Algorithmic management leverages data-driven software to optimize workforce scheduling, monitor productivity, and enhance decision-making efficiency, while manual oversight relies on human judgment to manage employee performance and resolve operational issues. The integration of AI technologies enables real-time analytics and predictive insights that manual methods often lack, driving higher scalability in managing large workforces. Explore the evolving balance between technology and human expertise in employment management.
Why it is important
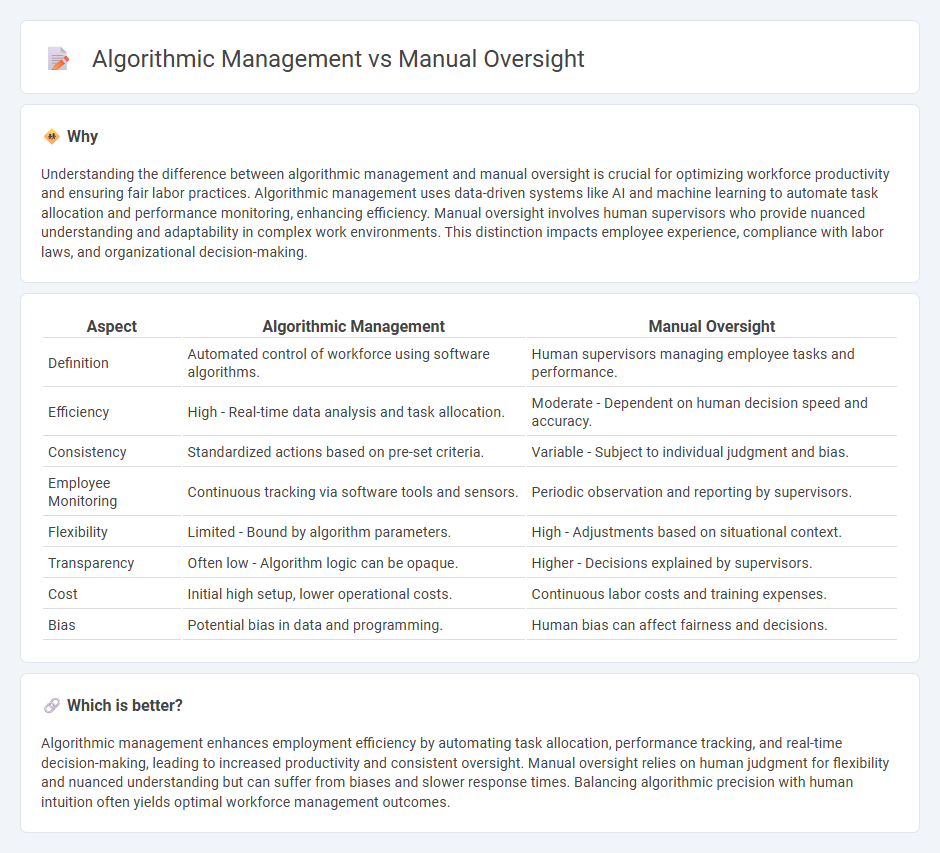
Understanding the difference between algorithmic management and manual oversight is crucial for optimizing workforce productivity and ensuring fair labor practices. Algorithmic management uses data-driven systems like AI and machine learning to automate task allocation and performance monitoring, enhancing efficiency. Manual oversight involves human supervisors who provide nuanced understanding and adaptability in complex work environments. This distinction impacts employee experience, compliance with labor laws, and organizational decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Algorithmic Management | Manual Oversight |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated control of workforce using software algorithms. | Human supervisors managing employee tasks and performance. |
| Efficiency | High - Real-time data analysis and task allocation. | Moderate - Dependent on human decision speed and accuracy. |
| Consistency | Standardized actions based on pre-set criteria. | Variable - Subject to individual judgment and bias. |
| Employee Monitoring | Continuous tracking via software tools and sensors. | Periodic observation and reporting by supervisors. |
| Flexibility | Limited - Bound by algorithm parameters. | High - Adjustments based on situational context. |
| Transparency | Often low - Algorithm logic can be opaque. | Higher - Decisions explained by supervisors. |
| Cost | Initial high setup, lower operational costs. | Continuous labor costs and training expenses. |
| Bias | Potential bias in data and programming. | Human bias can affect fairness and decisions. |
Which is better?
Algorithmic management enhances employment efficiency by automating task allocation, performance tracking, and real-time decision-making, leading to increased productivity and consistent oversight. Manual oversight relies on human judgment for flexibility and nuanced understanding but can suffer from biases and slower response times. Balancing algorithmic precision with human intuition often yields optimal workforce management outcomes.
Connection
Algorithmic management utilizes data-driven algorithms to optimize workforce scheduling, productivity tracking, and task allocation, enhancing operational efficiency. Manual oversight remains critical for addressing algorithmic limitations, ensuring ethical standards, and managing complex human factors that algorithms may overlook. The synergy between algorithmic management and manual oversight fosters balanced decision-making, combining computational precision with human judgment in employment contexts.
Key Terms
Human Judgment
Manual oversight leverages human judgment to interpret contextual nuances and ethical considerations that algorithms may overlook, ensuring decisions align with organizational values and social norms. Algorithmic management excels in processing large data sets for efficiency and consistency but can lack the flexibility and empathy inherent in human evaluation. Explore deeper insights into balancing these approaches to optimize decision-making and operational outcomes.
Automation Bias
Manual oversight relies on human judgment to monitor processes, often reducing automation bias by allowing critical evaluation of algorithmic decisions. Algorithmic management, while efficient in scaling operations, risks fostering automation bias as employees may over-rely on algorithms without questioning potential errors or limitations. Explore the impact of automation bias on performance and ways to balance manual and algorithmic approaches for optimal operational outcomes.
Decision Transparency
Manual oversight in decision-making relies on human judgment to interpret data and apply ethical considerations, promoting clear accountability and transparent rationale. Algorithmic management automates decisions using data-driven models, which can enhance efficiency but often lacks straightforward explainability, resulting in opaque decision processes. Explore the nuances of decision transparency to understand how balancing human insight with algorithmic precision shapes organizational trust and fairness.
Source and External Links
Congressional Oversight Manual - This manual provides guidance on congressional oversight, describing it as the review, monitoring, and supervision of federal agencies and programs, emphasizing the expert judgment involved in oversight decisions and strategies.
Oversight Manuals - A collection of resources and manuals offering introductions and best practices for legislative oversight, including the Congressional Oversight Manual and guides to procedural rules in the U.S. House of Representatives.
Congressional Oversight Manual, December 19, 2014 - This manual, developed by the Congressional Research Service since 1978, serves as a comprehensive resource to support congressional oversight activities and investigations, updated periodically to reflect changing circumstances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com