Laddered bond ETFs spread investments across multiple bonds with staggered maturities, providing steady income and reduced interest rate risk. Defined maturity ETFs hold bonds that all mature on the same date, offering predictable cash flow and return of principal at maturity. Explore the benefits and trade-offs of each strategy to optimize your fixed-income portfolio.
Why it is important
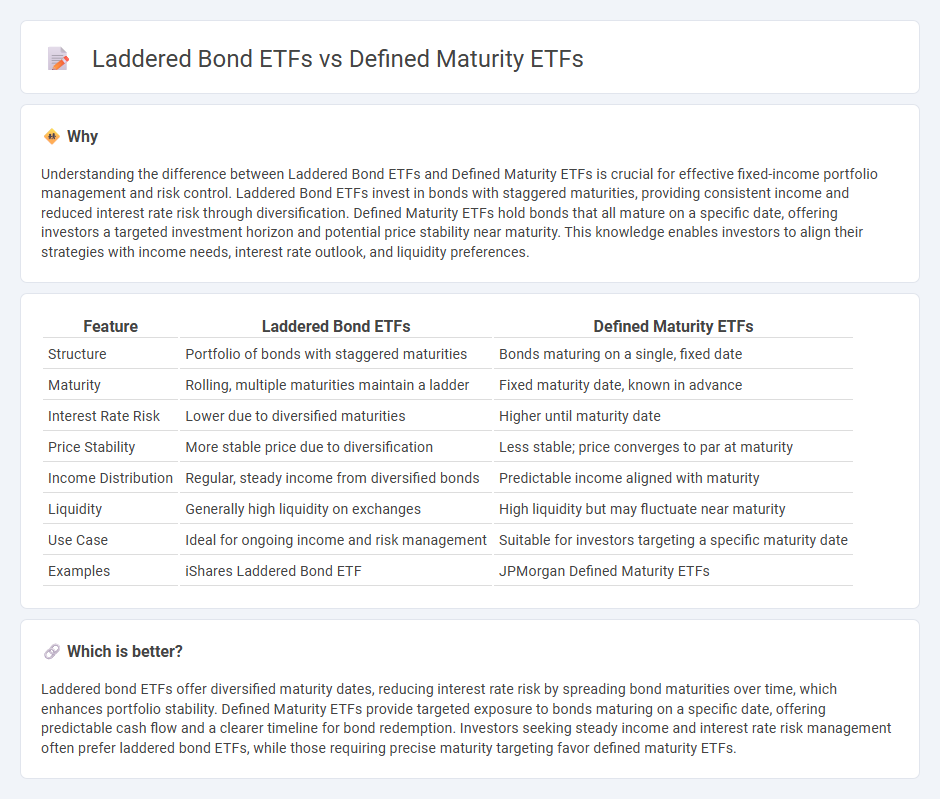
Understanding the difference between Laddered Bond ETFs and Defined Maturity ETFs is crucial for effective fixed-income portfolio management and risk control. Laddered Bond ETFs invest in bonds with staggered maturities, providing consistent income and reduced interest rate risk through diversification. Defined Maturity ETFs hold bonds that all mature on a specific date, offering investors a targeted investment horizon and potential price stability near maturity. This knowledge enables investors to align their strategies with income needs, interest rate outlook, and liquidity preferences.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Laddered Bond ETFs | Defined Maturity ETFs |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Portfolio of bonds with staggered maturities | Bonds maturing on a single, fixed date |
| Maturity | Rolling, multiple maturities maintain a ladder | Fixed maturity date, known in advance |
| Interest Rate Risk | Lower due to diversified maturities | Higher until maturity date |
| Price Stability | More stable price due to diversification | Less stable; price converges to par at maturity |
| Income Distribution | Regular, steady income from diversified bonds | Predictable income aligned with maturity |
| Liquidity | Generally high liquidity on exchanges | High liquidity but may fluctuate near maturity |
| Use Case | Ideal for ongoing income and risk management | Suitable for investors targeting a specific maturity date |
| Examples | iShares Laddered Bond ETF | JPMorgan Defined Maturity ETFs |
Which is better?
Laddered bond ETFs offer diversified maturity dates, reducing interest rate risk by spreading bond maturities over time, which enhances portfolio stability. Defined Maturity ETFs provide targeted exposure to bonds maturing on a specific date, offering predictable cash flow and a clearer timeline for bond redemption. Investors seeking steady income and interest rate risk management often prefer laddered bond ETFs, while those requiring precise maturity targeting favor defined maturity ETFs.
Connection
Laddered bond ETFs and Defined Maturity ETFs are connected through their structured approach to managing bond maturity risk and interest rate exposure. Laddered bond ETFs maintain a portfolio with staggered maturities to smooth out reinvestment risk, while Defined Maturity ETFs hold bonds that all mature in the same month and year, providing a predictable income timeline. Both strategies aim to optimize yield and reduce volatility by aligning bond maturities to investor cash flow needs and market conditions.
Key Terms
Fixed Maturity Date
Defined Maturity ETFs offer fixed maturity dates, allowing investors to anticipate when their principal will be returned, enhancing cash flow predictability compared to Laddered bond ETFs, which stagger bond maturities over time to manage interest rate risk. This structure provides a clear timeline for portfolio rebalancing and potential reinvestment opportunities, aligning with specific investment horizons. Explore the differences in risk management and income strategies between these ETF types for more informed fixed-income investing.
Reinvestment Risk
Defined Maturity ETFs minimize reinvestment risk by holding bonds that mature on a fixed date, allowing predictable cash flows and avoiding the need to reinvest at uncertain future rates. Laddered bond ETFs spread maturities across multiple dates, providing steady income but exposing investors to reinvestment risk as bonds mature at different intervals. Explore more to understand how these strategies affect portfolio stability and yield optimization.
Portfolio Turnover
Defined Maturity ETFs offer targeted exposure with fixed maturity dates, resulting in lower portfolio turnover compared to Laddered bond ETFs, which continuously buy and sell bonds to maintain staggered maturity dates. Lower portfolio turnover in Defined Maturity ETFs can lead to reduced trading costs and tax efficiency, making them attractive for long-term investors. Explore the nuances of both ETF structures to optimize your fixed income investment strategy.
Source and External Links
TDAM | ETFs - Target Maturity Bonds - TD Bank - Defined Maturity ETFs, or Target Maturity Bond ETFs, invest in a portfolio of investment-grade bonds held until a set maturity date, providing reduced short-term volatility and clear cash flow expectations, combining bond fund benefits with ETF liquidity and transparency.
RBC Target Maturity Bond ETFs brochure - These ETFs mature in a specified year, distributing net asset value to unitholders at maturity and then closing, offering bond-like defined maturity, diversified fixed income portfolios, monthly income, and transparency.
BulletShares(r) fixed income ETFs - Invesco - BulletShares ETFs have defined maturity dates when they terminate and distribute their net asset value, simulating the experience of holding individual bonds to maturity, ideal for bond laddering and long-term income strategies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com