Passive house construction significantly reduces energy consumption by utilizing advanced insulation, airtightness, and high-performance windows, resulting in lower operational costs compared to traditional construction methods. Traditional construction typically relies on conventional materials and standard insulation that can lead to higher energy expenses and environmental impact over the building's lifecycle. Explore the benefits of passive house design to discover innovative opportunities in sustainable entrepreneurship.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between passive house and traditional construction is crucial for entrepreneurs focused on sustainable building and energy efficiency markets. A passive house reduces energy consumption by up to 90% compared to traditional buildings, presenting significant cost savings and environmental benefits. Entrepreneurs can leverage this knowledge to target eco-conscious customers and comply with tightening energy regulations. Mastery of these construction methods enhances innovation and competitive advantage in the green building industry.
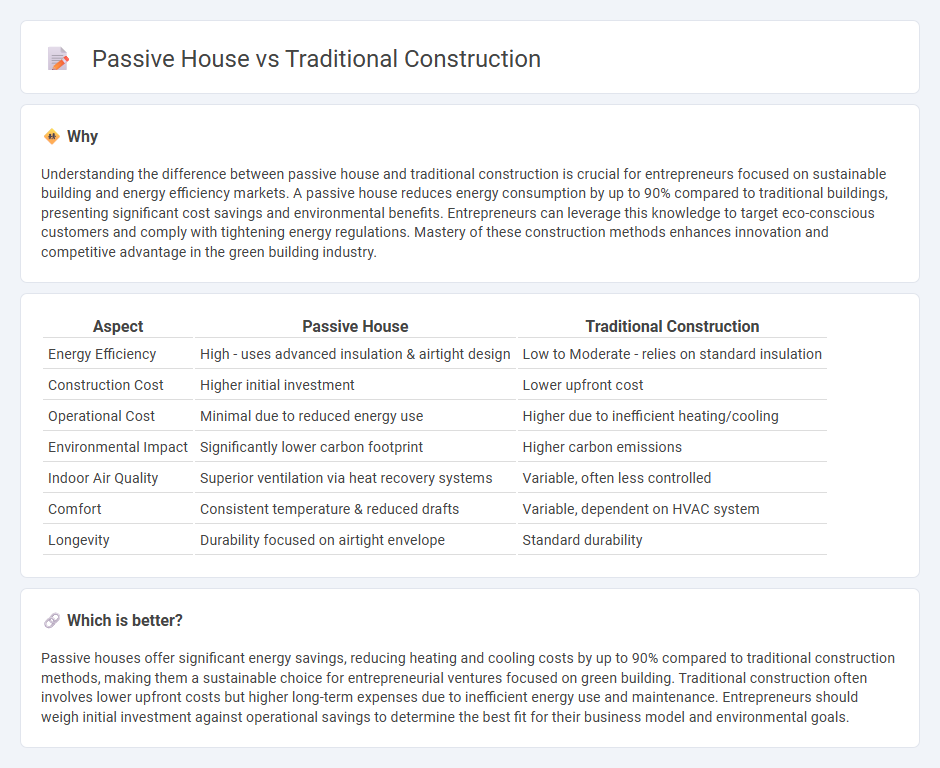
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Passive House | Traditional Construction |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | High - uses advanced insulation & airtight design | Low to Moderate - relies on standard insulation |
| Construction Cost | Higher initial investment | Lower upfront cost |
| Operational Cost | Minimal due to reduced energy use | Higher due to inefficient heating/cooling |
| Environmental Impact | Significantly lower carbon footprint | Higher carbon emissions |
| Indoor Air Quality | Superior ventilation via heat recovery systems | Variable, often less controlled |
| Comfort | Consistent temperature & reduced drafts | Variable, dependent on HVAC system |
| Longevity | Durability focused on airtight envelope | Standard durability |
Which is better?
Passive houses offer significant energy savings, reducing heating and cooling costs by up to 90% compared to traditional construction methods, making them a sustainable choice for entrepreneurial ventures focused on green building. Traditional construction often involves lower upfront costs but higher long-term expenses due to inefficient energy use and maintenance. Entrepreneurs should weigh initial investment against operational savings to determine the best fit for their business model and environmental goals.
Connection
Passive house and traditional construction intersect in their shared focus on building structures, but passive house emphasizes energy efficiency through advanced insulation, airtightness, and ventilation systems, reducing environmental impact and operating costs. Traditional construction often relies on standard building materials and methods, which may lack the energy-saving innovations integral to passive house design. Integrating passive house principles into traditional construction can enhance sustainability and occupant comfort while preserving familiar building practices.
Key Terms
Energy Efficiency
Traditional construction methods often rely on standard insulation and ventilation practices, resulting in higher energy consumption compared to passive house standards that emphasize airtight building envelopes, superior insulation, and heat recovery ventilation systems. Passive houses can reduce heating and cooling energy use by up to 90%, significantly lowering utility costs and carbon footprints. Discover how adopting passive house principles can transform your building's energy efficiency and sustainability.
Building Materials
Traditional construction relies heavily on conventional materials like timber, concrete, and standard insulation, which often result in higher thermal conductivity and energy loss. Passive houses prioritize high-performance, eco-friendly materials such as advanced insulation panels, triple-glazed windows, and airtight membranes to significantly reduce energy consumption and enhance indoor comfort. Explore detailed comparisons to understand how material choices impact sustainability and energy efficiency in modern buildings.
Insulation Standards
Traditional construction methods typically use standard insulation materials like fiberglass or foam boards, meeting minimum building code requirements. Passive houses employ advanced insulation techniques, including continuous exterior insulation and airtight building envelopes, achieving significantly higher thermal performance and energy efficiency. Explore the detailed differences in insulation standards to understand the long-term benefits of passive house construction.
Source and External Links
What is Traditional Construction? - Traditional construction uses conventional, manual, and labor-intensive methods with natural materials like brick, stone, and timber, known for durability and centuries of use.
Prefabricated vs. Traditional Construction | 360Connect - Traditional construction involves assembling building components on-site from the ground up, contrasting with prefabricated methods where parts are made off-site and assembled quicker.
Design-Build vs. Traditional Construction - Element Homes - Traditional construction separates design and execution phases with detailed architectural plans handed to contractors, enhancing planning accuracy, lowering change orders, and improving cost control.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com