Thrift flipping involves purchasing undervalued secondhand items, refurbishing them, and selling at a profit, requiring minimal startup capital and low operational costs. In contrast, the food truck business demands higher initial investment, permits, and inventory management but offers the advantage of mobile food service and diverse customer reach. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which entrepreneurial path aligns best with your goals.
Why it is important
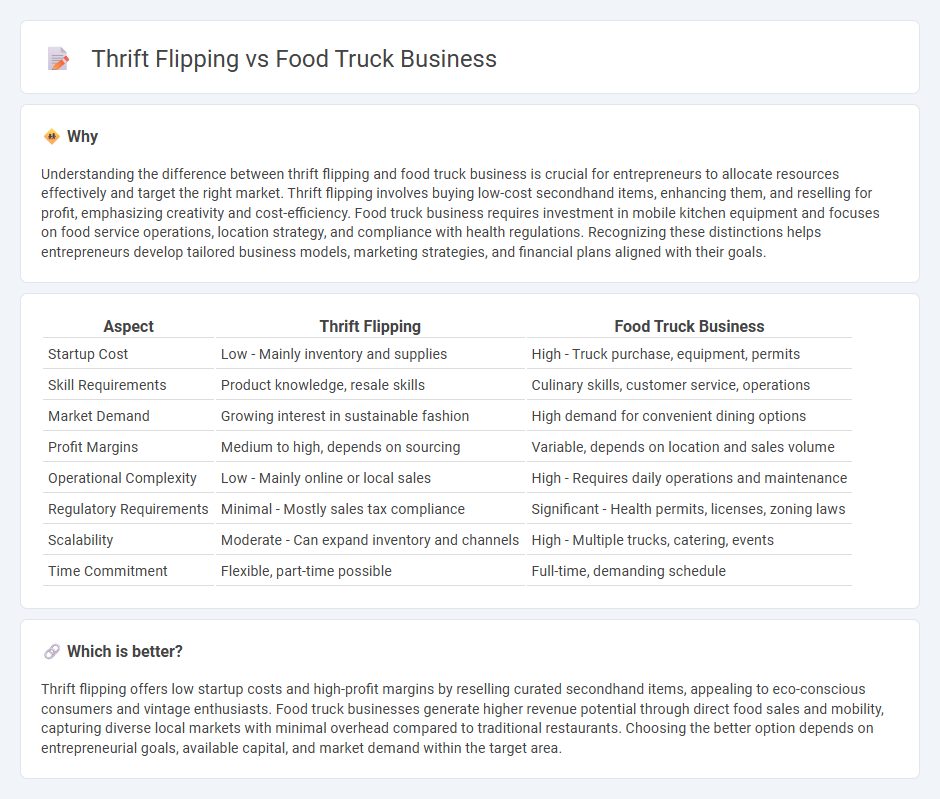
Understanding the difference between thrift flipping and food truck business is crucial for entrepreneurs to allocate resources effectively and target the right market. Thrift flipping involves buying low-cost secondhand items, enhancing them, and reselling for profit, emphasizing creativity and cost-efficiency. Food truck business requires investment in mobile kitchen equipment and focuses on food service operations, location strategy, and compliance with health regulations. Recognizing these distinctions helps entrepreneurs develop tailored business models, marketing strategies, and financial plans aligned with their goals.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Thrift Flipping | Food Truck Business |
|---|---|---|
| Startup Cost | Low - Mainly inventory and supplies | High - Truck purchase, equipment, permits |
| Skill Requirements | Product knowledge, resale skills | Culinary skills, customer service, operations |
| Market Demand | Growing interest in sustainable fashion | High demand for convenient dining options |
| Profit Margins | Medium to high, depends on sourcing | Variable, depends on location and sales volume |
| Operational Complexity | Low - Mainly online or local sales | High - Requires daily operations and maintenance |
| Regulatory Requirements | Minimal - Mostly sales tax compliance | Significant - Health permits, licenses, zoning laws |
| Scalability | Moderate - Can expand inventory and channels | High - Multiple trucks, catering, events |
| Time Commitment | Flexible, part-time possible | Full-time, demanding schedule |
Which is better?
Thrift flipping offers low startup costs and high-profit margins by reselling curated secondhand items, appealing to eco-conscious consumers and vintage enthusiasts. Food truck businesses generate higher revenue potential through direct food sales and mobility, capturing diverse local markets with minimal overhead compared to traditional restaurants. Choosing the better option depends on entrepreneurial goals, available capital, and market demand within the target area.
Connection
Thrift flipping and food truck businesses both exemplify low-investment entrepreneurship models that leverage creativity and resourcefulness to generate profits. Entrepreneurs in these fields tap into niche markets by transforming undervalued resources into high-demand products or services, maximizing minimal startup costs. This connection highlights the importance of innovation and adaptability in successful small business ventures.
Key Terms
Food truck business:
The food truck business offers dynamic opportunities in the mobile food service industry, capitalizing on low startup costs compared to traditional restaurants and the ability to reach diverse customer bases at various locations. Key advantages include flexibility in menu offerings, direct interaction with customers, and scalability through additional vehicles or catering services. Explore detailed strategies and market insights to maximize growth potential in the food truck business.
Permits and licensing
Food truck businesses require multiple permits including health permits, mobile food vendor licenses, and often fire safety inspections to legally operate, reflecting stringent regulations due to onsite food preparation. Thrift flipping typically involves less regulatory burden, often needing only a general business license and sometimes a resale certificate depending on local laws. Explore detailed permit requirements and licensing intricacies to choose the best path for your entrepreneurial venture.
Menu development
Food truck businesses thrive on dynamic menu development, emphasizing diverse, trendy, and locally sourced ingredients tailored to target customer preferences for fast, flavorful meals. Thrift flipping, in contrast, involves curating and refurbishing secondhand goods, where market research and product selection focus on style trends and condition rather than culinary creativity. Explore how specialized strategies in menu innovation and product curation drive success in these distinct entrepreneurial ventures.
Source and External Links
5 Food Truck Licenses and Permits Required in Oklahoma - Starting a food truck business involves creating a strong business plan, securing licenses and permits, finding funding, preparing a vehicle, planning locations, hiring staff, and marketing; food trucks have lower startup and operational costs than traditional restaurants, making them potentially more profitable.
The Inside Scoop on Starting a Food Truck in the U.S. - To start a food truck, conduct detailed market research to understand local demand, competition, successful trucks, and regulations, which will guide your concept, menu, equipment, and operational areas.
How to Start a Food Truck Business in 2025 - Starting costs for food trucks vary between $28,000 and $114,000, and success depends on providing high-quality food, leveraging social media, and possibly catering to supplement income during low foot traffic periods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com