The gig economy and self-employment represent distinct facets of modern work styles, with the gig economy relying on short-term, flexible jobs often facilitated by digital platforms, while self-employment entails running an independent business or freelancing with more control and long-term commitment. According to recent statistics, gig workers account for approximately 36% of the U.S. workforce, highlighting a significant shift toward flexible labor markets. Explore how these models impact income stability, labor rights, and economic growth in today's evolving economy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the gig economy and self-employment is crucial for accurately assessing income stability, tax obligations, and social benefits eligibility; gig economy workers typically engage in short-term, flexible jobs mediated by digital platforms, whereas self-employed individuals often operate independent businesses with ongoing client relationships. This distinction informs economic policy, labor rights, and financial planning strategies. Recognizing these differences helps economists analyze labor market trends and the impact on economic growth. Clarity on these terms enables workers to make informed decisions about their careers and legal responsibilities.
Comparison Table
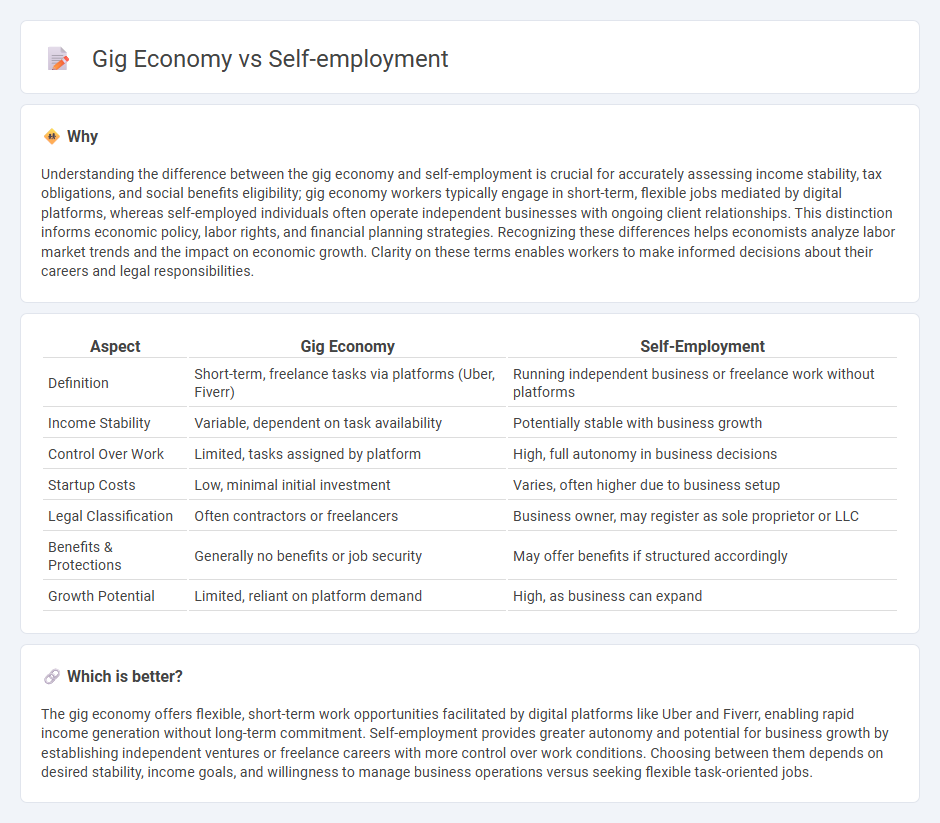
| Aspect | Gig Economy | Self-Employment |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, freelance tasks via platforms (Uber, Fiverr) | Running independent business or freelance work without platforms |
| Income Stability | Variable, dependent on task availability | Potentially stable with business growth |
| Control Over Work | Limited, tasks assigned by platform | High, full autonomy in business decisions |
| Startup Costs | Low, minimal initial investment | Varies, often higher due to business setup |
| Legal Classification | Often contractors or freelancers | Business owner, may register as sole proprietor or LLC |
| Benefits & Protections | Generally no benefits or job security | May offer benefits if structured accordingly |
| Growth Potential | Limited, reliant on platform demand | High, as business can expand |
Which is better?
The gig economy offers flexible, short-term work opportunities facilitated by digital platforms like Uber and Fiverr, enabling rapid income generation without long-term commitment. Self-employment provides greater autonomy and potential for business growth by establishing independent ventures or freelance careers with more control over work conditions. Choosing between them depends on desired stability, income goals, and willingness to manage business operations versus seeking flexible task-oriented jobs.
Connection
The gig economy and self-employment are interconnected as both emphasize flexible, independent work arrangements driven by digital platforms that match freelancers with short-term tasks or projects. Gig economy workers often operate as self-employed individuals, leveraging technology to offer services without traditional employer-employee relationships. This synergy fosters economic innovation by enabling diverse income streams and entrepreneurial opportunities in a rapidly evolving labor market.
Key Terms
Flexibility
Self-employment offers complete control over work schedules, enabling individuals to tailor their hours to personal needs without external constraints. The gig economy provides flexible, on-demand jobs allowing workers to pick tasks based on availability, though often with less predictability and benefits compared to traditional self-employment. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which flexibility model best suits your lifestyle and career goals.
Income Stability
Self-employment offers more predictable income streams through established client relationships and contracts, while gig economy work often involves irregular pay dependent on fluctuating demand and task availability. Income stability in self-employment benefits from ongoing projects and higher control over work schedules, contrasting with the gig economy's variability driven by platform algorithms and market trends. Explore deeper insights on income stability factors between self-employment and gig economy roles for informed career decisions.
Autonomy
Self-employment offers individuals complete control over their business decisions, schedules, and client selection, resulting in higher autonomy compared to gig economy roles where platform algorithms often dictate work parameters. Gig workers benefit from flexible opportunities but face limitations in autonomy due to reliance on digital platforms, rating systems, and variable task availability. Explore deeper insights on how autonomy shapes the future of independent work in both self-employment and gig economy sectors.
Source and External Links
Self-employment - Wikipedia - Self-employment is working for oneself rather than an employer, with rising levels in the U.S. linked to income growth and job creation, particularly in non-metropolitan areas, contributing about 6% of U.S. GDP.
Self-employment | Explore Careers - CareerOneStop - Self-employment offers opportunities across various fields, including gig work, freelancing, and starting a business, with benefits like flexible scheduling and challenges requiring self-motivation.
VR&E Self-Employment Track | Veterans Affairs - The VR&E Self-Employment track assists eligible veterans with disabilities by providing business plan development, training, and resources to start and run their own businesses.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com