Career cushioning involves building skills and savings as a safety net while maintaining a current job, providing stability and long-term growth. Job hopping refers to frequently changing positions to gain diverse experience and potentially higher salaries, though it may affect job security. Explore more to understand which strategy aligns best with your professional goals.
Why it is important
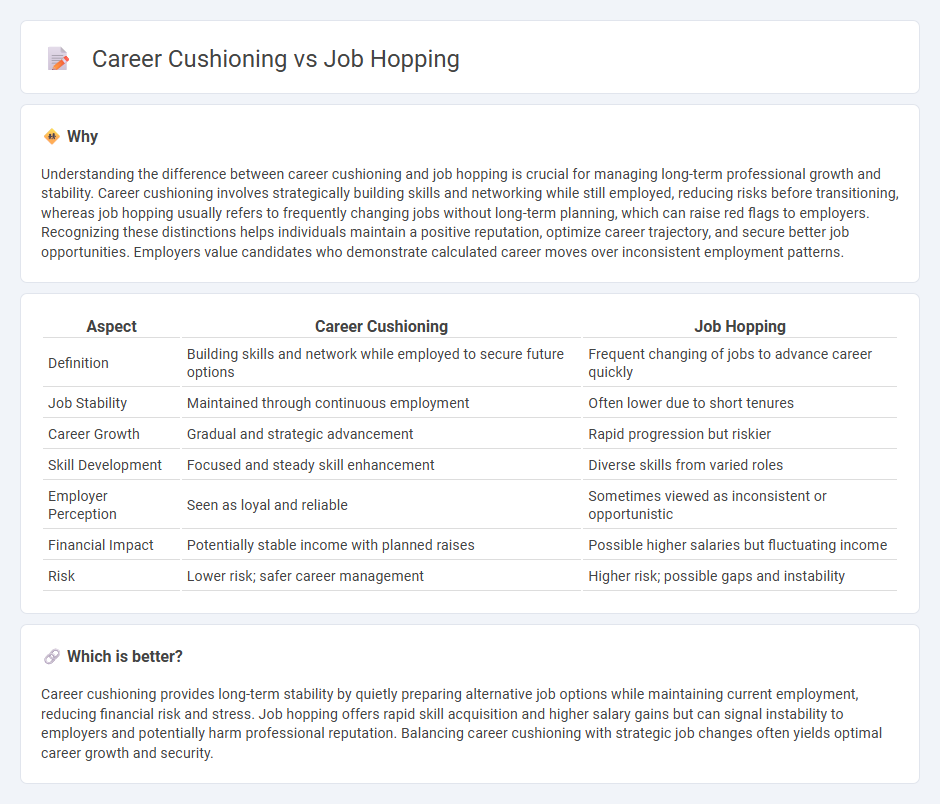
Understanding the difference between career cushioning and job hopping is crucial for managing long-term professional growth and stability. Career cushioning involves strategically building skills and networking while still employed, reducing risks before transitioning, whereas job hopping usually refers to frequently changing jobs without long-term planning, which can raise red flags to employers. Recognizing these distinctions helps individuals maintain a positive reputation, optimize career trajectory, and secure better job opportunities. Employers value candidates who demonstrate calculated career moves over inconsistent employment patterns.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Cushioning | Job Hopping |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Building skills and network while employed to secure future options | Frequent changing of jobs to advance career quickly |
| Job Stability | Maintained through continuous employment | Often lower due to short tenures |
| Career Growth | Gradual and strategic advancement | Rapid progression but riskier |
| Skill Development | Focused and steady skill enhancement | Diverse skills from varied roles |
| Employer Perception | Seen as loyal and reliable | Sometimes viewed as inconsistent or opportunistic |
| Financial Impact | Potentially stable income with planned raises | Possible higher salaries but fluctuating income |
| Risk | Lower risk; safer career management | Higher risk; possible gaps and instability |
Which is better?
Career cushioning provides long-term stability by quietly preparing alternative job options while maintaining current employment, reducing financial risk and stress. Job hopping offers rapid skill acquisition and higher salary gains but can signal instability to employers and potentially harm professional reputation. Balancing career cushioning with strategic job changes often yields optimal career growth and security.
Connection
Career cushioning involves building skills and networks as a safety net for potential job loss, which directly influences job hopping by making transitions smoother and less risky. Employees who practice career cushioning tend to change jobs more frequently to pursue better opportunities and avoid stagnation. This connection highlights a strategic approach to employment stability and professional growth in competitive job markets.
Key Terms
Job Stability
Job stability concerns are central to distinguishing job hopping from career cushioning; job hopping involves frequent changes that may signal unpredictability to employers, while career cushioning emphasizes securing backup opportunities without immediate resignation. Maintaining a balance between gaining diverse experience and demonstrating commitment enhances professional reputation and long-term career growth. Explore effective strategies for balancing job hopping and career cushioning to strengthen your job stability.
Skill Development
Job hopping allows professionals to rapidly acquire diverse skills by exposing them to various industries and roles, enhancing adaptability and broadening expertise. Career cushioning emphasizes continuous skill development within a current trajectory to ensure stability and growth, leveraging specialized knowledge and deepening proficiency. Discover how balancing both approaches can optimize your skill development strategy.
Risk Management
Job hopping involves frequently changing positions to gain new experiences, while career cushioning focuses on strategically building skills and networks to mitigate future employment risks. Effective risk management in career cushioning ensures stability by preparing for market shifts, unlike job hopping which can increase uncertainty. Explore detailed strategies to balance career growth with minimizing employment risks.
Source and External Links
What Is Job Hopping? (Plus Advantages and Disadvantages) - Indeed - Job hopping is the practice of holding multiple jobs in a short period, increasingly common today as workers seek better pay and titles, but still requiring explanation to hiring managers to show dependability.
Job-Hopping With Intention: Pros, Cons, and Considerations - Job hopping typically means staying at a job for 1-2 years and can reflect desires for new challenges, better career paths, or skill development, though it may still be viewed negatively by some employers.
Job Hopping | What is it and what are its advantages? - Iberdrola - Job hopping refers to frequent voluntary job changes, especially among young digital professionals, driven by a strong ambition for upward mobility and new challenges, and is increasingly valued by companies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com