Quiet quitting, characterized by doing only the minimum required work, contrasts sharply with presenteeism, where employees are physically present but mentally disengaged or unproductive. Both phenomena impact workplace productivity, employee well-being, and organizational culture in significant ways. Explore deeper insights on how quiet quitting and presenteeism influence modern employment dynamics.
Why it is important
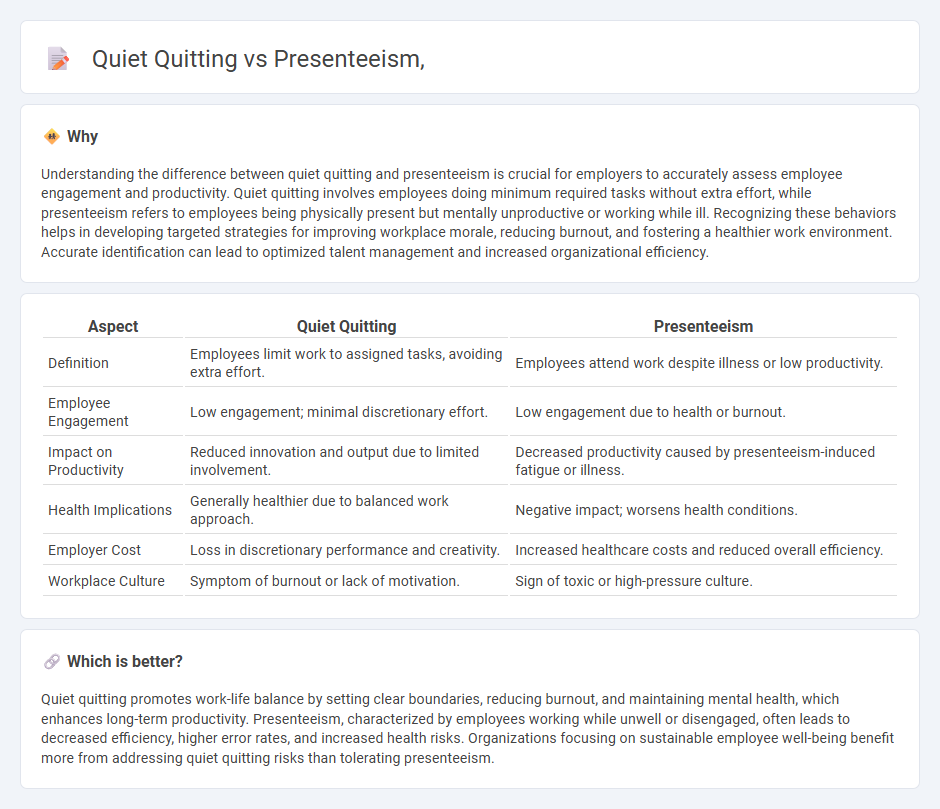
Understanding the difference between quiet quitting and presenteeism is crucial for employers to accurately assess employee engagement and productivity. Quiet quitting involves employees doing minimum required tasks without extra effort, while presenteeism refers to employees being physically present but mentally unproductive or working while ill. Recognizing these behaviors helps in developing targeted strategies for improving workplace morale, reducing burnout, and fostering a healthier work environment. Accurate identification can lead to optimized talent management and increased organizational efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quiet Quitting | Presenteeism |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Employees limit work to assigned tasks, avoiding extra effort. | Employees attend work despite illness or low productivity. |
| Employee Engagement | Low engagement; minimal discretionary effort. | Low engagement due to health or burnout. |
| Impact on Productivity | Reduced innovation and output due to limited involvement. | Decreased productivity caused by presenteeism-induced fatigue or illness. |
| Health Implications | Generally healthier due to balanced work approach. | Negative impact; worsens health conditions. |
| Employer Cost | Loss in discretionary performance and creativity. | Increased healthcare costs and reduced overall efficiency. |
| Workplace Culture | Symptom of burnout or lack of motivation. | Sign of toxic or high-pressure culture. |
Which is better?
Quiet quitting promotes work-life balance by setting clear boundaries, reducing burnout, and maintaining mental health, which enhances long-term productivity. Presenteeism, characterized by employees working while unwell or disengaged, often leads to decreased efficiency, higher error rates, and increased health risks. Organizations focusing on sustainable employee well-being benefit more from addressing quiet quitting risks than tolerating presenteeism.
Connection
Quiet quitting and presenteeism both reflect disengagement at work, where employees either limit their efforts to job descriptions or show up physically without full productivity. These behaviors stem from burnout, dissatisfaction, or lack of motivation, impacting overall workplace efficiency and morale. Organizations facing high rates of quiet quitting often report increased presenteeism, signaling widespread employee disengagement.
Key Terms
Productivity
Presenteeism occurs when employees are physically present at work but perform below their full capacity due to stress, illness, or disengagement, severely impacting productivity metrics. Quiet quitting reflects a mindset where employees fulfill only their job descriptions without extra effort, leading to minimal discretionary effort and stagnated innovation levels. Explore comprehensive strategies to enhance workforce productivity and address both presenteeism and quiet quitting effectively.
Engagement
Presenteeism occurs when employees are physically present but mentally disengaged, leading to reduced productivity and hidden costs for organizations. Quiet quitting reflects a decline in engagement where workers do the minimum required, avoiding extra effort or involvement beyond their job description. Explore how enhancing employee engagement strategies can effectively address both presenteeism and quiet quitting to boost workplace performance.
Workplace culture
Presenteeism involves employees being physically present but mentally disengaged at work, reflecting a culture where long hours are valued over productivity and well-being. Quiet quitting signifies a shift towards minimal effort and disengagement without formal resignation, highlighting employee dissatisfaction and lack of motivation within the workplace environment. Explore effective strategies to foster a positive workplace culture that addresses both issues and promotes employee engagement.
Source and External Links
Presenteeism - Wikipedia - Presenteeism is the act or culture of employees continuing to work despite illness or reduced productivity, often caused by illness, injury, or exhaustion, and driven by motives such as financial need, feelings of being irreplaceable, devotion to work, or management expectations.
Is presenteeism a problem? You may be encouraging it - BetterUp - Presenteeism occurs when employees prioritize showing up over taking care of themselves, leading to physical presence but reduced productivity due to illness, burnout, or personal issues, potentially causing workplace epidemics and increased errors.
What is presenteeism? - Future Forum - Presenteeism describes both working while sick and the pressure to perform by working long hours or being constantly available, reflecting flawed management assumptions that more visible hours equal better performance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com