Algorithmic management leverages data-driven algorithms and real-time analytics to optimize workforce scheduling, productivity, and performance evaluation, contrasting with traditional management's reliance on human judgment and experience. This approach enables precise task allocation and monitors employee compliance, enhancing operational efficiency while raising concerns about autonomy and privacy. Explore how these management paradigms impact employment dynamics and worker satisfaction.
Why it is important
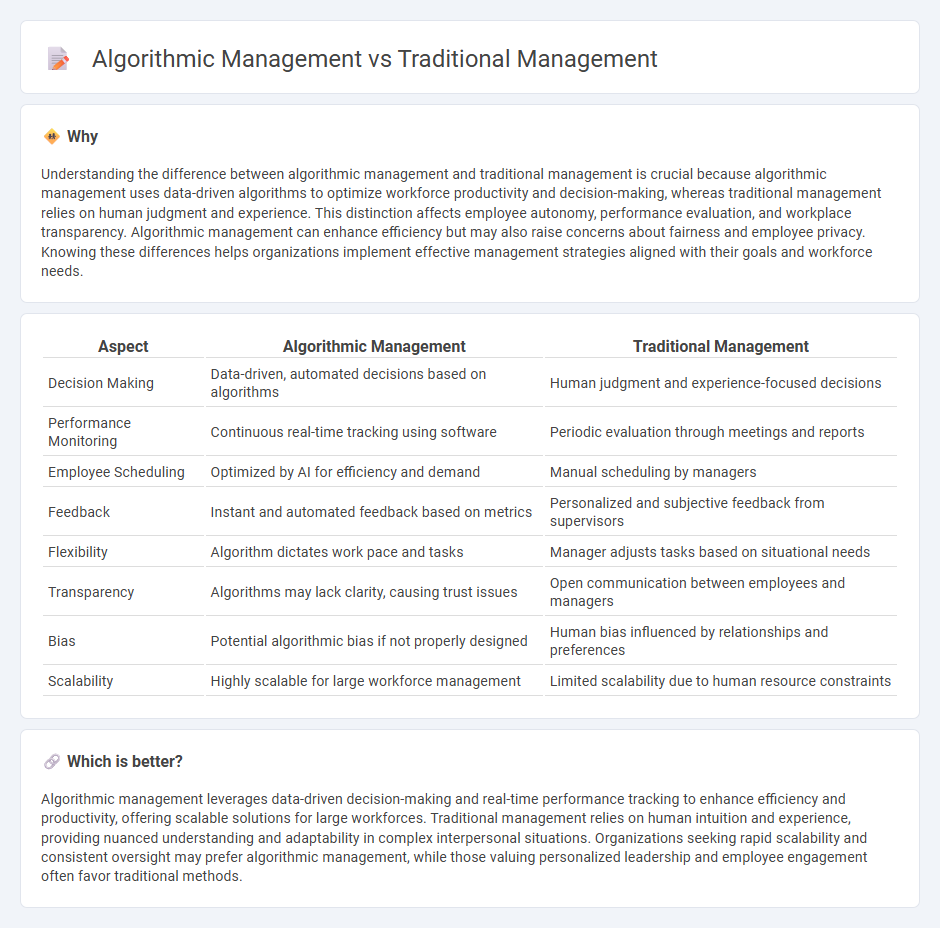
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and traditional management is crucial because algorithmic management uses data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce productivity and decision-making, whereas traditional management relies on human judgment and experience. This distinction affects employee autonomy, performance evaluation, and workplace transparency. Algorithmic management can enhance efficiency but may also raise concerns about fairness and employee privacy. Knowing these differences helps organizations implement effective management strategies aligned with their goals and workforce needs.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Traditional Management |
|---|---|---|
| Decision Making | Data-driven, automated decisions based on algorithms | Human judgment and experience-focused decisions |
| Performance Monitoring | Continuous real-time tracking using software | Periodic evaluation through meetings and reports |
| Employee Scheduling | Optimized by AI for efficiency and demand | Manual scheduling by managers |
| Feedback | Instant and automated feedback based on metrics | Personalized and subjective feedback from supervisors |
| Flexibility | Algorithm dictates work pace and tasks | Manager adjusts tasks based on situational needs |
| Transparency | Algorithms may lack clarity, causing trust issues | Open communication between employees and managers |
| Bias | Potential algorithmic bias if not properly designed | Human bias influenced by relationships and preferences |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large workforce management | Limited scalability due to human resource constraints |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven decision-making and real-time performance tracking to enhance efficiency and productivity, offering scalable solutions for large workforces. Traditional management relies on human intuition and experience, providing nuanced understanding and adaptability in complex interpersonal situations. Organizations seeking rapid scalability and consistent oversight may prefer algorithmic management, while those valuing personalized leadership and employee engagement often favor traditional methods.
Connection
Algorithmic management integrates data-driven decision-making and automated monitoring with traditional management's human oversight and strategic planning, enhancing workforce productivity and operational efficiency. By combining real-time analytics from algorithmic systems with the experiential judgment of traditional managers, organizations optimize scheduling, performance evaluation, and task allocation. This hybrid approach leverages technology to support managerial roles while maintaining the nuanced understanding essential for employee engagement and motivation.
Key Terms
Decision-making authority
Traditional management centralizes decision-making authority within hierarchical structures, relying on human judgment and experience to guide organizational actions. Algorithmic management distributes decision-making through automated systems that analyze data patterns and execute predefined rules to optimize processes. Explore how blending these approaches can transform leadership and operational efficiency in modern workplaces.
Performance monitoring
Traditional management relies on manual performance monitoring through periodic evaluations and supervisor observations, which can lead to subjective assessments and delayed feedback. Algorithmic management uses data-driven analytics and real-time tracking to provide continuous, objective performance insights and personalized recommendations for improvement. Explore further to understand how these contrasting approaches impact workforce productivity and decision-making.
Task allocation
Traditional management relies on human judgment and experience to allocate tasks, often considering employee skills, availability, and workload. Algorithmic management uses data-driven algorithms and real-time analytics to optimize task distribution efficiently, enhancing productivity and scalability. Explore the differences in detail to understand how each approach impacts workforce performance and operational outcomes.
Source and External Links
The Death of Traditional Management: Analyzing the Shift - Traditional management is characterized by hierarchical structures, autocratic leadership, and rigid protocols, rooted in early 20th-century theories emphasizing centralized decision-making and strict division of labor, but it is now being replaced by more modern, flexible management styles due to its limitations on creativity and employee engagement.
Moving Beyond Traditional Management - Evolve2B - Traditional management, originating around 1900, is based on a hierarchy where managers set strategic objectives and control worker output through strict standardization and accountability, treating employees as replaceable parts, which can limit effectiveness in modern businesses.
Ask Art: How is Traditional Management Different from Lean Management - Traditional management tends to view employees as costs to be minimized and focuses on incremental process improvements, often leading to rigid practices and making short-term targets prioritized over customer needs, contrasting with more engaged approaches like lean management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com