Employment trends increasingly highlight the distinction between digital nomadism and traditional remote work, with digital nomads embracing location-independent lifestyles by working while traveling globally. Remote work typically involves performing job duties from home or a fixed location, supported by stable internet and communication tools. Explore deeper insights into how these evolving work models impact productivity, work-life balance, and global employment opportunities.
Why it is important
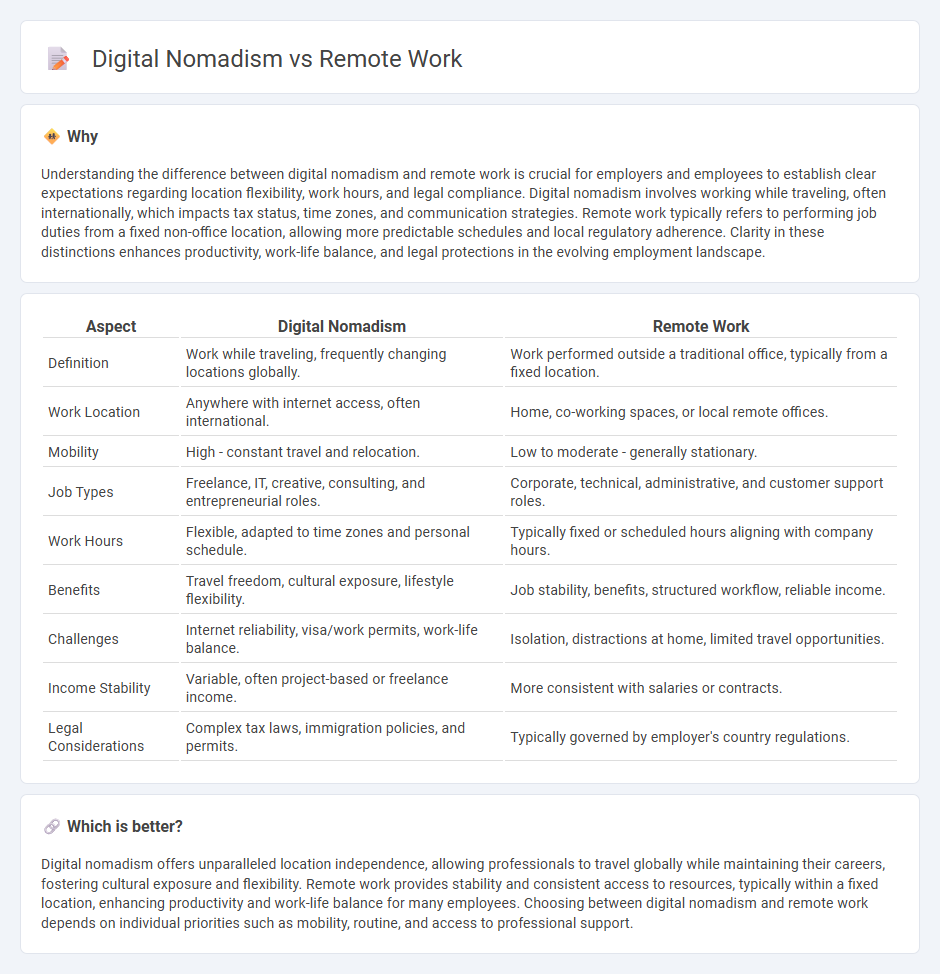
Understanding the difference between digital nomadism and remote work is crucial for employers and employees to establish clear expectations regarding location flexibility, work hours, and legal compliance. Digital nomadism involves working while traveling, often internationally, which impacts tax status, time zones, and communication strategies. Remote work typically refers to performing job duties from a fixed non-office location, allowing more predictable schedules and local regulatory adherence. Clarity in these distinctions enhances productivity, work-life balance, and legal protections in the evolving employment landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Digital Nomadism | Remote Work |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Work while traveling, frequently changing locations globally. | Work performed outside a traditional office, typically from a fixed location. |
| Work Location | Anywhere with internet access, often international. | Home, co-working spaces, or local remote offices. |
| Mobility | High - constant travel and relocation. | Low to moderate - generally stationary. |
| Job Types | Freelance, IT, creative, consulting, and entrepreneurial roles. | Corporate, technical, administrative, and customer support roles. |
| Work Hours | Flexible, adapted to time zones and personal schedule. | Typically fixed or scheduled hours aligning with company hours. |
| Benefits | Travel freedom, cultural exposure, lifestyle flexibility. | Job stability, benefits, structured workflow, reliable income. |
| Challenges | Internet reliability, visa/work permits, work-life balance. | Isolation, distractions at home, limited travel opportunities. |
| Income Stability | Variable, often project-based or freelance income. | More consistent with salaries or contracts. |
| Legal Considerations | Complex tax laws, immigration policies, and permits. | Typically governed by employer's country regulations. |
Which is better?
Digital nomadism offers unparalleled location independence, allowing professionals to travel globally while maintaining their careers, fostering cultural exposure and flexibility. Remote work provides stability and consistent access to resources, typically within a fixed location, enhancing productivity and work-life balance for many employees. Choosing between digital nomadism and remote work depends on individual priorities such as mobility, routine, and access to professional support.
Connection
Digital nomadism and remote work are interconnected through the utilization of digital technologies that enable professionals to perform their job duties from any location worldwide. This shift in employment trends has led to increased demand for flexible work arrangements and the adoption of cloud-based collaboration tools. Companies benefit from accessing a global talent pool while employees enjoy greater work-life balance and geographic freedom.
Key Terms
Telecommuting
Telecommuting enables employees to work from remote locations, maintaining regular communication with their offices via digital tools like video conferencing and project management software. Unlike digital nomadism, which emphasizes continuous travel and location independence, telecommuting prioritizes consistent productivity and structured work schedules in a fixed remote environment. Explore how telecommuting strategies can enhance work-life balance and organizational efficiency.
Location Independence
Remote work offers flexibility to perform job duties from any location with internet access, facilitating a work-life balance without the constraints of a fixed office. Digital nomadism extends remote work by combining employment with continuous travel, emphasizing complete location independence and cultural immersion. Explore the key distinctions and benefits of remote work versus digital nomadism to determine which lifestyle suits your professional goals.
Work-Life Balance
Remote work offers structured flexibility, allowing individuals to maintain a stable routine while balancing professional tasks and personal life within a fixed location. Digital nomadism emphasizes location independence, enabling professionals to blend travel experiences with work but may challenge consistent work-life boundaries due to constant environmental changes. Explore how each lifestyle uniquely supports or hinders work-life balance to determine the best fit for your career and well-being.
Source and External Links
What Is Remote Work? Ultimate Guide - Remote work refers to a professional setup where employees perform their jobs from home or any location outside the traditional office, enabled by digital tools like Slack and Zoom, and it is becoming a standard part of work culture with many companies adopting hybrid or fully remote models.
How to Embrace Remote Work - Successful remote work relies heavily on digital communication tools and intentional efforts to build company culture remotely, including clear agreed-upon rules and regular meetings to maintain strong team relationships despite physical distance.
What is the definition of remote work? - Officially, remote work is a flexible work arrangement under a written agreement where employees work at an alternative site rather than the regular agency or office location, sometimes outside the local commuting area, and is not expected to be onsite regularly.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com