Alt protein and synthetic biology foods represent innovative sectors transforming the food industry by addressing sustainability and ethical concerns. Entrepreneurs in these fields develop plant-based, cultured, and bioengineered products designed to reduce environmental impact and improve food security. Explore the future potential and investment opportunities within alternative protein and synthetic biology ventures.
Why it is important
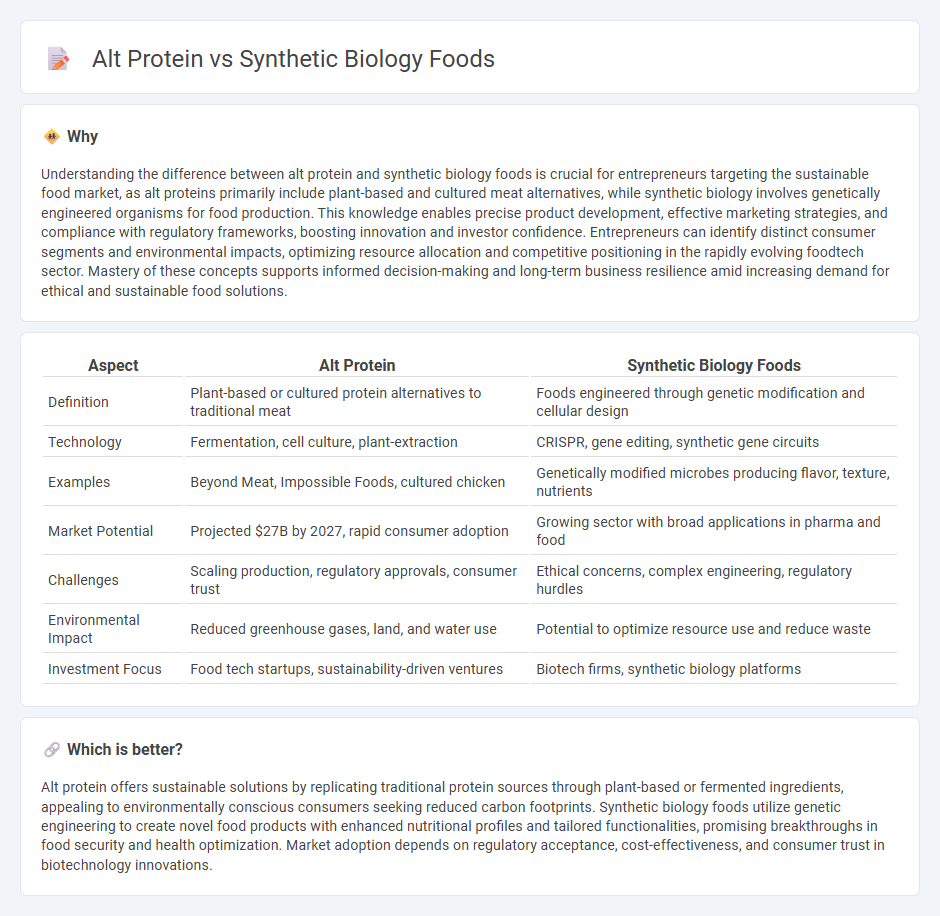
Understanding the difference between alt protein and synthetic biology foods is crucial for entrepreneurs targeting the sustainable food market, as alt proteins primarily include plant-based and cultured meat alternatives, while synthetic biology involves genetically engineered organisms for food production. This knowledge enables precise product development, effective marketing strategies, and compliance with regulatory frameworks, boosting innovation and investor confidence. Entrepreneurs can identify distinct consumer segments and environmental impacts, optimizing resource allocation and competitive positioning in the rapidly evolving foodtech sector. Mastery of these concepts supports informed decision-making and long-term business resilience amid increasing demand for ethical and sustainable food solutions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Synthetic Biology Foods |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Plant-based or cultured protein alternatives to traditional meat | Foods engineered through genetic modification and cellular design |
| Technology | Fermentation, cell culture, plant-extraction | CRISPR, gene editing, synthetic gene circuits |
| Examples | Beyond Meat, Impossible Foods, cultured chicken | Genetically modified microbes producing flavor, texture, nutrients |
| Market Potential | Projected $27B by 2027, rapid consumer adoption | Growing sector with broad applications in pharma and food |
| Challenges | Scaling production, regulatory approvals, consumer trust | Ethical concerns, complex engineering, regulatory hurdles |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced greenhouse gases, land, and water use | Potential to optimize resource use and reduce waste |
| Investment Focus | Food tech startups, sustainability-driven ventures | Biotech firms, synthetic biology platforms |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers sustainable solutions by replicating traditional protein sources through plant-based or fermented ingredients, appealing to environmentally conscious consumers seeking reduced carbon footprints. Synthetic biology foods utilize genetic engineering to create novel food products with enhanced nutritional profiles and tailored functionalities, promising breakthroughs in food security and health optimization. Market adoption depends on regulatory acceptance, cost-effectiveness, and consumer trust in biotechnology innovations.
Connection
Alt protein and synthetic biology foods are revolutionizing the entrepreneurship landscape by enabling the development of sustainable, lab-grown alternatives to traditional animal products. Startups leverage synthetic biology techniques such as gene editing and cell culture to create scalable, environmentally friendly protein sources like cultured meat and fermented proteins. This synergy drives innovation in food tech, attracting significant venture capital and accelerating the shift toward a more sustainable global food system.
Key Terms
Genetic Engineering
Synthetic biology foods leverage advanced genetic engineering techniques to design organisms with tailored traits, enabling the production of novel flavors, enhanced nutrition, and improved sustainability. Alternative proteins commonly include plant-based or fermentation-derived products but often employ less complex genetic modifications focused on optimizing yield and texture rather than creating entirely new biological pathways. Explore how genetic engineering drives innovation in both fields to revolutionize food production and sustainability efforts.
Fermentation Technology
Fermentation technology in synthetic biology foods involves using genetically engineered microorganisms to produce specific nutrients or flavors, enhancing the nutritional profile and taste compared to traditional alt proteins derived from plant or animal sources. This approach allows precise control over the production process, resulting in scalable, sustainable, and efficient biosynthesis of complex proteins and bioactive compounds. Explore the latest advancements in fermentation technology to understand its transformative impact on the future of alternative protein foods.
Cell-based Meat
Cell-based meat, a form of synthetic biology food, is produced by culturing animal cells directly to create real meat without raising animals. Unlike traditional alternative proteins derived from plants or fermentation, cell-based meat offers identical texture, flavor, and nutritional profiles to conventional meat. Explore in-depth insights on cell-based meat technologies and their impact on sustainable food systems.
Source and External Links
Synthetic Biology: The Future of Food? - Organic Consumers - Synthetic biology in food, or "synbio," enables creation of planet-friendly foods like the Impossible Burger, which uses genetically engineered yeast to produce a heme-like protein essential for its meat-like taste and texture.
Synthetic Biology Is Changing What We Eat. Here's What You Need ... - Civil Eats - This field uses gene editing and fermentation to produce food proteins such as the engineered heme in Impossible Burgers, enabling meat-like flavor and texture from plants.
What Products are the Result of Synthetic Biology? - Hudson Robotics - Synthetic biology creates novel foods, such as plant-based meats and artificial sweeteners, by genetically engineering microbes to produce desired proteins or molecules, exemplified by Impossible Foods' use of soy leghemoglobin produced via yeast.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com