Tipflation occurs when consumers increase tipping amounts despite rising prices, reflecting shifts in spending behavior amid inflation. Skimpflation describes businesses reducing service quality or product quantity while maintaining or raising prices to offset higher costs. Explore these evolving economic trends to understand their impact on consumer habits and market dynamics.
Why it is important
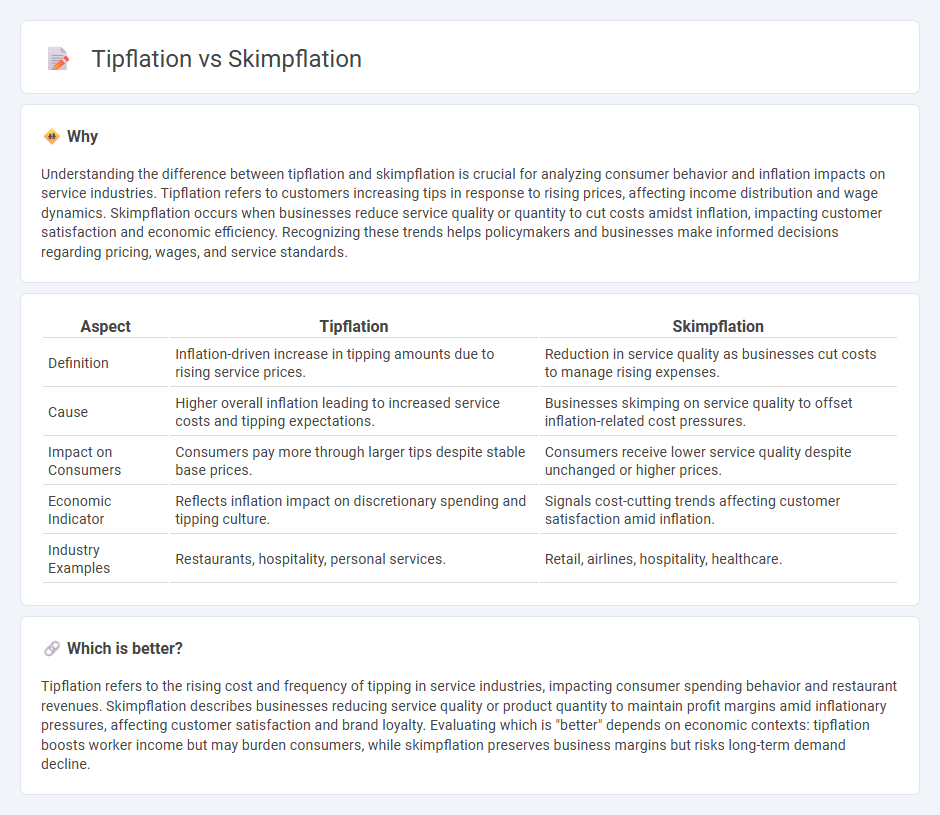
Understanding the difference between tipflation and skimpflation is crucial for analyzing consumer behavior and inflation impacts on service industries. Tipflation refers to customers increasing tips in response to rising prices, affecting income distribution and wage dynamics. Skimpflation occurs when businesses reduce service quality or quantity to cut costs amidst inflation, impacting customer satisfaction and economic efficiency. Recognizing these trends helps policymakers and businesses make informed decisions regarding pricing, wages, and service standards.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tipflation | Skimpflation |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Inflation-driven increase in tipping amounts due to rising service prices. | Reduction in service quality as businesses cut costs to manage rising expenses. |
| Cause | Higher overall inflation leading to increased service costs and tipping expectations. | Businesses skimping on service quality to offset inflation-related cost pressures. |
| Impact on Consumers | Consumers pay more through larger tips despite stable base prices. | Consumers receive lower service quality despite unchanged or higher prices. |
| Economic Indicator | Reflects inflation impact on discretionary spending and tipping culture. | Signals cost-cutting trends affecting customer satisfaction amid inflation. |
| Industry Examples | Restaurants, hospitality, personal services. | Retail, airlines, hospitality, healthcare. |
Which is better?
Tipflation refers to the rising cost and frequency of tipping in service industries, impacting consumer spending behavior and restaurant revenues. Skimpflation describes businesses reducing service quality or product quantity to maintain profit margins amid inflationary pressures, affecting customer satisfaction and brand loyalty. Evaluating which is "better" depends on economic contexts: tipflation boosts worker income but may burden consumers, while skimpflation preserves business margins but risks long-term demand decline.
Connection
Tipflation and skimpflation are interconnected economic phenomena that impact consumer spending and business practices during inflationary periods. Tipflation occurs when customers increase tipping amounts to offset rising prices, while skimpflation happens when businesses reduce the quality or quantity of products and services to maintain profit margins. Both contribute to inflation's complex effects by influencing consumer behavior and altering the value exchange between businesses and consumers.
Key Terms
Consumer Experience
Skimpflation and tipflation directly impact the modern consumer experience by altering service expectations and spending behavior. Skimpflation refers to reduced service quality despite steady prices, causing dissatisfaction, while tipflation involves increased tipping demands, raising overall costs for customers. Explore how these trends influence your daily expenses and service satisfaction.
Service Quality
Skimpflation occurs when businesses reduce service quality or cut corners to save costs without raising prices, impacting customer satisfaction and loyalty. Tipflation refers to increased tipping demands as wages stagnate, pressuring customers to compensate for lower employee pay. Explore the effects of these trends on the hospitality industry to understand how service expectations are evolving.
Pricing Models
Skimpflation occurs when businesses reduce the quality or quantity of products or services while maintaining prices, affecting consumer perception and value. Tipflation refers to the increasing expectations for gratuities, causing consumers to spend more despite stable service costs. Explore the nuances between these pricing models to understand their impact on consumer behavior and business strategies.
Source and External Links
What Is Skimpflation and How to Avoid It? - Skimpflation is the practice of reducing the quality of a product or service, such as using cheaper ingredients, while keeping prices the same to maintain profits despite rising costs, but it risks damaging reputation and sales.
Beyond Inflation Numbers: Shrinkflation and Skimpflation - Skimpflation occurs when businesses "skimp" on the quality or service by spending less, making customers do more work themselves, as seen with self-checkout systems that reduce labor costs but lower service.
Shrinkflation - Skimpflation involves a reduction in quality or reformulation of a product to manage rising production costs without raising prices, distinguishing it from shrinkflation which reduces product size or quantity instead.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com