The employment landscape is evolving with career lattices offering structured yet flexible advancement within organizations, contrasting sharply with the gig economy's project-based, independent work model. Career lattices emphasize skill development and lateral moves, promoting long-term growth, while the gig economy focuses on short-term tasks and diverse income streams with minimal job security. Explore how these employment trends impact workforce strategies and personal career planning.
Why it is important
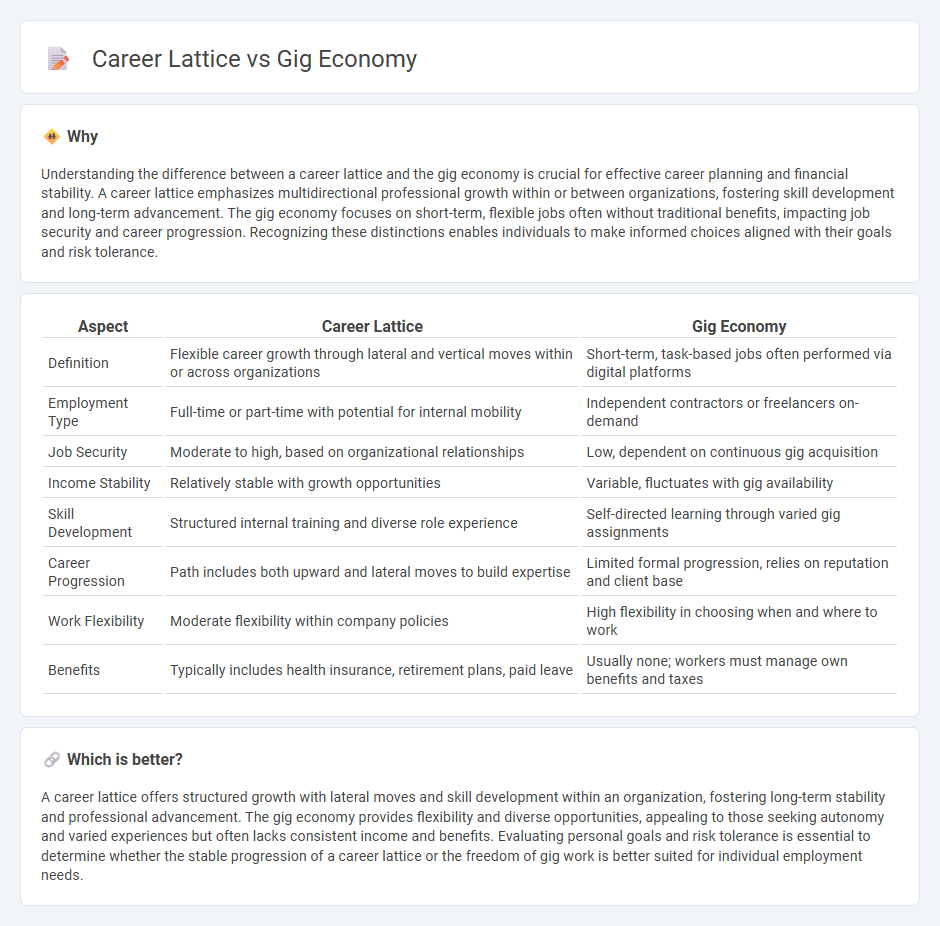
Understanding the difference between a career lattice and the gig economy is crucial for effective career planning and financial stability. A career lattice emphasizes multidirectional professional growth within or between organizations, fostering skill development and long-term advancement. The gig economy focuses on short-term, flexible jobs often without traditional benefits, impacting job security and career progression. Recognizing these distinctions enables individuals to make informed choices aligned with their goals and risk tolerance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Career Lattice | Gig Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flexible career growth through lateral and vertical moves within or across organizations | Short-term, task-based jobs often performed via digital platforms |
| Employment Type | Full-time or part-time with potential for internal mobility | Independent contractors or freelancers on-demand |
| Job Security | Moderate to high, based on organizational relationships | Low, dependent on continuous gig acquisition |
| Income Stability | Relatively stable with growth opportunities | Variable, fluctuates with gig availability |
| Skill Development | Structured internal training and diverse role experience | Self-directed learning through varied gig assignments |
| Career Progression | Path includes both upward and lateral moves to build expertise | Limited formal progression, relies on reputation and client base |
| Work Flexibility | Moderate flexibility within company policies | High flexibility in choosing when and where to work |
| Benefits | Typically includes health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave | Usually none; workers must manage own benefits and taxes |
Which is better?
A career lattice offers structured growth with lateral moves and skill development within an organization, fostering long-term stability and professional advancement. The gig economy provides flexibility and diverse opportunities, appealing to those seeking autonomy and varied experiences but often lacks consistent income and benefits. Evaluating personal goals and risk tolerance is essential to determine whether the stable progression of a career lattice or the freedom of gig work is better suited for individual employment needs.
Connection
Career lattice structures emphasize lateral and diagonal movements within or between organizations, aligning closely with the gig economy's flexible job roles and project-based work. The gig economy provides diverse opportunities that support career lattice progression by enabling workers to gain varied skills and experiences outside traditional hierarchical paths. This connection enhances workforce adaptability and continuous skill development amid evolving employment landscapes.
Key Terms
Flexibility
The gig economy offers unparalleled flexibility, enabling workers to choose projects, set schedules, and balance multiple income streams without long-term commitment. In contrast, the career lattice provides structured growth with lateral moves and skill development opportunities while maintaining adaptability within an organization. Explore how these models can reshape your professional journey and work-life balance.
Job Security
The gig economy offers flexible work arrangements but often lacks traditional job security, with workers facing income instability and limited benefits. In contrast, a career lattice promotes upward mobility through lateral movement within an organization, providing greater job security and continuous skill development. Explore how these models impact your long-term employment stability and career growth.
Advancement Pathways
The gig economy offers flexible, short-term work opportunities without guaranteed advancement pathways, emphasizing immediate task-based income rather than structured career growth. In contrast, the career lattice model promotes multidirectional advancement within an organization, allowing employees to develop diverse skills and move laterally or upward to broaden their professional experience. Explore how understanding these advancement pathways can shape your long-term career strategy.
Source and External Links
Gig Economy - Overview, Advantages, Disadvantages - The gig economy is a flexible labor market where organizations hire independent contractors or freelancers for temporary, project-based work through digital platforms, offering flexible, efficient services and enabling a significant portion of the workforce to earn income this way.
The Pros and Cons of the Gig Economy - The gig economy encompasses short-term "gigs" or freelance work across various industries connected via digital platforms, supporting workforce flexibility and autonomy, and experiencing rapid growth in participation and market value globally.
What is the Gig Economy? - The gig economy is a free market system characterized by temporary jobs and independent contractors who work remotely and worldwide via digital platforms, representing a cultural and economic shift in how work is organized and performed.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com