Labor hoarding involves retaining employees during economic downturns to preserve skills and maintain operational stability, whereas outsourcing shifts tasks to external providers to reduce costs and increase flexibility. Companies weigh labor hoarding against outsourcing based on factors like workforce expertise, cost efficiency, and long-term strategic goals. Explore the advantages and trade-offs between labor hoarding and outsourcing to optimize your employment strategy.
Why it is important
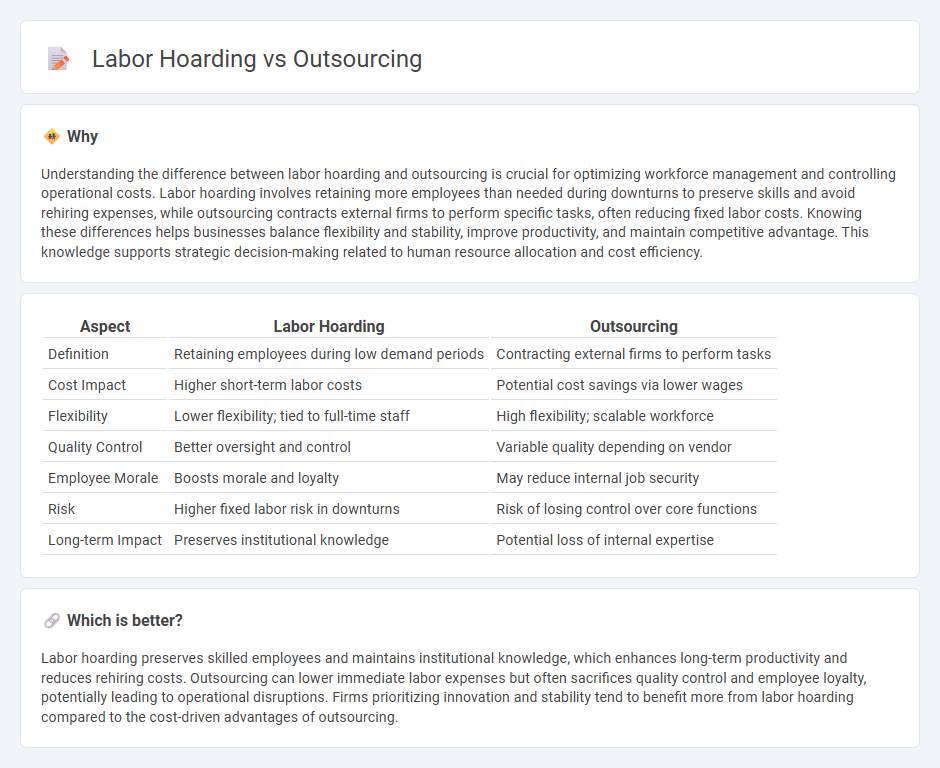
Understanding the difference between labor hoarding and outsourcing is crucial for optimizing workforce management and controlling operational costs. Labor hoarding involves retaining more employees than needed during downturns to preserve skills and avoid rehiring expenses, while outsourcing contracts external firms to perform specific tasks, often reducing fixed labor costs. Knowing these differences helps businesses balance flexibility and stability, improve productivity, and maintain competitive advantage. This knowledge supports strategic decision-making related to human resource allocation and cost efficiency.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Labor Hoarding | Outsourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Retaining employees during low demand periods | Contracting external firms to perform tasks |
| Cost Impact | Higher short-term labor costs | Potential cost savings via lower wages |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility; tied to full-time staff | High flexibility; scalable workforce |
| Quality Control | Better oversight and control | Variable quality depending on vendor |
| Employee Morale | Boosts morale and loyalty | May reduce internal job security |
| Risk | Higher fixed labor risk in downturns | Risk of losing control over core functions |
| Long-term Impact | Preserves institutional knowledge | Potential loss of internal expertise |
Which is better?
Labor hoarding preserves skilled employees and maintains institutional knowledge, which enhances long-term productivity and reduces rehiring costs. Outsourcing can lower immediate labor expenses but often sacrifices quality control and employee loyalty, potentially leading to operational disruptions. Firms prioritizing innovation and stability tend to benefit more from labor hoarding compared to the cost-driven advantages of outsourcing.
Connection
Labor hoarding involves companies retaining more employees than needed during downturns to preserve organizational knowledge and maintain productivity, while outsourcing shifts specific tasks or functions to external providers to reduce costs. Both strategies reflect different approaches to managing workforce flexibility and operational efficiency in response to changing economic conditions. Understanding the balance between labor hoarding and outsourcing helps firms optimize labor costs and maintain competitive advantage.
Key Terms
Cost efficiency
Outsourcing often reduces labor costs by leveraging external providers with lower wages and flexible contracts, enhancing cost efficiency in volatile markets. Labor hoarding incurs fixed costs by retaining employees during downturns, potentially leading to higher short-term expenses but preserving skilled labor for future productivity. Explore in-depth analyses to determine which strategy best aligns with your business's cost optimization goals.
Workforce flexibility
Outsourcing enhances workforce flexibility by allowing companies to adjust labor capacity quickly in response to market demand, reducing long-term employment costs and operational risks. Labor hoarding, conversely, maintains a stable internal workforce to preserve firm-specific skills and employee morale but limits adaptability during economic downturns. Explore further how these strategies impact organizational agility and financial performance.
Job security
Outsourcing often reduces job security by transferring roles to external providers, while labor hoarding preserves employment during downturns by retaining excess staff despite reduced demand. Companies practicing labor hoarding invest in workforce stability, which can enhance employee morale but may increase operational costs. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies impact job security and organizational resilience.
Source and External Links
What Is Outsourcing? (Including Types and Advantages) | Indeed.com - Outsourcing is the practice of hiring outside contractors or companies to perform tasks or create goods, helping businesses reduce labor costs, increase efficiency, and gain skills they lack in-house.
What is Outsourcing and How Does it Work? - TechTarget - Outsourcing involves contracting a third-party provider to handle tasks or services, often including IT, customer service, manufacturing, or financial functions, requiring strong relationship management beyond service agreements.
What is Outsourcing? Definition, Advantages, and Examples - Outsourcing allows companies to reduce costs, access specialized expertise, and focus on core activities by contracting third-party providers for functions like IT support, customer service, or accounting, while facing challenges in communication and economic impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com