The passion economy empowers individuals to monetize unique skills and personal creativity, often enabling sustainable, long-term business ventures. In contrast, the gig economy centers on short-term, task-based work typically facilitated through digital platforms, emphasizing flexibility and immediate income. Explore the key differences to understand which economic model aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
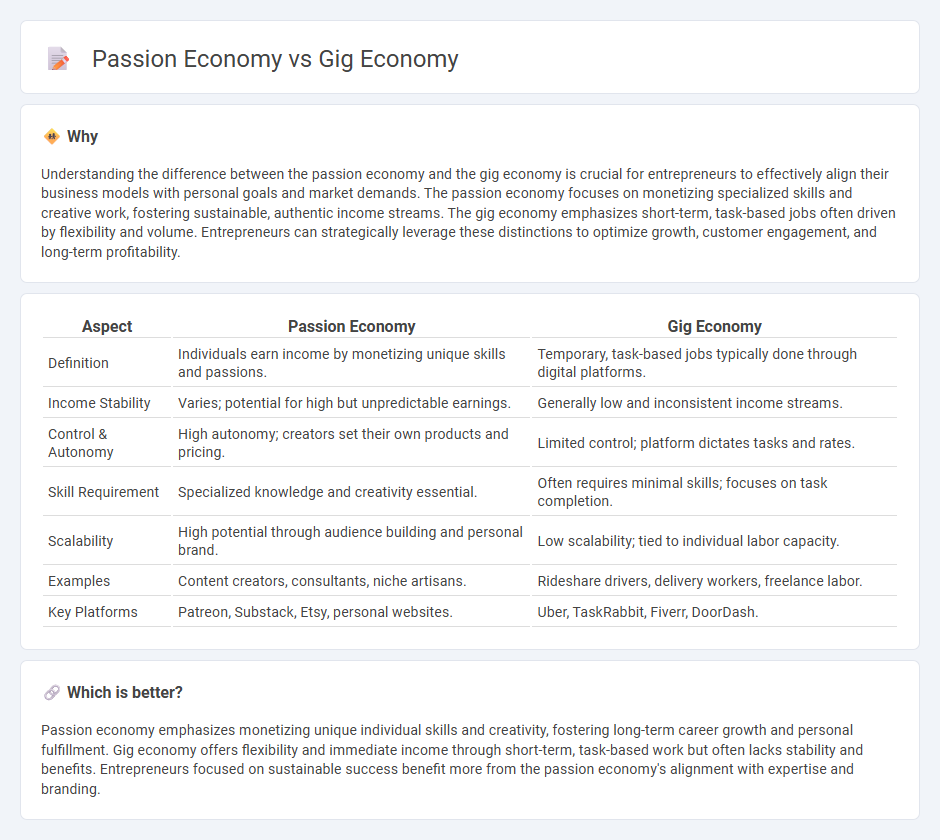
Understanding the difference between the passion economy and the gig economy is crucial for entrepreneurs to effectively align their business models with personal goals and market demands. The passion economy focuses on monetizing specialized skills and creative work, fostering sustainable, authentic income streams. The gig economy emphasizes short-term, task-based jobs often driven by flexibility and volume. Entrepreneurs can strategically leverage these distinctions to optimize growth, customer engagement, and long-term profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passion Economy | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Individuals earn income by monetizing unique skills and passions. | Temporary, task-based jobs typically done through digital platforms. |
| Income Stability | Varies; potential for high but unpredictable earnings. | Generally low and inconsistent income streams. |
| Control & Autonomy | High autonomy; creators set their own products and pricing. | Limited control; platform dictates tasks and rates. |
| Skill Requirement | Specialized knowledge and creativity essential. | Often requires minimal skills; focuses on task completion. |
| Scalability | High potential through audience building and personal brand. | Low scalability; tied to individual labor capacity. |
| Examples | Content creators, consultants, niche artisans. | Rideshare drivers, delivery workers, freelance labor. |
| Key Platforms | Patreon, Substack, Etsy, personal websites. | Uber, TaskRabbit, Fiverr, DoorDash. |
Which is better?
Passion economy emphasizes monetizing unique individual skills and creativity, fostering long-term career growth and personal fulfillment. Gig economy offers flexibility and immediate income through short-term, task-based work but often lacks stability and benefits. Entrepreneurs focused on sustainable success benefit more from the passion economy's alignment with expertise and branding.
Connection
Passion economy drives the gig economy by enabling individuals to monetize specialized skills and personal interests through flexible, freelance work. Platforms like Etsy, Patreon, and Upwork empower creators and freelancers to reach niche audiences, transforming passion into sustainable income streams. This synergy fosters innovation and economic diversity by prioritizing personalized, project-based opportunities over traditional employment models.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers workers short-term, flexible jobs that prioritize immediate income over long-term growth, often involving tasks like ride-sharing or freelance delivery. In contrast, the passion economy emphasizes leveraging individual skills and creativity, allowing people to build personalized careers with greater autonomy and sustainable income through platforms like Patreon or Substack. Explore how flexibility is redefined in these evolving economic models to find the best fit for your work style.
Monetization
The gig economy emphasizes short-term jobs and task-based monetization through platforms like Uber and Fiverr, enabling flexible income but often lacking long-term growth potential. In contrast, the passion economy centers on creators monetizing unique skills and personal brands via subscriptions, content platforms, and direct audience engagement, fostering sustainable and scalable revenue streams. Explore how these economies redefine earning opportunities and shape the future of work.
Autonomy
The gig economy offers task-based jobs with limited autonomy, where workers often follow predefined guidelines and schedules set by platforms like Uber or TaskRabbit. In contrast, the passion economy empowers individuals to leverage unique skills and creativity, granting higher autonomy to build personal brands and control work directions on platforms such as Patreon or Substack. Explore how autonomy shapes the future of work by diving deeper into the distinctions between these economies.
Source and External Links
What is the Gig Economy?| Definition from TechTarget - The gig economy is a free market system where temporary positions are common and organizations hire independent workers for short-term commitments, enabled largely by digital platforms that connect workers worldwide.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy allows workers to take on short-term projects or gigs, providing flexibility and autonomy, and is rapidly growing with millions of participants and a projected market value exceeding $2 trillion by 2033.
Gig economy - Wikipedia - The gig economy involves freelancers and independent contractors doing short-term jobs facilitated by digital platforms, offering flexibility to workers and cost savings to companies by avoiding traditional employment benefits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com