Slowbalization shifts global trade patterns toward regional networks, reducing dependency on distant suppliers and increasing economic resilience. Supply chain diversification spreads sourcing across multiple countries, mitigating risks from geopolitical tensions and disruptions. Explore how these strategies reshape economic stability and growth in today's interconnected markets.
Why it is important
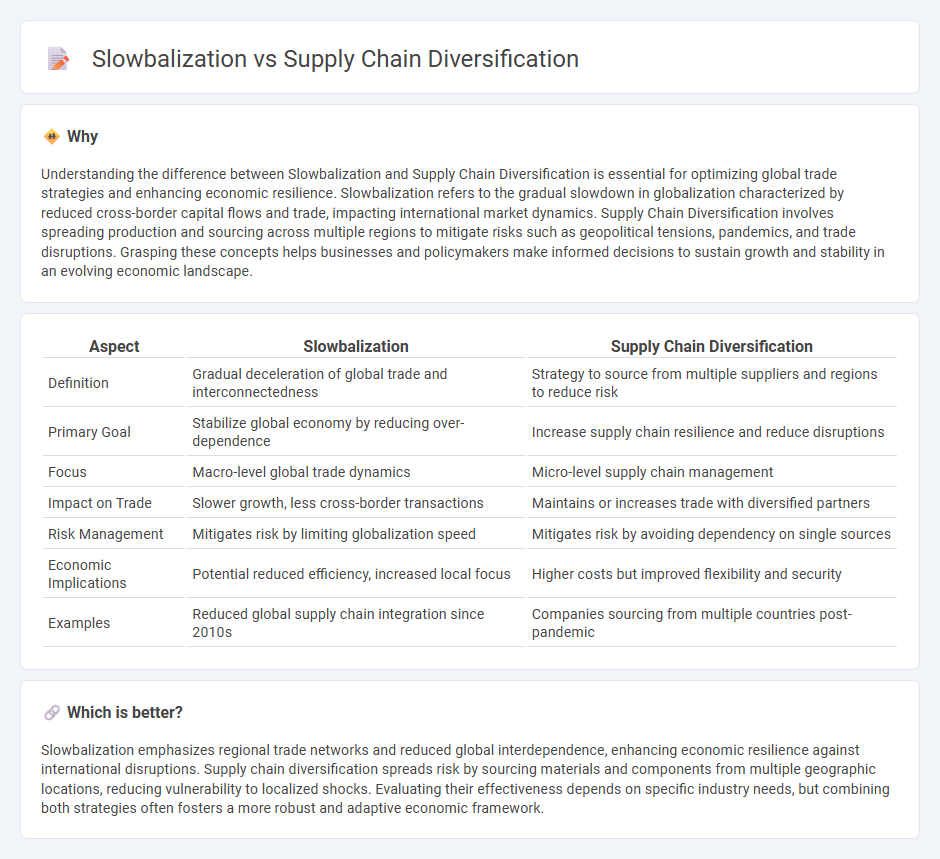
Understanding the difference between Slowbalization and Supply Chain Diversification is essential for optimizing global trade strategies and enhancing economic resilience. Slowbalization refers to the gradual slowdown in globalization characterized by reduced cross-border capital flows and trade, impacting international market dynamics. Supply Chain Diversification involves spreading production and sourcing across multiple regions to mitigate risks such as geopolitical tensions, pandemics, and trade disruptions. Grasping these concepts helps businesses and policymakers make informed decisions to sustain growth and stability in an evolving economic landscape.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Slowbalization | Supply Chain Diversification |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Gradual deceleration of global trade and interconnectedness | Strategy to source from multiple suppliers and regions to reduce risk |
| Primary Goal | Stabilize global economy by reducing over-dependence | Increase supply chain resilience and reduce disruptions |
| Focus | Macro-level global trade dynamics | Micro-level supply chain management |
| Impact on Trade | Slower growth, less cross-border transactions | Maintains or increases trade with diversified partners |
| Risk Management | Mitigates risk by limiting globalization speed | Mitigates risk by avoiding dependency on single sources |
| Economic Implications | Potential reduced efficiency, increased local focus | Higher costs but improved flexibility and security |
| Examples | Reduced global supply chain integration since 2010s | Companies sourcing from multiple countries post-pandemic |
Which is better?
Slowbalization emphasizes regional trade networks and reduced global interdependence, enhancing economic resilience against international disruptions. Supply chain diversification spreads risk by sourcing materials and components from multiple geographic locations, reducing vulnerability to localized shocks. Evaluating their effectiveness depends on specific industry needs, but combining both strategies often fosters a more robust and adaptive economic framework.
Connection
Slowbalization, characterized by reduced global trade growth and increased economic nationalism, drives companies to diversify supply chains to mitigate risks associated with geopolitical tensions and disruptions. Supply chain diversification enhances resilience by sourcing from multiple regions, reducing dependency on a single country or supplier. This strategic shift aligns with slowbalization trends, promoting localized production and regional trade networks to sustain economic stability.
Key Terms
Globalization
Supply chain diversification enhances global resilience by spreading risk across multiple regions, reducing dependency on single sources amid rising geopolitical tensions and trade disruptions. Slowbalization reflects a moderated globalization trend where companies prioritize regional hubs and shorter supply chains to improve flexibility and sustainability. Explore how these strategies reshape global trade dynamics and impact economic growth worldwide.
Resilience
Supply chain diversification enhances resilience by reducing dependency on a single source, mitigating risks associated with geopolitical tensions, natural disasters, and supply disruptions. Slowbalization emphasizes regionalization and gradual reshoring, fostering stronger local partnerships and shorter supply chains that improve adaptability and responsiveness. Explore the strategic approaches to supply chain resilience and their impacts on global business continuity.
Trade Barriers
Trade barriers such as tariffs, quotas, and regulatory restrictions significantly impact supply chain diversification by prompting companies to seek alternative sourcing and production locations to maintain cost efficiency and market access. Slowbalization, characterized by a gradual reduction in global trade intensity and increased regionalization, further amplifies the role of non-tariff barriers and geopolitical risks in shaping supply chain networks. Explore how evolving trade policies reshape global commerce dynamics and supply chain strategies.
Source and External Links
The high impact of supply chain diversification - Delivered - Supply chain diversification involves developing flexibility and redundancy by using multiple suppliers, manufacturing locations, and logistics options to increase resilience, agility, and reduce risk, with many companies realigning strategies to enhance responsiveness and competitiveness.
5 reasons to implement supply chain diversification - Diversification reduces risk by avoiding dependency on a single supplier or region, builds resilience by enabling supply chain adaptability to disruptions, and improves agility by allowing production and sales across multiple regions.
Supply Chain Diversification and Resilience - A multi-country trade model shows that diversification of import sources enhances resilience against trade shocks despite some efficiency trade-offs, especially when shocks are likely and imports are upstream and exposure-prone, thus improving expected welfare.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com