Zero-day work contracts often involve employees starting tasks immediately without formal agreements, contrasting with freelancing where individuals operate under negotiated terms with defined project scopes. This distinction affects income stability, legal protections, and tax obligations, making each option suited to different economic contexts. Explore our detailed analysis to better understand the economic implications and benefits of zero-day contracts versus freelancing.
Why it is important
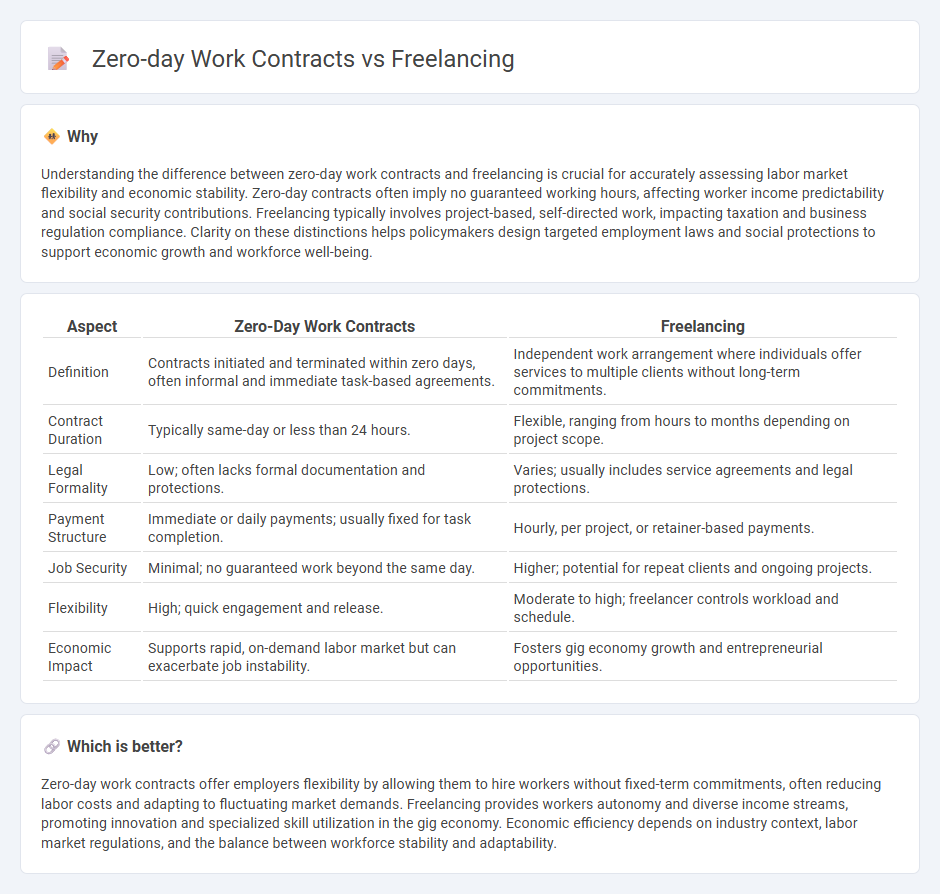
Understanding the difference between zero-day work contracts and freelancing is crucial for accurately assessing labor market flexibility and economic stability. Zero-day contracts often imply no guaranteed working hours, affecting worker income predictability and social security contributions. Freelancing typically involves project-based, self-directed work, impacting taxation and business regulation compliance. Clarity on these distinctions helps policymakers design targeted employment laws and social protections to support economic growth and workforce well-being.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Zero-Day Work Contracts | Freelancing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Contracts initiated and terminated within zero days, often informal and immediate task-based agreements. | Independent work arrangement where individuals offer services to multiple clients without long-term commitments. |
| Contract Duration | Typically same-day or less than 24 hours. | Flexible, ranging from hours to months depending on project scope. |
| Legal Formality | Low; often lacks formal documentation and protections. | Varies; usually includes service agreements and legal protections. |
| Payment Structure | Immediate or daily payments; usually fixed for task completion. | Hourly, per project, or retainer-based payments. |
| Job Security | Minimal; no guaranteed work beyond the same day. | Higher; potential for repeat clients and ongoing projects. |
| Flexibility | High; quick engagement and release. | Moderate to high; freelancer controls workload and schedule. |
| Economic Impact | Supports rapid, on-demand labor market but can exacerbate job instability. | Fosters gig economy growth and entrepreneurial opportunities. |
Which is better?
Zero-day work contracts offer employers flexibility by allowing them to hire workers without fixed-term commitments, often reducing labor costs and adapting to fluctuating market demands. Freelancing provides workers autonomy and diverse income streams, promoting innovation and specialized skill utilization in the gig economy. Economic efficiency depends on industry context, labor market regulations, and the balance between workforce stability and adaptability.
Connection
Zero-day work contracts and freelancing share a reliance on flexible, short-term agreements that emphasize project-based deliverables rather than long-term employment commitments. Freelancers often engage in zero-day contracts, allowing businesses to quickly scale labor resources without incurring long-term obligations or benefits. This dynamic supports the gig economy by promoting agility and cost-efficiency in workforce management.
Key Terms
Job Security
Freelancing offers flexibility but often lacks the job security provided by zero-day work contracts that guarantee consistent income and benefits. Zero-day contracts minimize financial uncertainty by ensuring continuous employment and legal protections under labor regulations. Explore the advantages and challenges of both models to determine which job security approach suits your career goals best.
Income Stability
Freelancing offers flexibility but often comes with irregular income, making financial planning challenging compared to zero-day work contracts, which provide fixed daily payments ensuring consistent cash flow. Zero-day contracts minimize income volatility by guaranteeing payment regardless of workload fluctuations, appealing to professionals seeking steady earnings. Explore detailed comparisons to determine which income model best supports your financial stability goals.
Worker Autonomy
Freelancing offers workers significant autonomy, allowing them to choose projects, set schedules, and negotiate terms directly with clients, enhancing flexibility and control over their workload. Zero-day work contracts, often time-bound and rigid, limit autonomy by imposing strict deadlines and predefined tasks, reducing workers' ability to manage their workflow independently. Explore deeper insights on how these employment models impact worker autonomy and job satisfaction.
Source and External Links
Freelancing 101: What is Freelancing? - GCF Global - Freelancing is a form of self-employment where you work independently for multiple clients without exclusivity, allowing freedom of location, schedule, and choice of projects.
What Is Freelancing? Basics and Popular Jobs in 2025 - Upwork - Freelancing involves doing specific work for clients on a project basis without full-time commitment, requiring skills selection, portfolio building, strategic applications, and self-management.
25 best freelance websites to find work in 2025 - Hostinger - Freelancing is a flexible work style offering professional skills independently to clients, with benefits such as flexible hours, rate negotiation, and opportunities for beginner growth through online platforms.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com