Ghost work involves completing microtasks or digital labor for clients through online platforms, often lacking formal employment benefits and job security. Agency work refers to temporary employment sourced by staffing agencies, providing workers with assignments in various industries while offering some legal protections and structured contracts. Explore the differences between ghost work and agency work to understand their impact on the future of employment.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between ghost work and agency work is crucial for accurately assessing job security, worker rights, and payment structures. Ghost work involves invisible, often digital labor without direct client interaction, while agency work refers to temporary assignments arranged through staffing firms. This distinction impacts legal protections, benefits eligibility, and classification for taxation. Employers and workers must recognize these differences to navigate employment contracts and labor regulations effectively.
Comparison Table
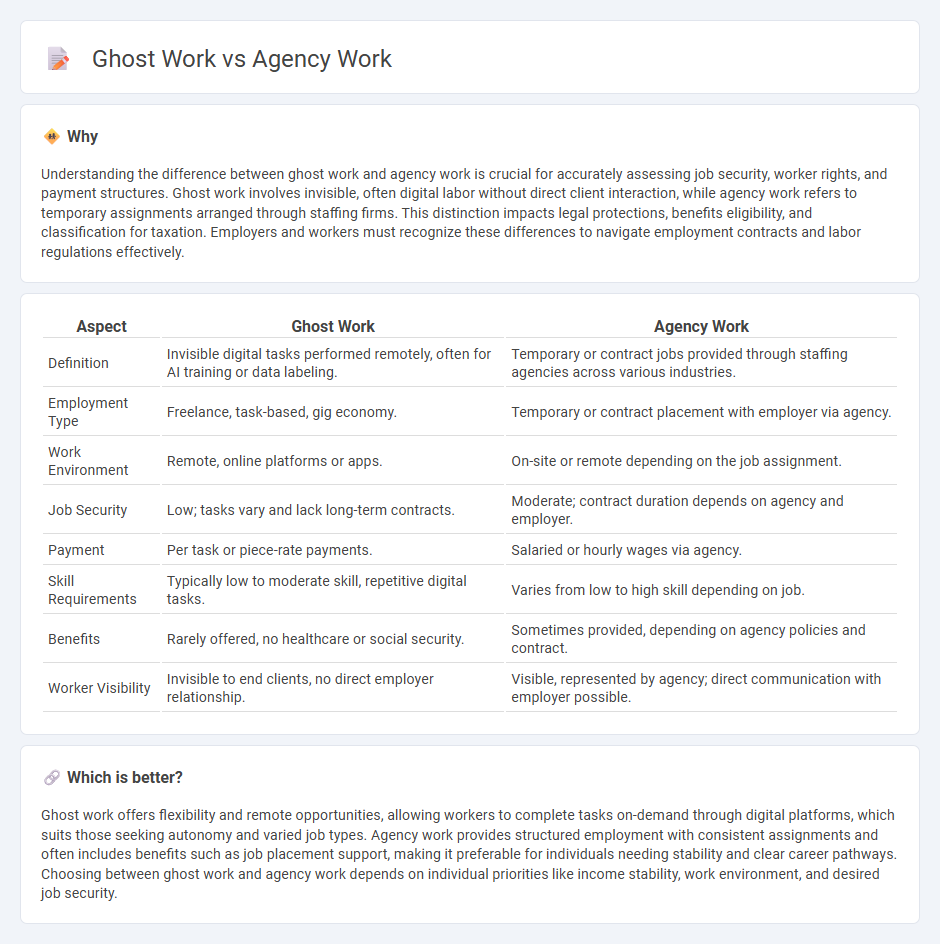
| Aspect | Ghost Work | Agency Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Invisible digital tasks performed remotely, often for AI training or data labeling. | Temporary or contract jobs provided through staffing agencies across various industries. |
| Employment Type | Freelance, task-based, gig economy. | Temporary or contract placement with employer via agency. |
| Work Environment | Remote, online platforms or apps. | On-site or remote depending on the job assignment. |
| Job Security | Low; tasks vary and lack long-term contracts. | Moderate; contract duration depends on agency and employer. |
| Payment | Per task or piece-rate payments. | Salaried or hourly wages via agency. |
| Skill Requirements | Typically low to moderate skill, repetitive digital tasks. | Varies from low to high skill depending on job. |
| Benefits | Rarely offered, no healthcare or social security. | Sometimes provided, depending on agency policies and contract. |
| Worker Visibility | Invisible to end clients, no direct employer relationship. | Visible, represented by agency; direct communication with employer possible. |
Which is better?
Ghost work offers flexibility and remote opportunities, allowing workers to complete tasks on-demand through digital platforms, which suits those seeking autonomy and varied job types. Agency work provides structured employment with consistent assignments and often includes benefits such as job placement support, making it preferable for individuals needing stability and clear career pathways. Choosing between ghost work and agency work depends on individual priorities like income stability, work environment, and desired job security.
Connection
Ghost work involves freelance or contract tasks often mediated through digital platforms, relying on remote, flexible labor. Agency work serves as an intermediary, connecting these independent workers with clients seeking skilled or temporary services. Both models emphasize adaptable employment arrangements driven by technology and shifting labor market demands.
Key Terms
Temporary Staffing
Temporary staffing agencies provide businesses with skilled workers for short-term projects, ensuring flexibility and rapid deployment without long-term commitments. Ghost work involves remote, often anonymous tasks completed by freelancers or crowdworkers through online platforms, lacking traditional employment structures and benefits. Explore how these distinct models shape the future workforce and optimize operational efficiency.
Platform Labor
Platform labor encompasses agency work, where intermediaries connect workers with clients, and ghost work, involving hidden online tasks often performed behind the scenes. Agency work typically offers more visibility and structured communication between labor providers and consumers, whereas ghost work remains largely invisible, obscuring the human effort behind AI training and content moderation. Explore the complexities and implications of platform labor to understand its evolving impact on the gig economy.
Employment Relationship
Agency work involves a formal employment relationship where workers are hired by an agency and assigned to client companies, ensuring legal protections and benefits. Ghost work lacks a direct employer-employee relationship, with individuals performing tasks remotely for digital platforms, often classified as independent contractors without traditional employment rights. Explore deeper insights on how these models impact worker rights and job security.
Source and External Links
Agency Work - Agency work is a form of employment where workers have a contract with an employment agency and are deployed to user firms under their supervision.
USAJOBS - This is the official federal government employment site where job seekers can find and apply for federal jobs.
Staffing Agency Jobs in Florida - This page offers various staffing agency jobs available in Florida, including roles such as registered nurses and physical therapists.
Adecco - Adecco provides temporary and direct hire job opportunities across multiple industries and locations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com