No-code tools empower entrepreneurs to quickly build and scale digital products without extensive technical skills, drastically reducing startup costs and time to market. Franchise models offer a proven business structure with established brand recognition and support systems, minimizing operational uncertainties for new business owners. Explore the advantages and challenges of both approaches to determine which path aligns best with your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
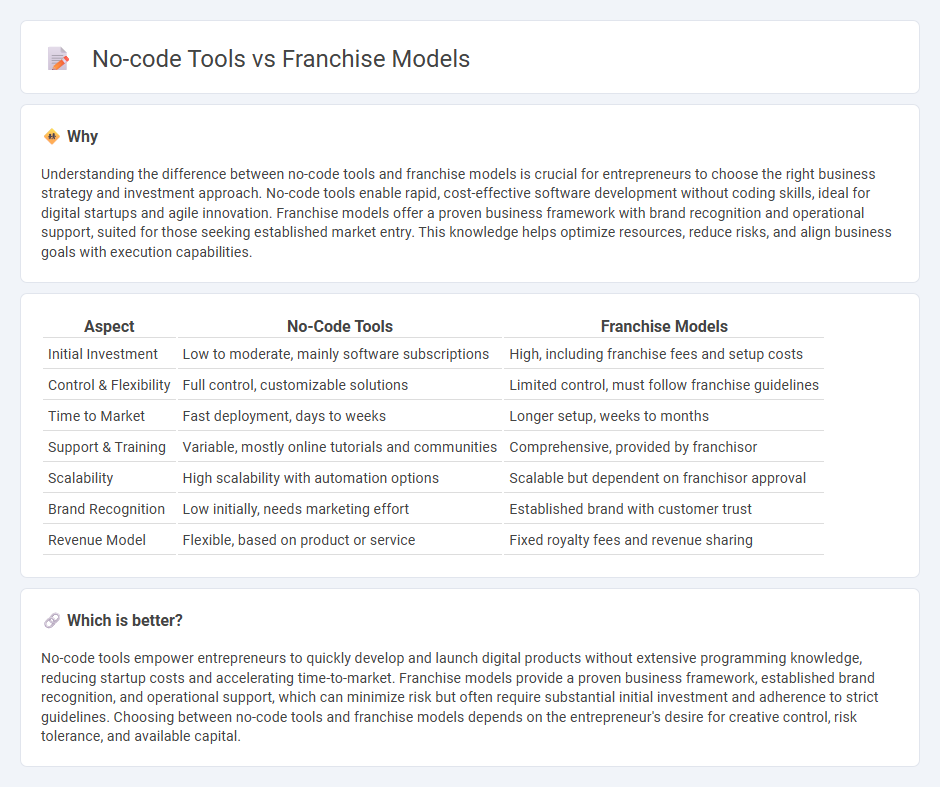
Understanding the difference between no-code tools and franchise models is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business strategy and investment approach. No-code tools enable rapid, cost-effective software development without coding skills, ideal for digital startups and agile innovation. Franchise models offer a proven business framework with brand recognition and operational support, suited for those seeking established market entry. This knowledge helps optimize resources, reduce risks, and align business goals with execution capabilities.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | No-Code Tools | Franchise Models |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Investment | Low to moderate, mainly software subscriptions | High, including franchise fees and setup costs |
| Control & Flexibility | Full control, customizable solutions | Limited control, must follow franchise guidelines |
| Time to Market | Fast deployment, days to weeks | Longer setup, weeks to months |
| Support & Training | Variable, mostly online tutorials and communities | Comprehensive, provided by franchisor |
| Scalability | High scalability with automation options | Scalable but dependent on franchisor approval |
| Brand Recognition | Low initially, needs marketing effort | Established brand with customer trust |
| Revenue Model | Flexible, based on product or service | Fixed royalty fees and revenue sharing |
Which is better?
No-code tools empower entrepreneurs to quickly develop and launch digital products without extensive programming knowledge, reducing startup costs and accelerating time-to-market. Franchise models provide a proven business framework, established brand recognition, and operational support, which can minimize risk but often require substantial initial investment and adherence to strict guidelines. Choosing between no-code tools and franchise models depends on the entrepreneur's desire for creative control, risk tolerance, and available capital.
Connection
No-code tools enable entrepreneurs to quickly develop and customize business solutions without deep technical expertise, aligning perfectly with franchise models that require scalable and replicable systems. These tools simplify the operational and marketing processes for franchisees, enhancing consistency and efficiency across multiple locations. The integration of no-code platforms with franchise strategies accelerates business growth by reducing development time and lowering entry barriers for new franchise owners.
Key Terms
Licensing
Franchise models rely heavily on licensing agreements that grant franchisees the right to operate under a brand while adhering to strict operational guidelines, ensuring consistency and brand integrity. No-code tools offer licensing options that empower users to build and deploy custom applications without deep technical skills, accelerating digital transformation and reducing dependency on developers. Explore how licensing differences impact scalability and control in both franchise and no-code ecosystems.
Scalability
Franchise models offer structured scalability through proven business systems and brand consistency, enabling rapid expansion with lower operational risks. No-code tools accelerate scalability by allowing businesses to quickly build and modify digital solutions without extensive coding, reducing time-to-market and development costs. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which approach best aligns with your growth strategy and scalability goals.
Customizability
Franchise models offer structured business blueprints with limited customizability, ensuring brand consistency across locations. No-code tools provide extensive customization options for users to tailor applications and workflows without programming skills. Explore how each approach balances control and flexibility to determine the best fit for your business needs.
Source and External Links
Types of Franchise Models Explained - HigherVisibility - Franchise models include product distribution, where franchisees sell franchisor products with autonomy; and manufacturing franchises, where franchisees manufacture and distribute products under strict franchisor guidelines, ensuring quality consistency, with examples like Coca-Cola and Subway.
Types of Franchise Business Models - Legalkart - Four main franchise models are COCO (company owned/company operated), COFO (company owned/franchise operated), FOCO (franchise owned/company operated), and FOFO (franchise owned/franchise operated), differing in ownership and operational roles; examples include Reliance Jio Mart for COCO.
Compare and Understand the Best Franchise Business Models for ... - Business format franchises require franchisees to follow comprehensive franchisor systems--including branding and operations--with advantages like support and proven models but less flexibility, while manufacturing franchises enable franchisees to produce franchisor products with controlled quality and exclusive rights.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com