Algorithmic management leverages data-driven software to optimize workforce scheduling, performance tracking, and task allocation, revolutionizing traditional human resources management practices. While human resources management focuses on interpersonal skills, employee relations, and organizational culture, algorithmic management enhances efficiency through automation and predictive analytics. Explore the evolving impact of these two approaches on modern employment strategies.
Why it is important
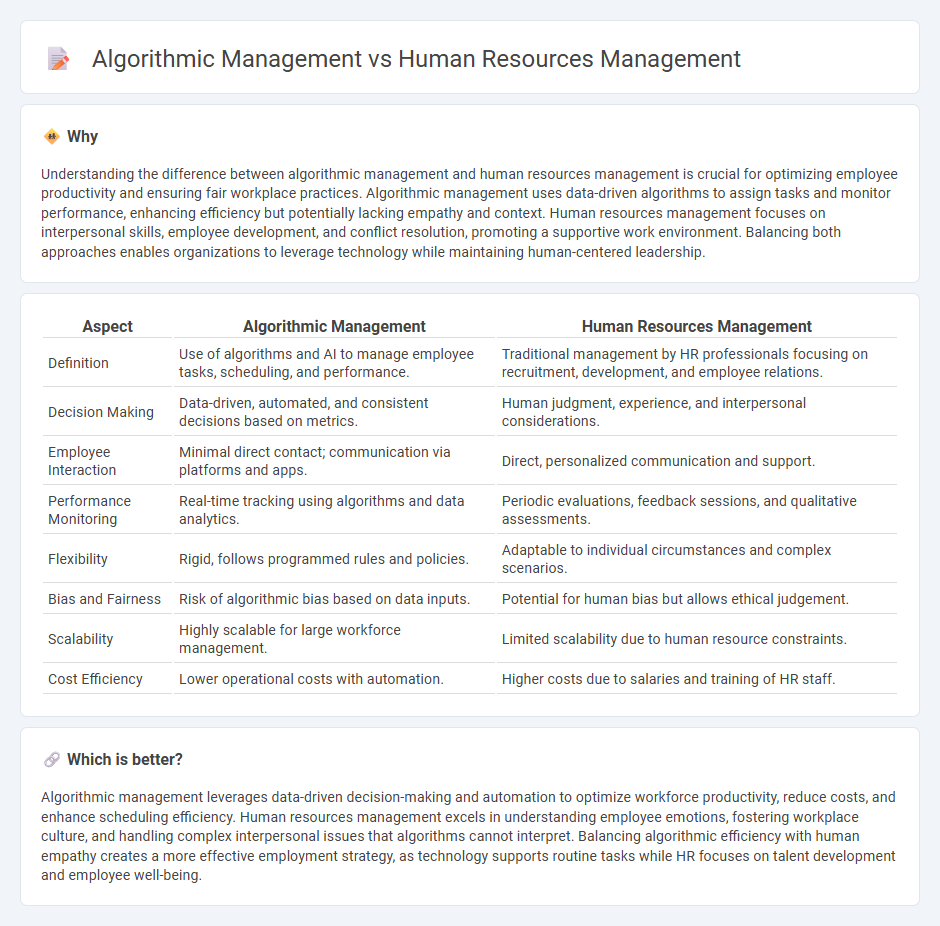
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and human resources management is crucial for optimizing employee productivity and ensuring fair workplace practices. Algorithmic management uses data-driven algorithms to assign tasks and monitor performance, enhancing efficiency but potentially lacking empathy and context. Human resources management focuses on interpersonal skills, employee development, and conflict resolution, promoting a supportive work environment. Balancing both approaches enables organizations to leverage technology while maintaining human-centered leadership.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Human Resources Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of algorithms and AI to manage employee tasks, scheduling, and performance. | Traditional management by HR professionals focusing on recruitment, development, and employee relations. |
| Decision Making | Data-driven, automated, and consistent decisions based on metrics. | Human judgment, experience, and interpersonal considerations. |
| Employee Interaction | Minimal direct contact; communication via platforms and apps. | Direct, personalized communication and support. |
| Performance Monitoring | Real-time tracking using algorithms and data analytics. | Periodic evaluations, feedback sessions, and qualitative assessments. |
| Flexibility | Rigid, follows programmed rules and policies. | Adaptable to individual circumstances and complex scenarios. |
| Bias and Fairness | Risk of algorithmic bias based on data inputs. | Potential for human bias but allows ethical judgement. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable for large workforce management. | Limited scalability due to human resource constraints. |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs with automation. | Higher costs due to salaries and training of HR staff. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management leverages data-driven decision-making and automation to optimize workforce productivity, reduce costs, and enhance scheduling efficiency. Human resources management excels in understanding employee emotions, fostering workplace culture, and handling complex interpersonal issues that algorithms cannot interpret. Balancing algorithmic efficiency with human empathy creates a more effective employment strategy, as technology supports routine tasks while HR focuses on talent development and employee well-being.
Connection
Algorithmic management integrates data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce scheduling, performance monitoring, and task allocation, enhancing efficiency in human resources management. Human resources harness these algorithmic tools to improve recruitment processes, employee evaluation, and retention strategies by leveraging predictive analytics and real-time data. This synergy streamlines decision-making, reduces operational costs, and fosters a more agile and responsive employment environment.
Key Terms
**Human Resources Management:**
Human Resources Management (HRM) centers on strategic recruitment, employee development, and fostering workplace culture to enhance organizational performance. It emphasizes human-centric approaches like talent management, employee engagement, and conflict resolution to optimize workforce productivity. Explore how HRM practices transform businesses by prioritizing people over processes.
Recruitment
Human resources management leverages interpersonal skills and psychological insights to evaluate candidate fit and cultural alignment during recruitment. Algorithmic management utilizes data-driven tools and automated processes to screen resumes, assess qualifications, and predict candidate success with machine learning models. Explore the evolving impact of technology in recruitment to optimize talent acquisition strategies.
Performance Appraisal
Human resources management emphasizes personalized performance appraisal through direct supervisor evaluation, feedback, and development plans, fostering employee growth and engagement. Algorithmic management relies on data-driven metrics and automated algorithms to assess performance, offering efficiency and scalability but often lacking contextual understanding and human judgment. Explore how integrating both methods can optimize performance appraisal in modern workplaces.
Source and External Links
Human resource management - HRM Functions - ADP - Human resource management involves creating personnel policies and procedures that support business objectives and strategic plans, focusing on talent acquisition, employee engagement, performance measurement, and professional development.
Human resource management - Wikipedia - HRM is a strategic approach to managing people effectively in organizations, focusing on staffing, training and development, and employee maintenance to sustain motivation and productivity.
What Is Human Resource Management? Careers, Skills ... - Coursera - HRM manages employees to advance company goals by investing in employee development, fostering positive work culture, and ensuring legal compliance and employee protection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com