Thrift flipping involves purchasing secondhand items, enhancing their value, and reselling them for profit, capitalizing on sustainable business practices and niche markets. Dropshipping allows entrepreneurs to sell products directly from suppliers without holding inventory, reducing overhead and streamlining operations. Explore the advantages and challenges of each model to determine the best fit for your entrepreneurial goals.
Why it is important
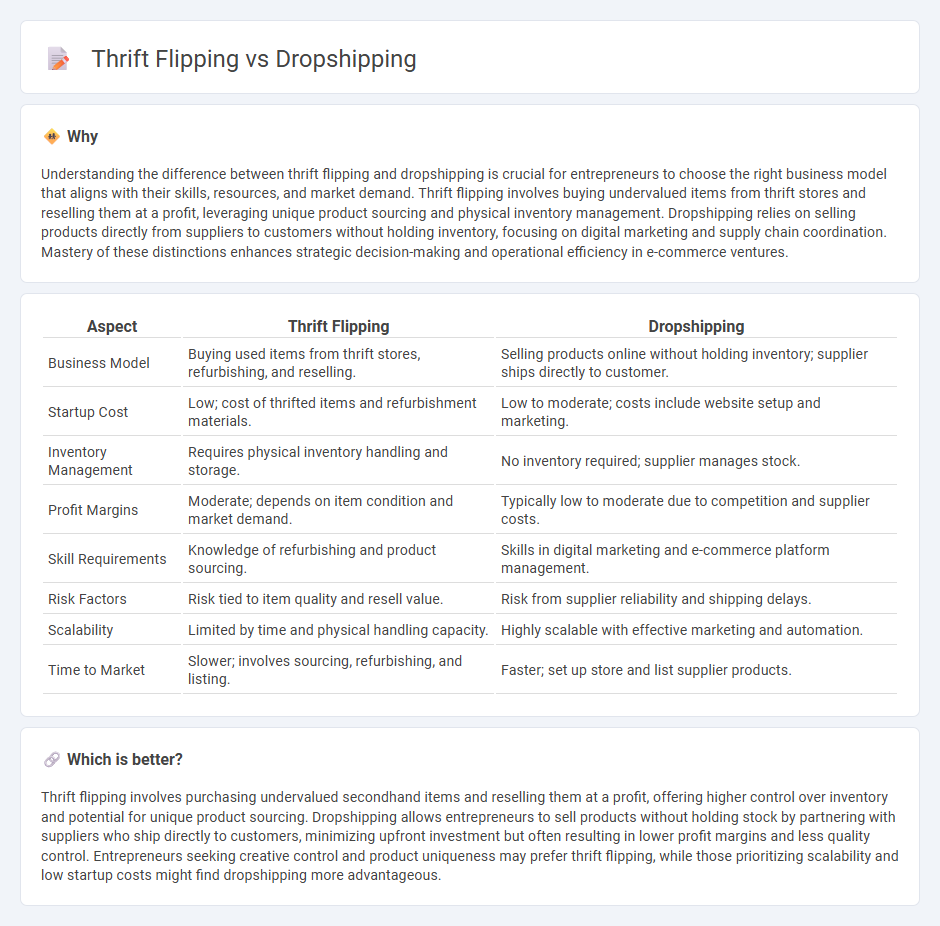
Understanding the difference between thrift flipping and dropshipping is crucial for entrepreneurs to choose the right business model that aligns with their skills, resources, and market demand. Thrift flipping involves buying undervalued items from thrift stores and reselling them at a profit, leveraging unique product sourcing and physical inventory management. Dropshipping relies on selling products directly from suppliers to customers without holding inventory, focusing on digital marketing and supply chain coordination. Mastery of these distinctions enhances strategic decision-making and operational efficiency in e-commerce ventures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Thrift Flipping | Dropshipping |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Buying used items from thrift stores, refurbishing, and reselling. | Selling products online without holding inventory; supplier ships directly to customer. |
| Startup Cost | Low; cost of thrifted items and refurbishment materials. | Low to moderate; costs include website setup and marketing. |
| Inventory Management | Requires physical inventory handling and storage. | No inventory required; supplier manages stock. |
| Profit Margins | Moderate; depends on item condition and market demand. | Typically low to moderate due to competition and supplier costs. |
| Skill Requirements | Knowledge of refurbishing and product sourcing. | Skills in digital marketing and e-commerce platform management. |
| Risk Factors | Risk tied to item quality and resell value. | Risk from supplier reliability and shipping delays. |
| Scalability | Limited by time and physical handling capacity. | Highly scalable with effective marketing and automation. |
| Time to Market | Slower; involves sourcing, refurbishing, and listing. | Faster; set up store and list supplier products. |
Which is better?
Thrift flipping involves purchasing undervalued secondhand items and reselling them at a profit, offering higher control over inventory and potential for unique product sourcing. Dropshipping allows entrepreneurs to sell products without holding stock by partnering with suppliers who ship directly to customers, minimizing upfront investment but often resulting in lower profit margins and less quality control. Entrepreneurs seeking creative control and product uniqueness may prefer thrift flipping, while those prioritizing scalability and low startup costs might find dropshipping more advantageous.
Connection
Thrift flipping and dropshipping both exemplify low-cost entry strategies in entrepreneurship, leveraging existing market demand to generate profit. Thrift flipping involves purchasing undervalued secondhand items and reselling them at a higher price, while dropshipping allows entrepreneurs to sell products without holding inventory, relying on suppliers to ship directly to customers. Both methods minimize upfront investment and inventory risks, making them accessible pathways for aspiring entrepreneurs to build scalable businesses.
Key Terms
Inventory Management
Dropshipping eliminates the need for physical inventory by relying on suppliers to fulfill orders directly, reducing storage costs and risks associated with unsold stock. Thrift flipping requires sourcing secondhand items, managing physical inventory, and handling quality checks before resale, demanding more hands-on inventory control. Explore deeper strategies in inventory management to optimize your chosen e-commerce model effectively.
Sourcing
Dropshipping relies on sourcing products directly from suppliers or manufacturers who handle inventory and shipping, minimizing upfront costs and storage needs. Thrift flipping involves sourcing unique, low-cost items from thrift stores or garage sales, then refurbishing or upcycling them for resale at a higher value. Explore detailed strategies and sourcing tips for both models to maximize your e-commerce success.
Profit Margin
Dropshipping typically offers lower profit margins ranging from 10% to 30% due to wholesale pricing and competitive market rates, whereas thrift flipping can yield higher margins, often exceeding 50% by sourcing unique, undervalued items from thrift stores and reselling them online. Profitability in thrift flipping depends on expert knowledge of market trends and product conditions, allowing sellers to strategically price rare finds. Explore in-depth strategies and case studies to maximize your profit margins in either business model.
Source and External Links
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? - Wix.com - Dropshipping is a retail fulfillment business where the seller creates an online store, markets products they do not stock, and when a customer orders, the seller buys the item from a third-party supplier who handles storage and shipping directly to the customer.
What Is Dropshipping and How Does It Work? (2025) - Shopify - Dropshipping is a business model where the store owner partners with suppliers who manage inventory and shipping, while the store sells products online and forwards customer orders to those suppliers for fulfillment.
Drop shipping - Wikipedia - Drop shipping is a retail method where sellers accept orders without inventory, then transfer order and shipping details to manufacturers or wholesalers who ship items directly, allowing sellers to avoid warehousing costs but with less control over product quality and shipping.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com