Impact investing targets measurable social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns, directing capital to projects with clear, positive impacts. ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to guide investment decisions, aiming to mitigate risks and support sustainable practices. Discover more about how these strategies shape sustainable finance and responsible investing.
Why it is important
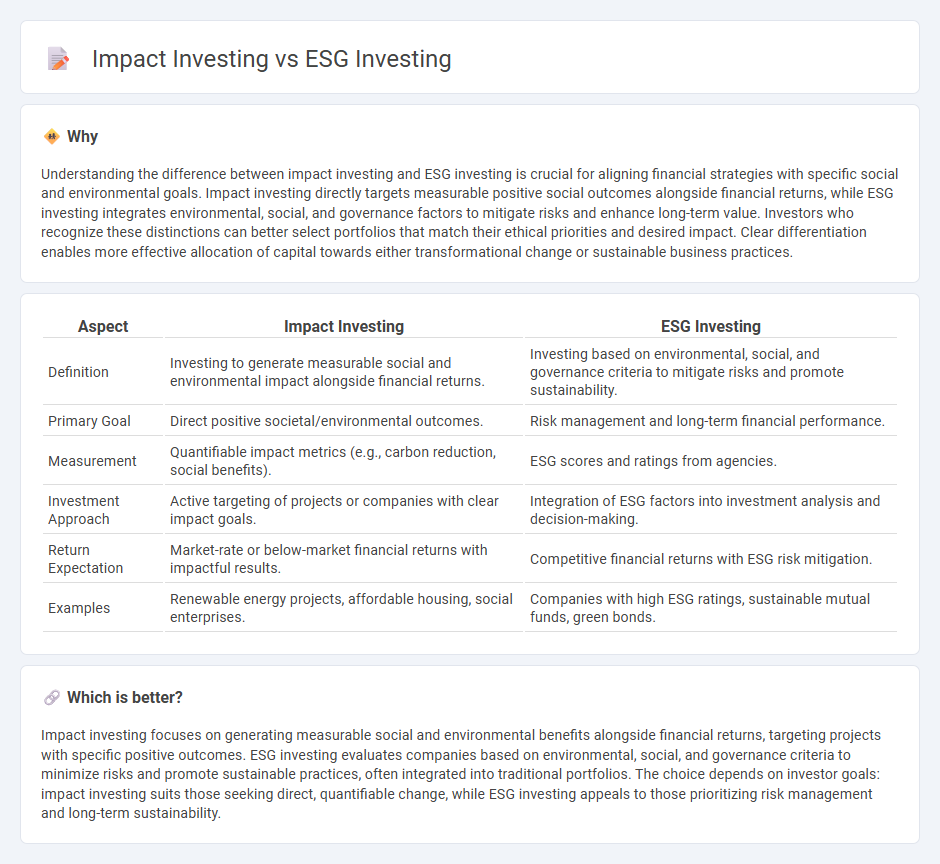
Understanding the difference between impact investing and ESG investing is crucial for aligning financial strategies with specific social and environmental goals. Impact investing directly targets measurable positive social outcomes alongside financial returns, while ESG investing integrates environmental, social, and governance factors to mitigate risks and enhance long-term value. Investors who recognize these distinctions can better select portfolios that match their ethical priorities and desired impact. Clear differentiation enables more effective allocation of capital towards either transformational change or sustainable business practices.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Impact Investing | ESG Investing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Investing to generate measurable social and environmental impact alongside financial returns. | Investing based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to mitigate risks and promote sustainability. |
| Primary Goal | Direct positive societal/environmental outcomes. | Risk management and long-term financial performance. |
| Measurement | Quantifiable impact metrics (e.g., carbon reduction, social benefits). | ESG scores and ratings from agencies. |
| Investment Approach | Active targeting of projects or companies with clear impact goals. | Integration of ESG factors into investment analysis and decision-making. |
| Return Expectation | Market-rate or below-market financial returns with impactful results. | Competitive financial returns with ESG risk mitigation. |
| Examples | Renewable energy projects, affordable housing, social enterprises. | Companies with high ESG ratings, sustainable mutual funds, green bonds. |
Which is better?
Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social and environmental benefits alongside financial returns, targeting projects with specific positive outcomes. ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to minimize risks and promote sustainable practices, often integrated into traditional portfolios. The choice depends on investor goals: impact investing suits those seeking direct, quantifiable change, while ESG investing appeals to those prioritizing risk management and long-term sustainability.
Connection
Impact investing and ESG investing both prioritize sustainable financial returns by integrating environmental, social, and governance criteria into investment decisions, fostering positive societal and environmental outcomes. Impact investing focuses on generating measurable social or environmental impact alongside financial returns, while ESG investing assesses corporate behavior and risk factors to identify responsible investments. Together, they drive capital toward companies that contribute to long-term sustainability and ethical practices in the finance sector.
Key Terms
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Criteria
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) investing integrates criteria such as carbon emissions reduction, labor practices, and board diversity to evaluate a company's sustainability and ethical impact, aiming for long-term financial returns. Impact investing specifically targets measurable positive social or environmental outcomes, often prioritizing projects like renewable energy or affordable housing with intentional value beyond profit. Explore detailed strategies, metrics, and case studies to deepen your understanding of ESG and impact investing distinctions.
Intentionality
ESG investing evaluates companies based on environmental, social, and governance criteria to mitigate risk and enhance long-term value, while impact investing targets intentional positive social and environmental outcomes alongside financial returns. The key difference lies in the deliberate commitment to measurable impact in impact investing versus the integration of ESG factors primarily for risk management in ESG investing. Explore further to understand how these strategies align with your sustainability goals.
Measurement of Impact
ESG investing evaluates environmental, social, and governance factors primarily through standardized metrics and corporate disclosures to assess risk and long-term value. Impact investing targets measurable social or environmental outcomes, using specific key performance indicators (KPIs) aligned with the investor's intentional goals to track real-world change. Explore how precise impact measurement distinguishes these investment strategies.
Source and External Links
Environmental, social, and governance - Wikipedia - ESG investing is an investment principle that prioritizes environmental, social, and corporate governance issues using strategies like positive selection, activism, engagement, exclusion, and integration to influence investment decisions.
What is ESG Investing? - ESG investing refers to investing sustainably by prioritizing optimal environmental, social, and governance factors, with roots in historical ethical investment practices and formalized through frameworks like the UN Principles for Responsible Investments since 2006.
What is ESG investing? - Deutsche Bank Wealth Management - ESG investing considers environmental, social, and governance criteria alongside traditional financial factors, representing a holistic approach to support broad societal goals and has grown to $35.3 trillion in assets globally by 2020.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com