Entrepreneurship in alt protein and fermentation-derived ingredients is revolutionizing the food industry by offering sustainable, innovative alternatives to traditional animal-based products. These ventures harness biotechnology to develop scalable, eco-friendly solutions that address growing consumer demand for ethical and healthy food options. Explore how entrepreneurs are reshaping nutrition and sustainability through cutting-edge fermentation processes.
Why it is important
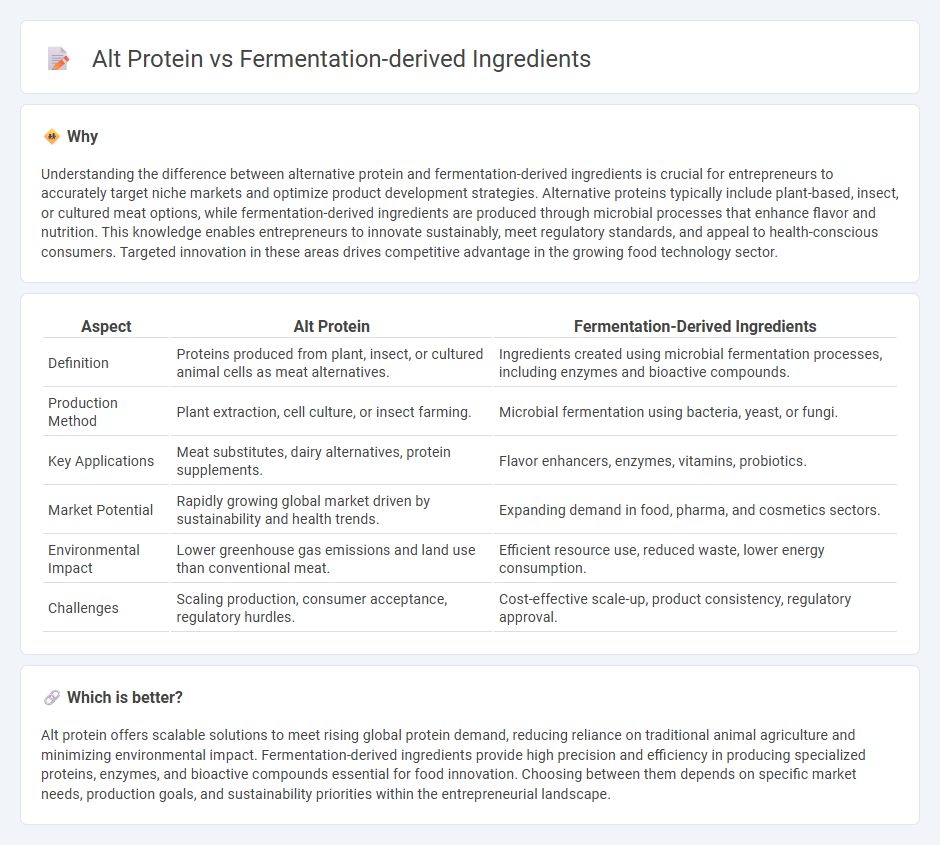
Understanding the difference between alternative protein and fermentation-derived ingredients is crucial for entrepreneurs to accurately target niche markets and optimize product development strategies. Alternative proteins typically include plant-based, insect, or cultured meat options, while fermentation-derived ingredients are produced through microbial processes that enhance flavor and nutrition. This knowledge enables entrepreneurs to innovate sustainably, meet regulatory standards, and appeal to health-conscious consumers. Targeted innovation in these areas drives competitive advantage in the growing food technology sector.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Alt Protein | Fermentation-Derived Ingredients |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Proteins produced from plant, insect, or cultured animal cells as meat alternatives. | Ingredients created using microbial fermentation processes, including enzymes and bioactive compounds. |
| Production Method | Plant extraction, cell culture, or insect farming. | Microbial fermentation using bacteria, yeast, or fungi. |
| Key Applications | Meat substitutes, dairy alternatives, protein supplements. | Flavor enhancers, enzymes, vitamins, probiotics. |
| Market Potential | Rapidly growing global market driven by sustainability and health trends. | Expanding demand in food, pharma, and cosmetics sectors. |
| Environmental Impact | Lower greenhouse gas emissions and land use than conventional meat. | Efficient resource use, reduced waste, lower energy consumption. |
| Challenges | Scaling production, consumer acceptance, regulatory hurdles. | Cost-effective scale-up, product consistency, regulatory approval. |
Which is better?
Alt protein offers scalable solutions to meet rising global protein demand, reducing reliance on traditional animal agriculture and minimizing environmental impact. Fermentation-derived ingredients provide high precision and efficiency in producing specialized proteins, enzymes, and bioactive compounds essential for food innovation. Choosing between them depends on specific market needs, production goals, and sustainability priorities within the entrepreneurial landscape.
Connection
Alt protein and fermentation-derived ingredients are closely connected through sustainable food production methods that leverage microbial fermentation to create high-quality, plant-based proteins. Fermentation-derived ingredients enhance the texture, flavor, and nutritional profile of alt proteins, making them a vital component in developing meat alternatives and innovative food products. Entrepreneurs in the alt protein industry drive innovation by utilizing advanced fermentation technologies to scale production and meet growing consumer demand for sustainable protein sources.
Key Terms
Precision Fermentation
Precision fermentation produces targeted proteins and enzymes with high purity, offering greater control compared to traditional fermentation-derived ingredients used in food and beverages. Alternative protein sources leverage precision fermentation to create sustainable, animal-free proteins closely mimicking animal counterparts in taste and texture. Explore the latest advancements in precision fermentation to understand its transformative impact on alternative protein innovation.
Cell-based Protein
Cell-based protein, cultivated directly from animal cells, offers a precise and scalable alternative to traditional fermentation-derived ingredients, which rely on microbial processes to produce proteins and bioactive compounds. This technology addresses sustainability and ethical concerns by eliminating the need for animal farming while delivering meat identical in structure and taste to conventional products. Explore the future of sustainable nutrition by learning more about cell-based protein innovations.
Microbial Biomass
Fermentation-derived ingredients leverage microbial biomass to produce nutrient-dense proteins with high efficiency and sustainability compared to traditional alternative proteins like plant-based or cultured meat. Microbial biomass offers a scalable source of complete proteins, essential amino acids, and bioactive compounds, making it a promising solution for global food security and environmental impact reduction. Explore the latest advancements and benefits of microbial biomass in alternative protein development to understand its transformative potential.
Source and External Links
Fulfilling the Promises of Fermentation-Derived Foods - Fermentation-derived ingredients are produced inside advanced bioreactors where the growth substrate is fully metabolized into edible biomass such as whole microbial or animal cells or secreted proteins, unlike traditional fermented foods where substrate is only partially converted and remains largely unchanged in form.
What is fermentation for alternative proteins? | GFI - Fermentation-derived ingredients include biomass fermentation products where microorganisms grow rapidly to produce protein-rich food ingredients, such as mycoprotein used by Quorn, and precision fermentation to produce specific recombinant proteins.
Fermentation derived ingredients - GEA - Controlled fermentation processes create a wide range of ingredients including probiotics, cultures, enzymes, and bioengineered flavors, harnessing sanitary and scalable bioreactor technology for reliable production.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com