Lifestyle businesses focus on creating a balanced work-life environment tailored to the entrepreneur's personal interests and goals, often prioritizing passion over rapid growth. Microbusinesses operate on a smaller scale with limited employees and revenue but emphasize scalability and profitability within niche markets. Explore further to understand how these distinct approaches can shape your entrepreneurial journey.
Why it is important
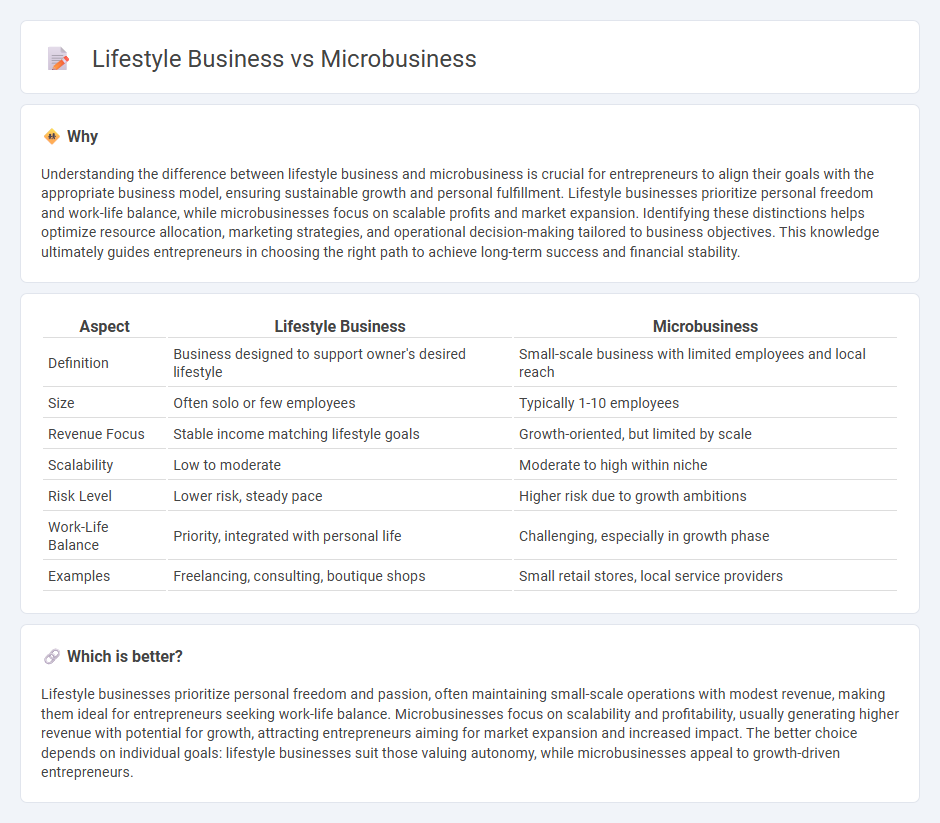
Understanding the difference between lifestyle business and microbusiness is crucial for entrepreneurs to align their goals with the appropriate business model, ensuring sustainable growth and personal fulfillment. Lifestyle businesses prioritize personal freedom and work-life balance, while microbusinesses focus on scalable profits and market expansion. Identifying these distinctions helps optimize resource allocation, marketing strategies, and operational decision-making tailored to business objectives. This knowledge ultimately guides entrepreneurs in choosing the right path to achieve long-term success and financial stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Lifestyle Business | Microbusiness |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Business designed to support owner's desired lifestyle | Small-scale business with limited employees and local reach |
| Size | Often solo or few employees | Typically 1-10 employees |
| Revenue Focus | Stable income matching lifestyle goals | Growth-oriented, but limited by scale |
| Scalability | Low to moderate | Moderate to high within niche |
| Risk Level | Lower risk, steady pace | Higher risk due to growth ambitions |
| Work-Life Balance | Priority, integrated with personal life | Challenging, especially in growth phase |
| Examples | Freelancing, consulting, boutique shops | Small retail stores, local service providers |
Which is better?
Lifestyle businesses prioritize personal freedom and passion, often maintaining small-scale operations with modest revenue, making them ideal for entrepreneurs seeking work-life balance. Microbusinesses focus on scalability and profitability, usually generating higher revenue with potential for growth, attracting entrepreneurs aiming for market expansion and increased impact. The better choice depends on individual goals: lifestyle businesses suit those valuing autonomy, while microbusinesses appeal to growth-driven entrepreneurs.
Connection
Lifestyle businesses and microbusinesses share a close connection through their focus on small-scale operations designed to support the owner's personal goals and maintain work-life balance. Both prioritize sustainability and flexibility over rapid growth, often leveraging niche markets and personal skills to generate steady income. This alignment fosters an entrepreneurial approach centered on autonomy, minimal risk, and direct control over business activities.
Key Terms
Scale
Microbusinesses prioritize manageable, small-scale operations designed for steady growth and community impact, often leveraging niche markets and localized customer bases. Lifestyle businesses emphasize creating sustainable income streams that support the owner's desired way of living, focusing less on expansion and more on work-life balance. Explore further to understand how these business models align with your goals and scalability preferences.
Work-life balance
Microbusinesses often prioritize scalable growth with structured workflows, while lifestyle businesses emphasize maintaining a flexible schedule to enhance work-life balance. Entrepreneurs in lifestyle businesses typically value personal fulfillment and time freedom over aggressive expansion, adapting operations to sustain their desired lifestyle. Discover more about how these business models impact work-life harmony and entrepreneurial goals.
Revenue goals
Microbusinesses typically aim for scalable revenue growth by targeting niche markets and reinvesting profits to expand operations. Lifestyle businesses prioritize steady income that supports personal quality of life without aggressive expansion or external funding requirements. Explore deeper insights to determine which revenue strategy aligns best with your entrepreneurial aspirations.
Source and External Links
Micro-Businesses and Startups: Key Differences | CO - Microbusinesses are companies with nine or fewer employees generating under $250,000 in annual revenue, often including freelancers, small retailers, and private practices, with advantages such as low overhead and flexibility but challenges in scaling and resource limitations.
What Do You Need to Start a Microbusiness? - Insureon - A microbusiness typically requires minimal startup capital (around $3,000), has no more than nine employees, can be home-based or storefront, and may be structured as a sole proprietorship with personal tax filing, commonly found in various freelance and small service professions.
Micro Business vs. Small Business - NerdWallet - Microbusinesses face challenges such as obtaining financing and attracting customers due to their small scale, but can leverage online lenders and low-cost digital marketing strategies to overcome these hurdles and build local customer bases effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com