Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies into a single entity, enhancing market share and operational efficiencies. Joint ventures involve collaboration between two or more businesses to pursue shared objectives while maintaining separate ownership. Explore the strategic benefits and challenges of each approach to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between roll-up acquisitions and joint ventures is crucial for entrepreneurs because roll-up acquisitions involve consolidating multiple companies under one umbrella to achieve economies of scale, while joint ventures represent collaborative partnerships without full ownership fusion. Knowing these distinctions aids in strategic decision-making, optimizes resource allocation, and minimizes legal and financial risks. Roll-up acquisitions often lead to faster market expansion and increased valuation, whereas joint ventures allow sharing of expertise and risk without complete integration. This knowledge empowers entrepreneurs to select the best growth strategy aligned with their business goals and market conditions.
Comparison Table
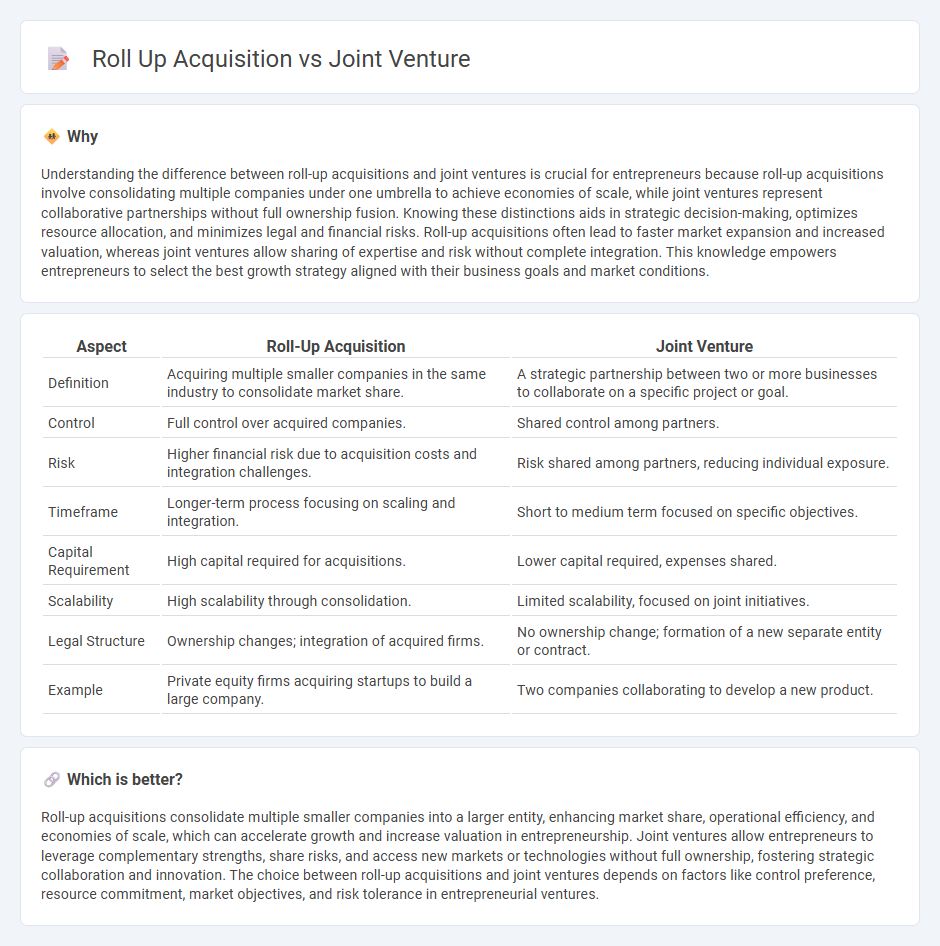
| Aspect | Roll-Up Acquisition | Joint Venture |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Acquiring multiple smaller companies in the same industry to consolidate market share. | A strategic partnership between two or more businesses to collaborate on a specific project or goal. |
| Control | Full control over acquired companies. | Shared control among partners. |
| Risk | Higher financial risk due to acquisition costs and integration challenges. | Risk shared among partners, reducing individual exposure. |
| Timeframe | Longer-term process focusing on scaling and integration. | Short to medium term focused on specific objectives. |
| Capital Requirement | High capital required for acquisitions. | Lower capital required, expenses shared. |
| Scalability | High scalability through consolidation. | Limited scalability, focused on joint initiatives. |
| Legal Structure | Ownership changes; integration of acquired firms. | No ownership change; formation of a new separate entity or contract. |
| Example | Private equity firms acquiring startups to build a large company. | Two companies collaborating to develop a new product. |
Which is better?
Roll-up acquisitions consolidate multiple smaller companies into a larger entity, enhancing market share, operational efficiency, and economies of scale, which can accelerate growth and increase valuation in entrepreneurship. Joint ventures allow entrepreneurs to leverage complementary strengths, share risks, and access new markets or technologies without full ownership, fostering strategic collaboration and innovation. The choice between roll-up acquisitions and joint ventures depends on factors like control preference, resource commitment, market objectives, and risk tolerance in entrepreneurial ventures.
Connection
Roll-up acquisitions and joint ventures are connected through their shared goal of business expansion and market consolidation. Roll-up acquisitions involve a company acquiring multiple smaller firms to increase market share, while joint ventures combine resources and expertise from two or more companies to enter new markets or develop innovations. Both strategies enable entrepreneurs to scale operations efficiently and leverage synergies for competitive advantage.
Key Terms
Collaboration structure
Joint ventures establish a collaborative business entity where two or more companies share ownership, risks, and profits, facilitating strategic alignment and resource pooling without full integration. Roll-up acquisitions involve a single company acquiring multiple smaller businesses to consolidate market share and streamline operations under unified control, prioritizing growth through ownership rather than partnership. Explore the nuances of these collaboration structures for optimized business synergy and expansion.
Ownership consolidation
Joint ventures involve shared ownership where multiple parties contribute resources and share control, maintaining distinct legal entities while collaborating on a specific project or business objective. Roll-up acquisitions consolidate ownership by merging multiple smaller companies into a single larger entity, streamlining operations and creating economies of scale under unified control. Explore further to understand how ownership consolidation strategies impact business growth and market presence.
Strategic control
Strategic control in a joint venture involves shared decision-making authority between partnering firms, allowing for collaborative management and risk distribution while aligning complementary strengths. In contrast, a roll-up acquisition consolidates multiple companies under a single controlling entity, enabling centralized strategic direction, streamlined operations, and potential market dominance. Explore further to understand how these structural differences impact competitive advantage and long-term growth strategies.
Source and External Links
Joint venture - A joint venture (JV) is a business entity created by two or more parties characterized by shared ownership, returns, risks, and governance, often formed to access new markets, share resources, or combine capabilities for specific projects or purposes.
Joint Venture (JV) - Top 10 Advantages - A JV is a commercial enterprise where multiple organizations pool resources to gain strategic advantages, share profits and losses, reduce financial burden, and enter new markets quickly with complementary expertise and capabilities.
joint venture | Wex | US Law | LII - A joint venture is a combination of two or more parties that collaborate on a single enterprise or project for profit, sharing contributions, control, and risks, distinct from partnerships or corporations and commonly used to enter foreign markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com