparent reporting and targeted climate action in finance.
Comparison Table
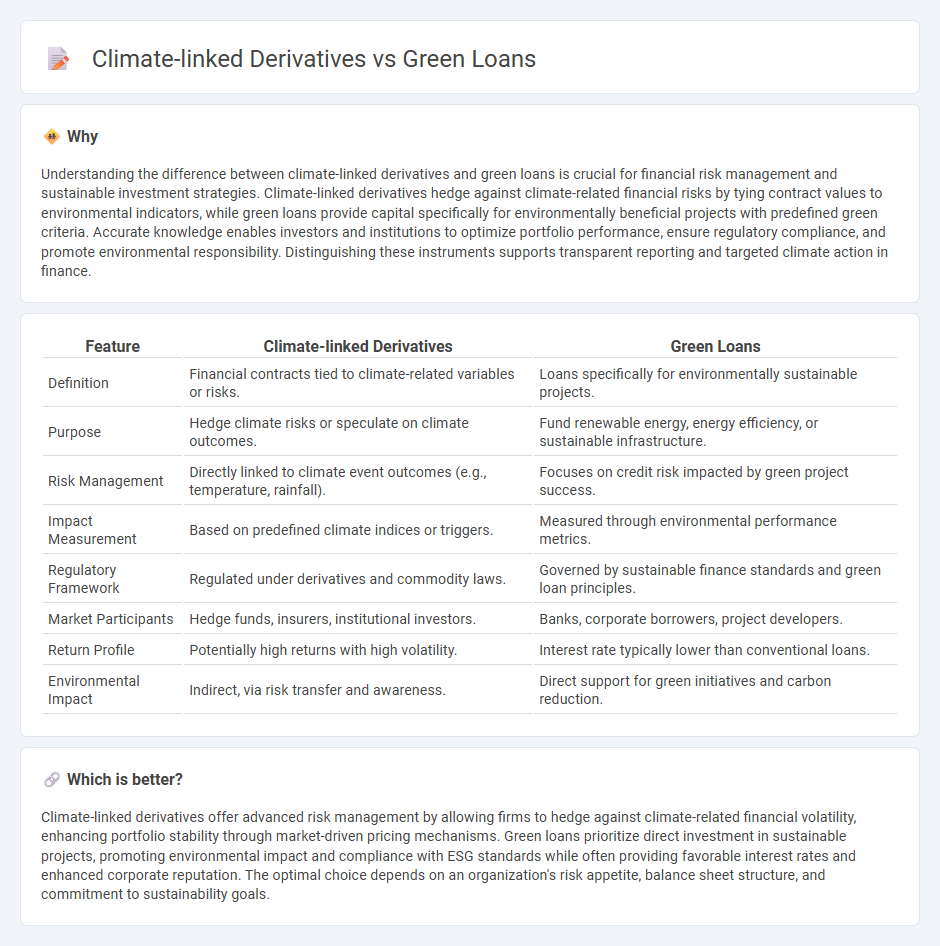
| Feature | Climate-linked Derivatives | Green Loans |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial contracts tied to climate-related variables or risks. | Loans specifically for environmentally sustainable projects. |
| Purpose | Hedge climate risks or speculate on climate outcomes. | Fund renewable energy, energy efficiency, or sustainable infrastructure. |
| Risk Management | Directly linked to climate event outcomes (e.g., temperature, rainfall). | Focuses on credit risk impacted by green project success. |
| Impact Measurement | Based on predefined climate indices or triggers. | Measured through environmental performance metrics. |
| Regulatory Framework | Regulated under derivatives and commodity laws. | Governed by sustainable finance standards and green loan principles. |
| Market Participants | Hedge funds, insurers, institutional investors. | Banks, corporate borrowers, project developers. |
| Return Profile | Potentially high returns with high volatility. | Interest rate typically lower than conventional loans. |
| Environmental Impact | Indirect, via risk transfer and awareness. | Direct support for green initiatives and carbon reduction. |
Which is better?
Climate-linked derivatives offer advanced risk management by allowing firms to hedge against climate-related financial volatility, enhancing portfolio stability through market-driven pricing mechanisms. Green loans prioritize direct investment in sustainable projects, promoting environmental impact and compliance with ESG standards while often providing favorable interest rates and enhanced corporate reputation. The optimal choice depends on an organization's risk appetite, balance sheet structure, and commitment to sustainability goals.
Connection
Climate-linked derivatives and green loans are interconnected financial instruments designed to mitigate environmental risks and promote sustainable investments. Climate-linked derivatives provide hedging mechanisms against climate-related risks such as carbon price fluctuations or weather events, while green loans fund projects with positive environmental impacts, often incorporating performance-based conditions tied to sustainability outcomes. This integration enhances risk management and supports capital allocation toward low-carbon and climate-resilient initiatives.
Key Terms
Sustainability-linked loans
Sustainability-linked loans (SLLs) tie borrowing costs to the borrower's achievement of predetermined environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance targets, offering dynamic incentives for corporate sustainability improvements. Unlike green loans, which fund specific green projects, SLLs provide flexibility by not restricting how proceeds are used but instead reinforcing overall sustainability commitments through measurable KPIs. Explore how SLLs align financing strategies with long-term ESG goals and drive market transformation toward responsible investment.
Emissions trading derivatives
Emissions trading derivatives are financial instruments designed to manage risks and opportunities associated with carbon markets, enabling companies to hedge against fluctuations in carbon credit prices. Unlike green loans that directly finance environmentally beneficial projects, emissions trading derivatives facilitate the trading and pricing of carbon allowances, playing a crucial role in carbon market liquidity and price discovery. Explore more about how emissions trading derivatives drive sustainability and market efficiency in climate finance.
Environmental performance targets
Green loans directly finance projects with measurable environmental benefits, often linked to specific sustainability criteria such as carbon reduction or renewable energy adoption. Climate-linked derivatives, on the other hand, are financial instruments designed to hedge or speculate based on climate risk, with payouts tied to predefined environmental performance targets like temperature thresholds or emission indices. Explore how these financial tools drive corporate environmental accountability and impact risk management strategies.
Source and External Links
Green Financing Loans - Fannie Mae - Fannie Mae offers Green Mortgage Loans that provide lower interest rates, additional loan proceeds, and support for energy and water efficiency improvements in properties with green certifications.
Green Loan Principles - The Green Loan Principles are guidelines developed by financial institutions to ensure green loans support environmentally sustainable economic activities with market integrity.
California Energy Efficiency Loans for Homes & Businesses - This program offers financing options that cover 100% of projects related to energy efficiency upgrades like solar installations and appliance replacements for homes and businesses in California.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com