Career lattice offers a flexible approach to employee growth by enabling lateral and vertical moves that enhance skills and experience without a traditional linear path. Matrix management structure involves multiple reporting lines, allowing employees to work on diverse projects across departments, fostering collaboration and versatility. Explore how these frameworks can transform your career trajectory and organizational dynamics.
Why it is important
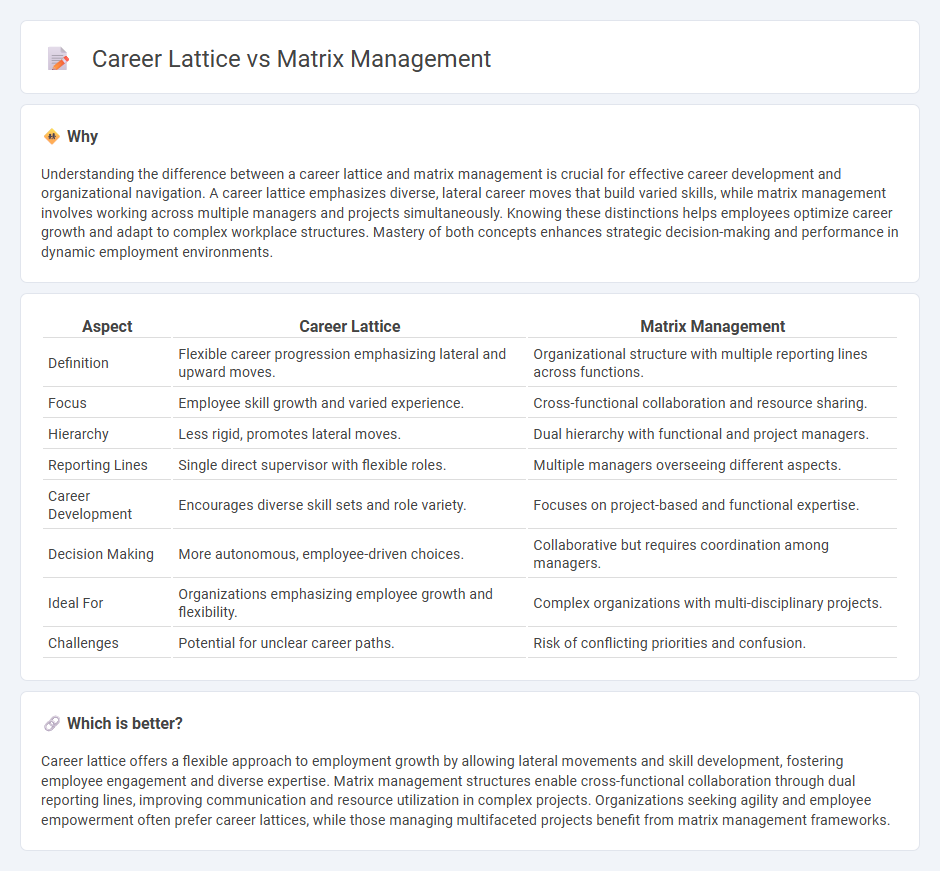
Understanding the difference between a career lattice and matrix management is crucial for effective career development and organizational navigation. A career lattice emphasizes diverse, lateral career moves that build varied skills, while matrix management involves working across multiple managers and projects simultaneously. Knowing these distinctions helps employees optimize career growth and adapt to complex workplace structures. Mastery of both concepts enhances strategic decision-making and performance in dynamic employment environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Lattice | Matrix Management |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flexible career progression emphasizing lateral and upward moves. | Organizational structure with multiple reporting lines across functions. |
| Focus | Employee skill growth and varied experience. | Cross-functional collaboration and resource sharing. |
| Hierarchy | Less rigid, promotes lateral moves. | Dual hierarchy with functional and project managers. |
| Reporting Lines | Single direct supervisor with flexible roles. | Multiple managers overseeing different aspects. |
| Career Development | Encourages diverse skill sets and role variety. | Focuses on project-based and functional expertise. |
| Decision Making | More autonomous, employee-driven choices. | Collaborative but requires coordination among managers. |
| Ideal For | Organizations emphasizing employee growth and flexibility. | Complex organizations with multi-disciplinary projects. |
| Challenges | Potential for unclear career paths. | Risk of conflicting priorities and confusion. |
Which is better?
Career lattice offers a flexible approach to employment growth by allowing lateral movements and skill development, fostering employee engagement and diverse expertise. Matrix management structures enable cross-functional collaboration through dual reporting lines, improving communication and resource utilization in complex projects. Organizations seeking agility and employee empowerment often prefer career lattices, while those managing multifaceted projects benefit from matrix management frameworks.
Connection
Career lattice and matrix management intersect by promoting dynamic, multi-directional career development within organizational structures. Career lattice enables employees to move laterally and vertically, aligning skill growth with diverse project teams typical in matrix management. This synergy fosters flexible talent deployment, enhanced collaboration, and optimized career progression paths.
Key Terms
Reporting Structure
Matrix management features dual reporting lines where employees report to both functional and project managers, enhancing cross-functional collaboration but potentially causing ambiguity in authority. Career lattice emphasizes lateral movement across roles and departments rather than upward progression, promoting skill diversification and flexible reporting structures based on project needs. Explore the differences in reporting structures further to determine which approach best suits organizational goals.
Cross-functional Teams
Matrix management structures employees under multiple managers, enhancing collaboration across different departments but often leading to complex reporting relationships and potential conflicts. Career lattice embraces lateral moves within cross-functional teams, promoting skill diversity and adaptability instead of linear progression. Explore more to understand how these approaches impact cross-functional team dynamics and career growth.
Lateral Mobility
Matrix management enhances lateral mobility by enabling employees to work across multiple projects and reports, fostering diverse skill development and collaboration. The career lattice concept emphasizes upward, lateral, and even downward movements, offering flexible career paths that accommodate changing roles and expertise within an organization. Explore how integrating matrix management practices with career lattice frameworks can optimize talent mobility and career growth.
Source and External Links
Matrix Management: Definition, Advantages and How It Works - Indeed - Matrix management is an organizational structure where employees report to multiple managers, and it requires clear assignment of reporting lines, effective communication, and continuous evaluation of what works in projects for efficient operations.
Matrix management - Wikipedia - Matrix management is a structure in which individuals report to more than one leader, involving solid line or dotted line reporting and enabling cross-functional collaboration, with variations such as strong, weak, and balanced matrix structures.
Matrix Management and Its Importance - Saviom Software - Implementing matrix management successfully involves securing stakeholder buy-in and setting SMART objectives to align diverse teams and clarify responsibilities across multiple reporting lines.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com