Labor hoarding involves retaining employees during economic downturns to preserve organizational knowledge and readiness for recovery, while contracting reduces workforce size to cut costs and increase operational flexibility. Companies practicing labor hoarding often invest in training and redeployment, mitigating the adverse impact of layoffs on morale and productivity. Discover more about how these contrasting employment strategies affect business resilience and workforce management.
Why it is important
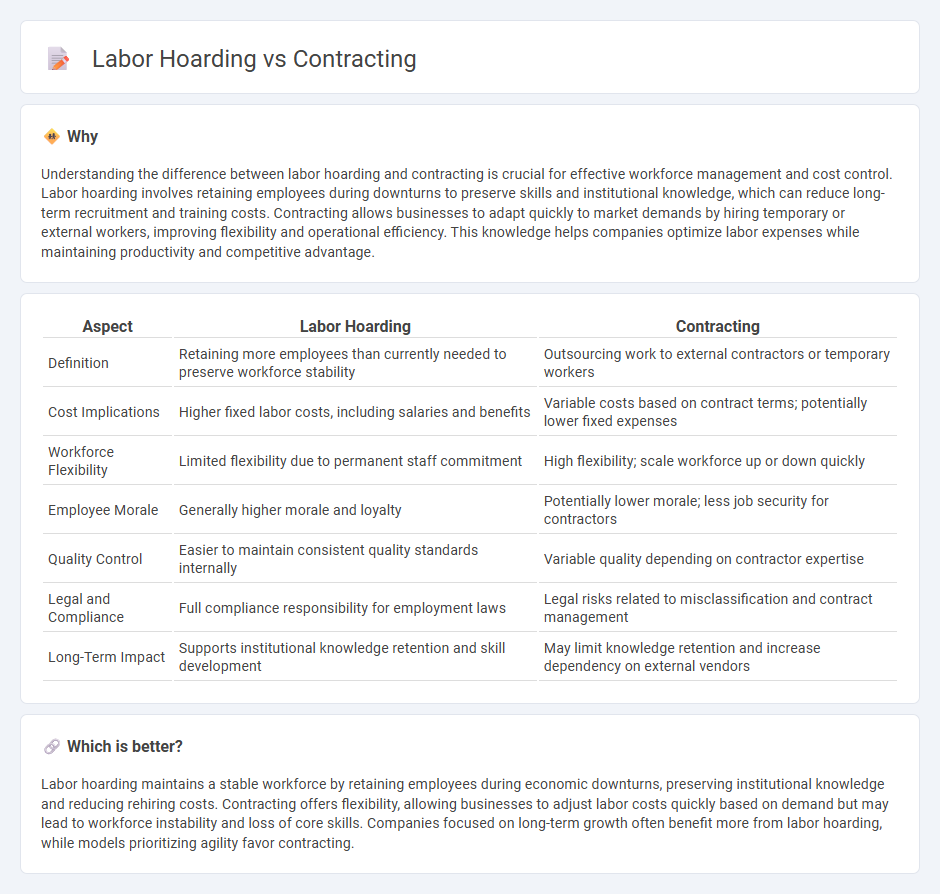
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and contracting is crucial for effective workforce management and cost control. Labor hoarding involves retaining employees during downturns to preserve skills and institutional knowledge, which can reduce long-term recruitment and training costs. Contracting allows businesses to adapt quickly to market demands by hiring temporary or external workers, improving flexibility and operational efficiency. This knowledge helps companies optimize labor expenses while maintaining productivity and competitive advantage.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Contracting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining more employees than currently needed to preserve workforce stability | Outsourcing work to external contractors or temporary workers |
| Cost Implications | Higher fixed labor costs, including salaries and benefits | Variable costs based on contract terms; potentially lower fixed expenses |
| Workforce Flexibility | Limited flexibility due to permanent staff commitment | High flexibility; scale workforce up or down quickly |
| Employee Morale | Generally higher morale and loyalty | Potentially lower morale; less job security for contractors |
| Quality Control | Easier to maintain consistent quality standards internally | Variable quality depending on contractor expertise |
| Legal and Compliance | Full compliance responsibility for employment laws | Legal risks related to misclassification and contract management |
| Long-Term Impact | Supports institutional knowledge retention and skill development | May limit knowledge retention and increase dependency on external vendors |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding maintains a stable workforce by retaining employees during economic downturns, preserving institutional knowledge and reducing rehiring costs. Contracting offers flexibility, allowing businesses to adjust labor costs quickly based on demand but may lead to workforce instability and loss of core skills. Companies focused on long-term growth often benefit more from labor hoarding, while models prioritizing agility favor contracting.
Connection
Labor hoarding occurs when firms retain more employees than needed during economic downturns, preserving skilled labor and reducing future hiring costs. Contracting, or outsourcing, shifts specific job functions to external agencies, allowing companies to manage workforce flexibility and expenses. Both strategies affect employment dynamics by balancing cost control with the need to maintain operational capacity.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Contracting offers businesses the flexibility to scale their workforce quickly by engaging external talent for specific projects, avoiding long-term commitments and reducing fixed labor costs. Labor hoarding, on the other hand, maintains a stable core workforce during downturns, preserving job-specific skills and minimizing rehiring costs but may increase short-term labor expenses. Explore how different industries balance contracting and labor hoarding to optimize workforce flexibility and operational efficiency.
Job Security
Contracting often leads to reduced job security as companies hire temporary workers to cut costs during downturns, whereas labor hoarding maintains employment levels despite economic fluctuations to preserve skilled labor and avoid future hiring costs. Labor hoarding supports long-term job security by retaining employees, fostering loyalty, and enhancing workforce stability. Explore the impacts of contracting and labor hoarding on job security in greater detail.
Workforce Utilization
Contracting involves reducing workforce size through layoffs or outsourcing to lower costs, whereas labor hoarding retains more employees than necessary during downturns to preserve skills and avoid rehiring costs. Effective workforce utilization balances these strategies by maintaining optimal employee levels to meet current demand without excessive labor expenses or lost capabilities. Explore deeper insights into workforce utilization to optimize organizational resilience and efficiency.
Source and External Links
How to Start a Contracting Business - U.S. Chamber of Commerce - This article provides practical tips for starting and managing a contracting business, including hiring and overseeing subcontractors with risk management and communication strategies.
Contracting assistance programs | U.S. Small Business Administration - The federal government supports small businesses in winning federal contracts through set-asides and subcontracting plans aimed at various socio-economic categories with specific contracting dollar goals.
CONTRACTING | definition in the Cambridge English Dictionary - "Contracting" means entering into a legal agreement to perform work or have work performed and also refers to shrinking in size or acquiring an illness in different contexts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com