Onshoring involves relocating business operations to a company's original country, boosting local employment and reducing supply chain risks. Reshoring focuses on bringing manufacturing or services back from overseas to the home country to regain control and enhance quality. Explore the economic impacts and strategic benefits of onshoring versus reshoring to understand their roles in modern business.
Why it is important
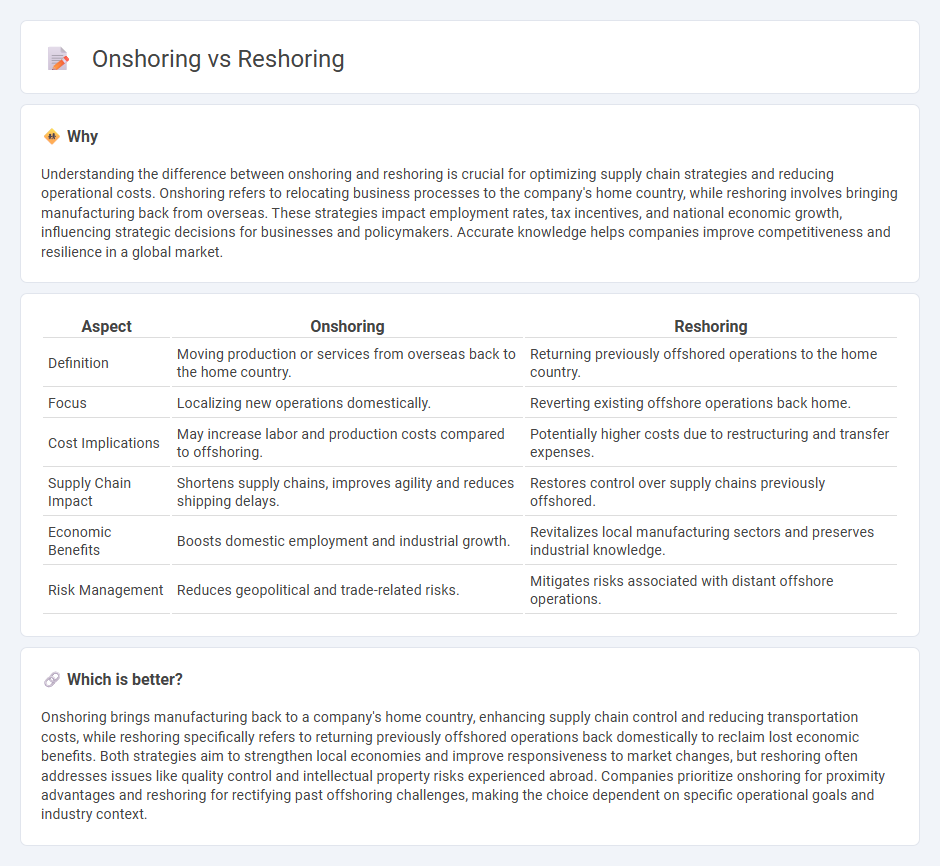
Understanding the difference between onshoring and reshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain strategies and reducing operational costs. Onshoring refers to relocating business processes to the company's home country, while reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back from overseas. These strategies impact employment rates, tax incentives, and national economic growth, influencing strategic decisions for businesses and policymakers. Accurate knowledge helps companies improve competitiveness and resilience in a global market.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Onshoring | Reshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Moving production or services from overseas back to the home country. | Returning previously offshored operations to the home country. |
| Focus | Localizing new operations domestically. | Reverting existing offshore operations back home. |
| Cost Implications | May increase labor and production costs compared to offshoring. | Potentially higher costs due to restructuring and transfer expenses. |
| Supply Chain Impact | Shortens supply chains, improves agility and reduces shipping delays. | Restores control over supply chains previously offshored. |
| Economic Benefits | Boosts domestic employment and industrial growth. | Revitalizes local manufacturing sectors and preserves industrial knowledge. |
| Risk Management | Reduces geopolitical and trade-related risks. | Mitigates risks associated with distant offshore operations. |
Which is better?
Onshoring brings manufacturing back to a company's home country, enhancing supply chain control and reducing transportation costs, while reshoring specifically refers to returning previously offshored operations back domestically to reclaim lost economic benefits. Both strategies aim to strengthen local economies and improve responsiveness to market changes, but reshoring often addresses issues like quality control and intellectual property risks experienced abroad. Companies prioritize onshoring for proximity advantages and reshoring for rectifying past offshoring challenges, making the choice dependent on specific operational goals and industry context.
Connection
Onshoring and reshoring both involve relocating production and services back to a company's home country to enhance supply chain resilience and reduce costs associated with offshore operations. Onshoring emphasizes establishing new domestic facilities, while reshoring focuses on bringing previously offshored activities back home. These strategies contribute to job creation, improved regulatory compliance, and strengthened economic growth within the domestic market.
Key Terms
Supply Chain
Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing and supply chain operations back to the company's original country to reduce logistics costs, improve quality control, and mitigate risks associated with long-distance supply chains. Onshoring specifically refers to relocating operations within the same country to streamline operations and enhance supply chain responsiveness. Explore detailed strategies and benefits of reshoring versus onshoring in supply chain management to optimize your business operations.
Production Location
Reshoring involves relocating production back to a company's original country, while onshoring refers to moving production to a different location within the same country. Companies choose reshoring to reduce supply chain risks and improve quality control near their headquarters, whereas onshoring aims to capitalize on regional advantages such as labor skills or resource availability. Explore more to understand how reshoring and onshoring strategies impact operational efficiency and cost management.
Cost Competitiveness
Reshoring and onshoring both aim to enhance cost competitiveness by reducing supply chain complexities, transportation expenses, and import tariffs. Reshoring involves bringing manufacturing back to the company's original country after offshoring, often to improve quality control and labor cost balance, while onshoring generally means producing within the same country to ensure proximity to the market. Discover how these strategies impact your business's financial efficiency and operational agility.
Source and External Links
Reshoring - SCRG - Reshoring is the process of bringing manufacturing operations back from a foreign country to a business's home country to regain control over quality, lead time, and supply chain visibility while reducing geopolitical risks.
What is Reshoring? Understanding Manufacturing Location Terms - Reshoring refers to the relocation of production back to the country where the company is headquartered from an outsourced overseas location, emphasizing a return to domestic manufacturing after a period of offshoring.
What is Reshoring? - Reshoring is the practice of bringing manufacturing and services back to the U.S. from overseas, aiming to strengthen the economy by creating jobs, reducing trade deficits, and lowering total product costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com