Fractional work offers flexible hours and project-based assignments, allowing professionals to balance multiple roles and gain diverse experiences. Full-time employment provides stability, consistent income, and access to benefits like healthcare and retirement plans. Explore the advantages and considerations of both to determine the best fit for your career goals.
Why it is important
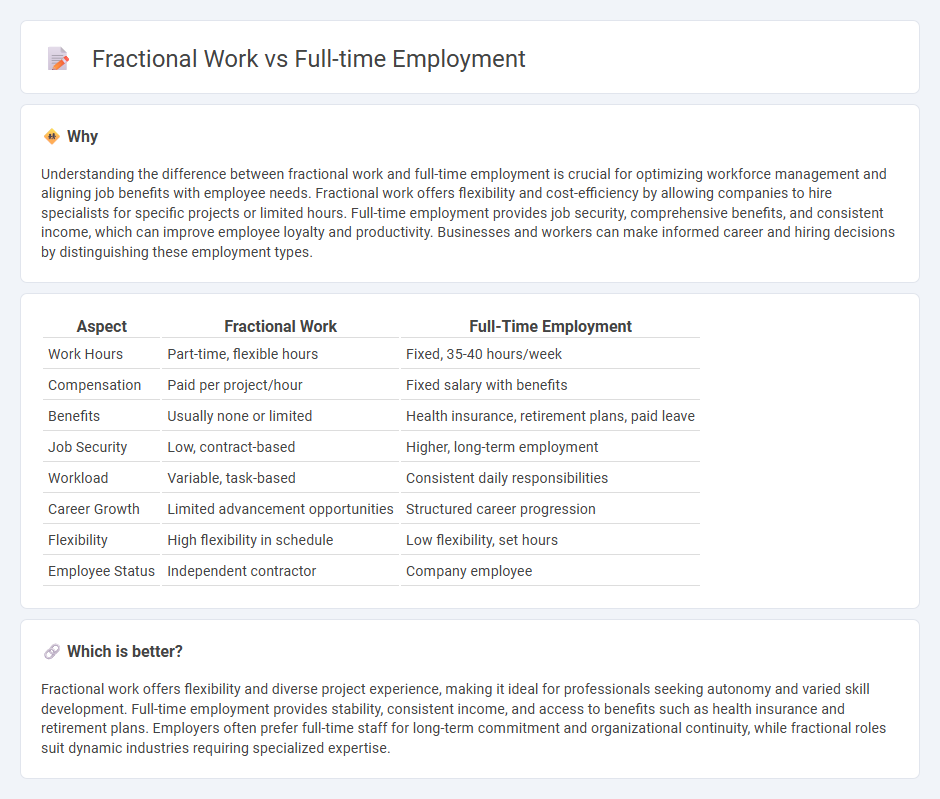
Understanding the difference between fractional work and full-time employment is crucial for optimizing workforce management and aligning job benefits with employee needs. Fractional work offers flexibility and cost-efficiency by allowing companies to hire specialists for specific projects or limited hours. Full-time employment provides job security, comprehensive benefits, and consistent income, which can improve employee loyalty and productivity. Businesses and workers can make informed career and hiring decisions by distinguishing these employment types.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Fractional Work | Full-Time Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Work Hours | Part-time, flexible hours | Fixed, 35-40 hours/week |
| Compensation | Paid per project/hour | Fixed salary with benefits |
| Benefits | Usually none or limited | Health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave |
| Job Security | Low, contract-based | Higher, long-term employment |
| Workload | Variable, task-based | Consistent daily responsibilities |
| Career Growth | Limited advancement opportunities | Structured career progression |
| Flexibility | High flexibility in schedule | Low flexibility, set hours |
| Employee Status | Independent contractor | Company employee |
Which is better?
Fractional work offers flexibility and diverse project experience, making it ideal for professionals seeking autonomy and varied skill development. Full-time employment provides stability, consistent income, and access to benefits such as health insurance and retirement plans. Employers often prefer full-time staff for long-term commitment and organizational continuity, while fractional roles suit dynamic industries requiring specialized expertise.
Connection
Fractional work offers flexibility by allowing employees to engage with multiple companies or projects, complementing the stability provided by full-time employment. Companies leverage fractional professionals to fill skill gaps or manage workloads without the long-term commitment associated with full-time roles. This hybrid workforce strategy enhances operational agility and enables businesses to optimize talent utilization efficiently.
Key Terms
Work hours
Full-time employment typically involves 35 to 40+ hours per week with a fixed schedule, offering consistent workloads and benefits like health insurance and retirement plans. Fractional work allows professionals to allocate a fraction of their time, often 10 to 20 hours per week, to multiple clients or projects, enhancing flexibility and specialized focus. Discover how different work hour structures can optimize productivity and work-life balance.
Benefits
Full-time employment offers comprehensive benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, which are often fully covered or subsidized by the employer. Fractional work, while lacking traditional benefits, provides flexibility and the potential for higher hourly earnings, but requires individuals to independently manage their health coverage and retirement savings. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which option aligns best with your career and lifestyle goals.
Job security
Full-time employment offers greater job security through consistent income, benefits, and legal protections, reducing financial uncertainty for workers. Fractional work, often project-based or part-time, provides flexibility but comes with variable income and limited access to traditional benefits, increasing potential risk. Explore the key differences in job security between full-time and fractional work to make informed career decisions.
Source and External Links
Full-time employment | EBSCO Research Starters - Full-time employment typically involves working a minimum of 30 hours per week, with benefits such as higher wages, health insurance, and vacation being common, and the Affordable Care Act defining full-time as 30 or more hours weekly but employers may set their own standards.
Full-Time vs. Part-Time: Hours, Benefits, & Laws - Paychex - Full-time employment is generally 35 to 40 hours weekly, with legal obligations for employers to provide statutory benefits and offer health insurance under the ACA for Applicable Large Employers.
What is A Full-Time Employee? Hours, Benefits, & Laws - Playroll - Full-time employees usually work 35 to 40 hours per week, receive ongoing employment status with benefits like health insurance and retirement plans, and are subject to labor laws including the FLSA and anti-discrimination regulations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com