Labor hoarding preserves workforce stability during demand fluctuations, reducing turnover costs and maintaining employee expertise. Cross-training enhances workforce flexibility by equipping employees with diverse skills, improving productivity and adaptability. Explore how businesses balance these strategies to optimize employment outcomes.
Why it is important
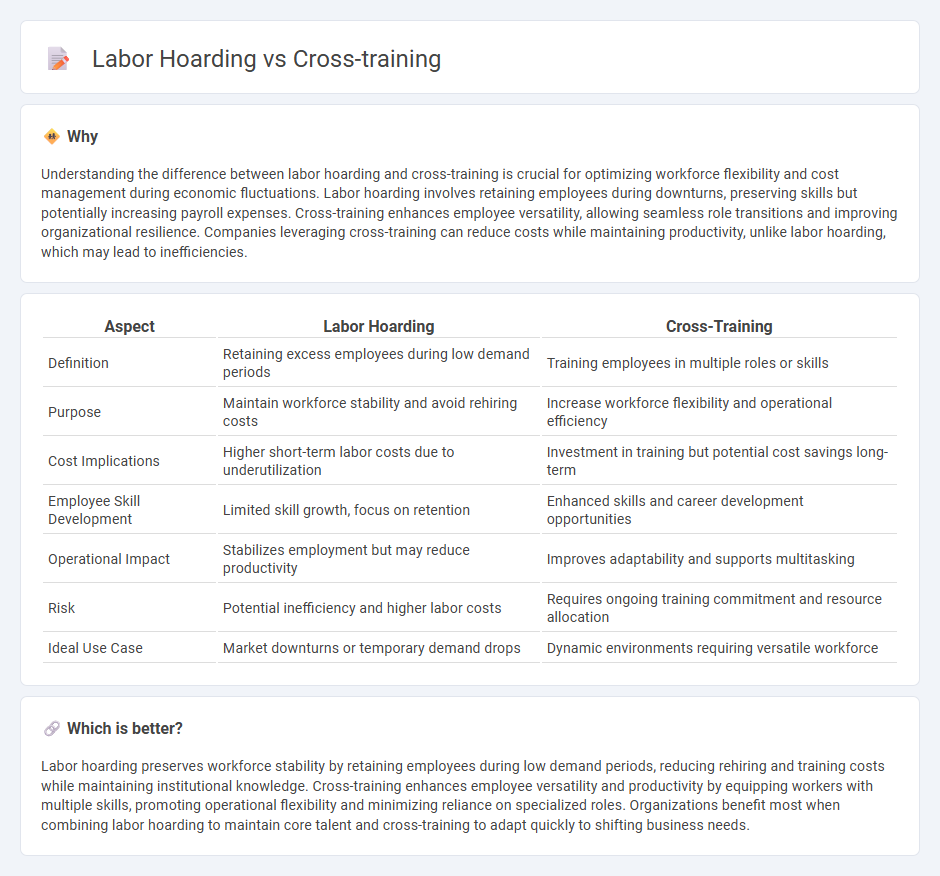
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and cross-training is crucial for optimizing workforce flexibility and cost management during economic fluctuations. Labor hoarding involves retaining employees during downturns, preserving skills but potentially increasing payroll expenses. Cross-training enhances employee versatility, allowing seamless role transitions and improving organizational resilience. Companies leveraging cross-training can reduce costs while maintaining productivity, unlike labor hoarding, which may lead to inefficiencies.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Cross-Training |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining excess employees during low demand periods | Training employees in multiple roles or skills |
| Purpose | Maintain workforce stability and avoid rehiring costs | Increase workforce flexibility and operational efficiency |
| Cost Implications | Higher short-term labor costs due to underutilization | Investment in training but potential cost savings long-term |
| Employee Skill Development | Limited skill growth, focus on retention | Enhanced skills and career development opportunities |
| Operational Impact | Stabilizes employment but may reduce productivity | Improves adaptability and supports multitasking |
| Risk | Potential inefficiency and higher labor costs | Requires ongoing training commitment and resource allocation |
| Ideal Use Case | Market downturns or temporary demand drops | Dynamic environments requiring versatile workforce |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves workforce stability by retaining employees during low demand periods, reducing rehiring and training costs while maintaining institutional knowledge. Cross-training enhances employee versatility and productivity by equipping workers with multiple skills, promoting operational flexibility and minimizing reliance on specialized roles. Organizations benefit most when combining labor hoarding to maintain core talent and cross-training to adapt quickly to shifting business needs.
Connection
Labor hoarding helps organizations retain skilled employees during economic downturns, preserving human capital for future productivity. Cross-training enhances workforce flexibility by equipping employees with multiple skills, allowing seamless task redistribution when labor hoarding occurs. Together, these strategies optimize operational efficiency and reduce turnover costs by maintaining a versatile, stable workforce.
Key Terms
Skill diversification
Cross-training enhances skill diversification by equipping employees with multiple competencies, enabling flexible task assignments and improved operational resilience. Labor hoarding maintains excess staffing during downturns but often limits skill development to core roles, reducing workforce adaptability. Explore the strategic benefits of skill diversification through cross-training to optimize workforce flexibility and productivity.
Workforce flexibility
Cross-training enhances workforce flexibility by equipping employees with multiple skills, enabling seamless task coverage and adaptation to fluctuating demands. Labor hoarding involves retaining excess staff during downturns to preserve organizational knowledge and maintain readiness for future growth. Explore how businesses balance these strategies to optimize agility and resilience in dynamic markets.
Employee retention
Cross-training enhances employee retention by equipping workers with diverse skills, increasing job satisfaction and adaptability within an organization. Labor hoarding, while preserving employment during downturns, may lead to reduced motivation if employees perceive limited growth opportunities. Explore detailed strategies to balance these approaches for optimal retention outcomes.
Source and External Links
Cross-training - Wikipedia - Cross-training is athletic training in sports other than the athlete's usual sport with the goal of improving overall performance by balancing muscle use and overcoming the shortcomings of a single training method.
Cross-Training: Benefits, Exercises, and Getting Started - WebMD - Cross-training involves combining different types of exercise to address strength, cardio, and flexibility, preventing overuse injuries and improving fitness by varying the routine.
Cross-Training Is Effective for All Athletes - Healthline - Cross-training is an exercise protocol using modes of training different from an athlete's main sport to develop specific fitness components and is commonly used during off-season periods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com