Secondment involves temporarily assigning an employee to another department or organization, typically maintaining benefits and job security with the original employer. Freelancing offers independent contract work, where individuals provide specialized services to multiple clients without long-term employment commitments. Explore the key differences and advantages of secondment versus freelancing to determine the best fit for your career goals.
Why it is important
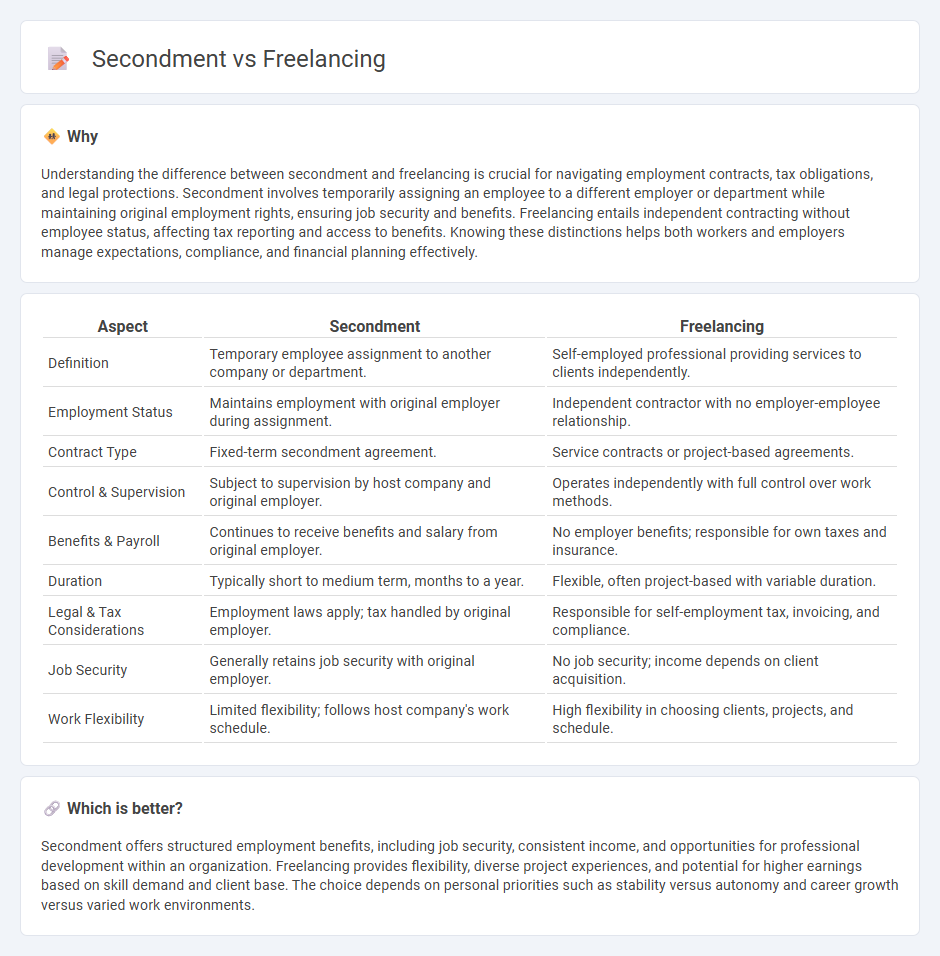
Understanding the difference between secondment and freelancing is crucial for navigating employment contracts, tax obligations, and legal protections. Secondment involves temporarily assigning an employee to a different employer or department while maintaining original employment rights, ensuring job security and benefits. Freelancing entails independent contracting without employee status, affecting tax reporting and access to benefits. Knowing these distinctions helps both workers and employers manage expectations, compliance, and financial planning effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Secondment | Freelancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Temporary employee assignment to another company or department. | Self-employed professional providing services to clients independently. |
| Employment Status | Maintains employment with original employer during assignment. | Independent contractor with no employer-employee relationship. |
| Contract Type | Fixed-term secondment agreement. | Service contracts or project-based agreements. |
| Control & Supervision | Subject to supervision by host company and original employer. | Operates independently with full control over work methods. |
| Benefits & Payroll | Continues to receive benefits and salary from original employer. | No employer benefits; responsible for own taxes and insurance. |
| Duration | Typically short to medium term, months to a year. | Flexible, often project-based with variable duration. |
| Legal & Tax Considerations | Employment laws apply; tax handled by original employer. | Responsible for self-employment tax, invoicing, and compliance. |
| Job Security | Generally retains job security with original employer. | No job security; income depends on client acquisition. |
| Work Flexibility | Limited flexibility; follows host company's work schedule. | High flexibility in choosing clients, projects, and schedule. |
Which is better?
Secondment offers structured employment benefits, including job security, consistent income, and opportunities for professional development within an organization. Freelancing provides flexibility, diverse project experiences, and potential for higher earnings based on skill demand and client base. The choice depends on personal priorities such as stability versus autonomy and career growth versus varied work environments.
Connection
Secondment and freelancing both involve temporary work arrangements that provide flexible employment solutions for businesses and professionals. They enable skill transfer, project-based expertise, and workforce agility by allowing employees or freelancers to contribute to different organizations without long-term commitments. These models support dynamic labor market needs, enhance career development, and improve resource allocation across industries.
Key Terms
Autonomy
Freelancing offers high autonomy, allowing professionals to choose clients, projects, and working hours, fostering entrepreneurial freedom. Secondment provides limited autonomy, as individuals temporarily work under another organization's guidelines, balancing exposure with structured oversight. Explore the distinct autonomy benefits of freelancing versus secondment to optimize your career strategy.
Contractual Relationship
Freelancing typically involves an independent contractor status with a client, where the freelancer controls work methods and retains autonomy over schedule and tools, reflecting a clear lack of employment contract. Secondment implies a temporary transfer of an employee from one employer to another, with employment terms largely maintained by the original employer, indicating a continued contractual employment relationship. Explore detailed distinctions and legal implications to better understand which arrangement suits your business needs.
Integration
Freelancing offers flexible work arrangements with limited integration into company culture, while secondment involves temporarily embedding employees within an organization to enhance collaboration and knowledge transfer. Secondment strengthens team cohesion by aligning secondees closely with internal processes and corporate values, unlike freelancing which often results in peripheral engagement. Explore the nuances of each approach to determine the best integration strategy for your workforce needs.
Source and External Links
What Is Freelancing? Basics and Popular Jobs in 2025 - Upwork - Freelancing is doing specific work for clients without full-time employment, requiring you to pick a niche, build a portfolio, set rates, promote yourself, manage projects, and handle taxes as a self-employed individual.
Freelancing 101: What is Freelancing? - GCF Global - Freelancing is a form of self-employment where you have freedom over your work location and schedule, working independently for various clients worldwide by offering your unique skills and expertise.
25 best freelance websites to find work in 2025 - Hostinger - Freelancing offers flexibility to choose your projects, set rates, and work independently, and beginners can start part-time while building their skills and client base using top freelance platforms like Fiverr and Toptal.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com