Digital nomad visas offer remote workers the freedom to live and work abroad without the constraints of a traditional employment contract tied to a specific country. Traditional employment visas require sponsorship from an employer and often limit job mobility within the host nation. Explore the differences to understand which visa suits your professional lifestyle best.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between digital nomad visas and traditional employment visas is crucial for navigating legal work authorization, tax obligations, and residency rights in foreign countries. Digital nomad visas typically cater to remote workers who maintain employment outside the host country, offering more flexibility and streamlined application processes without requiring local employment. Traditional employment visas mandate sponsorship by a local employer and often involve stricter regulations tied to labor markets, affecting job security and mobility. This distinction impacts compliance, financial planning, and personal freedom in global employment scenarios.
Comparison Table
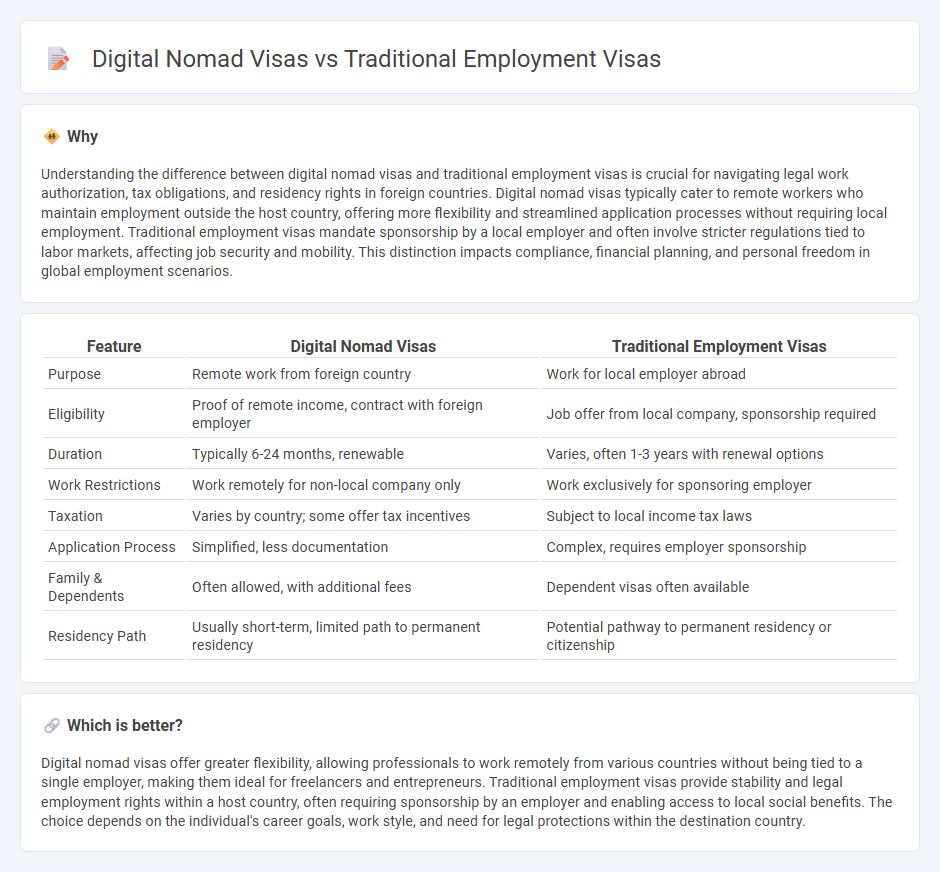
| Feature | Digital Nomad Visas | Traditional Employment Visas |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Remote work from foreign country | Work for local employer abroad |
| Eligibility | Proof of remote income, contract with foreign employer | Job offer from local company, sponsorship required |
| Duration | Typically 6-24 months, renewable | Varies, often 1-3 years with renewal options |
| Work Restrictions | Work remotely for non-local company only | Work exclusively for sponsoring employer |
| Taxation | Varies by country; some offer tax incentives | Subject to local income tax laws |
| Application Process | Simplified, less documentation | Complex, requires employer sponsorship |
| Family & Dependents | Often allowed, with additional fees | Dependent visas often available |
| Residency Path | Usually short-term, limited path to permanent residency | Potential pathway to permanent residency or citizenship |
Which is better?
Digital nomad visas offer greater flexibility, allowing professionals to work remotely from various countries without being tied to a single employer, making them ideal for freelancers and entrepreneurs. Traditional employment visas provide stability and legal employment rights within a host country, often requiring sponsorship by an employer and enabling access to local social benefits. The choice depends on the individual's career goals, work style, and need for legal protections within the destination country.
Connection
Digital nomad visas and traditional employment visas both regulate foreign nationals' ability to work legally within a host country, but they cater to distinct employment models; digital nomad visas target remote workers whose income is not tied to the local economy, whereas traditional employment visas require sponsorship by a local employer. Both visa types involve eligibility criteria, income thresholds, and documentation to ensure compliance with immigration laws and labor market impacts. Emerging trends show governments adapting visa policies to attract global talent, reflecting the evolving workforce where remote work and international mobility grow increasingly prevalent.
Key Terms
Work Sponsorship
Traditional employment visas generally require work sponsorship from an employer, ensuring legal authorization and labor market protections tied to specific job positions. Digital nomad visas offer greater flexibility by allowing remote work for foreign employers without local sponsorship, promoting location independence. Explore the benefits and requirements of these visa types to determine the best fit for your professional lifestyle.
Location Independence
Traditional employment visas require applicants to secure a job tied to a specific country, limiting the ability to work remotely, while digital nomad visas are designed to support location independence by allowing professionals to live and work remotely without a local employer. These visas often provide flexibility in terms of duration and residency, catering to freelancers, entrepreneurs, and remote employees seeking to maintain a stable income from abroad. Explore how digital nomad visas can empower your remote lifestyle and unlock global work opportunities.
Tax Residency
Traditional employment visas require individuals to establish tax residency in the host country, often resulting in dual taxation unless a tax treaty exists. Digital nomad visas typically allow remote workers to maintain tax residency in their home country, minimizing tax obligations abroad by leveraging international tax agreements and specific visa structures designed for non-resident workers. Explore the nuances of tax residency rules and how they impact your global income to make an informed decision on visa options.
Source and External Links
What Is a Work Visa? Permit Requirements - Traditional employment visas allow foreign nationals to work in a specific country for a designated period and can be categorized as temporary (e.g., tied to a specific job or employer) or permanent (granting indefinite residence and work rights).
The Different Types of U.S. Work Visas - The U.S. offers both permanent (immigrant) and temporary (non-immigrant) work visas, including categories like EB-1 for individuals with extraordinary ability, EB-2 for professionals with advanced degrees, and H-1B for skilled workers.
Everything You Need to Know About Work Visas - Work visas in the U.S. are issued based on job position, industry, and duration of work, with common temporary types including H-1B for skilled professionals and seasonal visas for industries with fluctuating labor needs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com