Ghost kitchens operate exclusively for delivery, minimizing overhead by eliminating dine-in space, while pop-up restaurants create temporary, experiential dining events that test markets and concepts. Both models leverage flexibility and lower costs to disrupt traditional restaurant operations in the evolving food industry landscape. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of ghost kitchens versus pop-up restaurants to understand their impact on entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
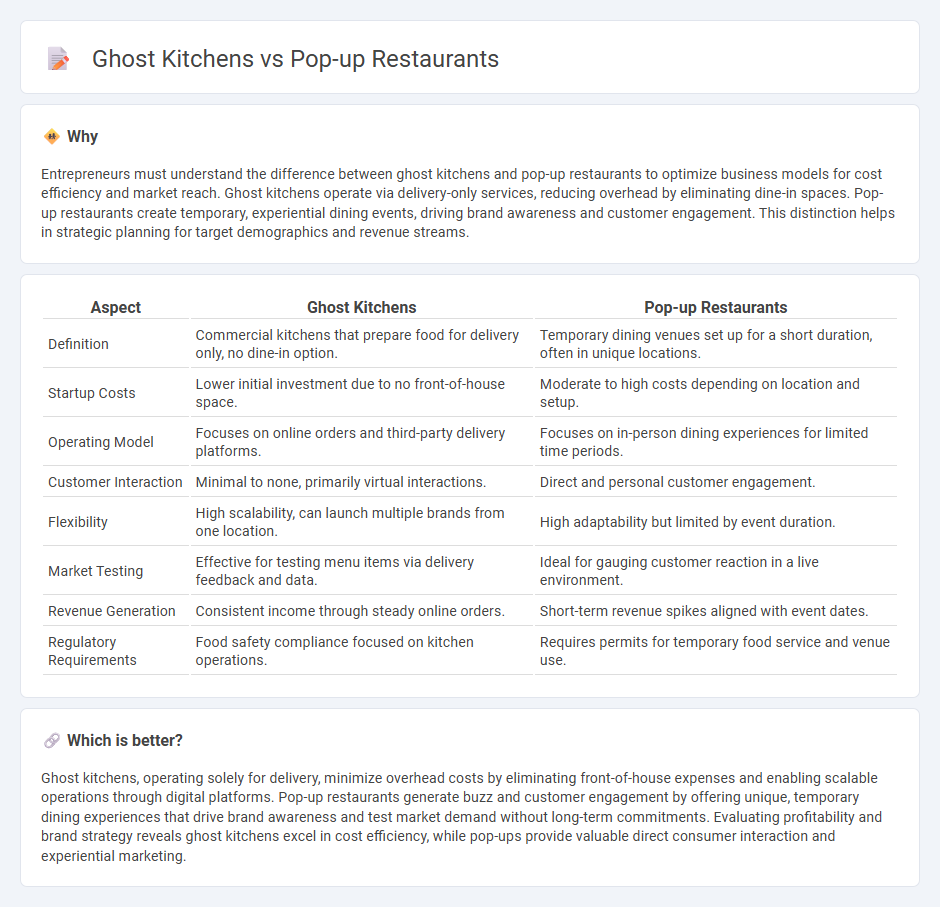
Entrepreneurs must understand the difference between ghost kitchens and pop-up restaurants to optimize business models for cost efficiency and market reach. Ghost kitchens operate via delivery-only services, reducing overhead by eliminating dine-in spaces. Pop-up restaurants create temporary, experiential dining events, driving brand awareness and customer engagement. This distinction helps in strategic planning for target demographics and revenue streams.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Ghost Kitchens | Pop-up Restaurants |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Commercial kitchens that prepare food for delivery only, no dine-in option. | Temporary dining venues set up for a short duration, often in unique locations. |
| Startup Costs | Lower initial investment due to no front-of-house space. | Moderate to high costs depending on location and setup. |
| Operating Model | Focuses on online orders and third-party delivery platforms. | Focuses on in-person dining experiences for limited time periods. |
| Customer Interaction | Minimal to none, primarily virtual interactions. | Direct and personal customer engagement. |
| Flexibility | High scalability, can launch multiple brands from one location. | High adaptability but limited by event duration. |
| Market Testing | Effective for testing menu items via delivery feedback and data. | Ideal for gauging customer reaction in a live environment. |
| Revenue Generation | Consistent income through steady online orders. | Short-term revenue spikes aligned with event dates. |
| Regulatory Requirements | Food safety compliance focused on kitchen operations. | Requires permits for temporary food service and venue use. |
Which is better?
Ghost kitchens, operating solely for delivery, minimize overhead costs by eliminating front-of-house expenses and enabling scalable operations through digital platforms. Pop-up restaurants generate buzz and customer engagement by offering unique, temporary dining experiences that drive brand awareness and test market demand without long-term commitments. Evaluating profitability and brand strategy reveals ghost kitchens excel in cost efficiency, while pop-ups provide valuable direct consumer interaction and experiential marketing.
Connection
Ghost kitchens and pop-up restaurants share a dynamic relationship in entrepreneurship by leveraging low-overhead, flexible dining concepts to rapidly test and scale new food offerings. Both models bypass traditional brick-and-mortar constraints, focusing on delivery and temporary setups that reduce initial capital investment and enable agile market responsiveness. Entrepreneurs utilize these platforms to innovate culinary experiences, optimize operational efficiency, and capitalize on evolving consumer preferences for convenience and novelty.
Key Terms
Temporary Location
Pop-up restaurants utilize temporary physical locations to create unique dining experiences, attracting customers through exclusivity and limited-time menus. Ghost kitchens operate without a storefront, focusing exclusively on delivery from commercial kitchen spaces to optimize cost efficiency and scalability. Explore deeper insights into how temporary locations shape the evolving landscape of the food industry.
Delivery-Only Model
Pop-up restaurants serve temporary, location-based dining experiences, while ghost kitchens operate exclusively as delivery-only outlets without a physical storefront. Ghost kitchens leverage optimized delivery logistics and digital ordering platforms to reduce overhead and increase market reach efficiently. Explore more about how the delivery-only model is reshaping the restaurant industry and consumer habits.
Overhead Costs
Pop-up restaurants typically incur higher overhead costs due to expenses related to temporary venue rental, staff, and extensive marketing campaigns, whereas ghost kitchens minimize overhead by operating solely as delivery-only commercial kitchens without customer-facing spaces. Ghost kitchens benefit from lower fixed costs such as rent and utilities, making them an efficient model for food entrepreneurs aiming to scale rapidly with less capital investment. Explore detailed cost analyses to determine which model suits your business goals best.
Source and External Links
Pop-up restaurant - Wikipedia - A pop-up restaurant is a temporary dining establishment often operating in unconventional spaces, popular since the 2000s, that allows chefs to experiment and gain exposure with lower startup costs using social media for promotion.
Why "pop-up" restaurants are everywhere now - YouTube - Pop-up restaurants have surged post-COVID, largely promoted through Instagram and social media, where chefs test new concepts and create viral moments leading to rapidly growing popularity and crowds.
Contemporary Arts Center Launches Series of Rotating Restaurant Pop-Ups - The Contemporary Arts Center in Cincinnati is hosting a rotating series of pop-up restaurants featuring local chefs and vendors, providing mentorship and community support to emerging food entrepreneurs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com