Price gouging involves sellers significantly increasing prices during high demand or emergencies, exploiting consumers' urgent needs, while predatory pricing refers to businesses setting prices extremely low to eliminate competition and establish market dominance. Both practices impact market dynamics and consumer welfare differently, with regulatory bodies scrutinizing their legality and consequences. Explore further to understand the economic implications and legal frameworks surrounding these pricing strategies.
Why it is important
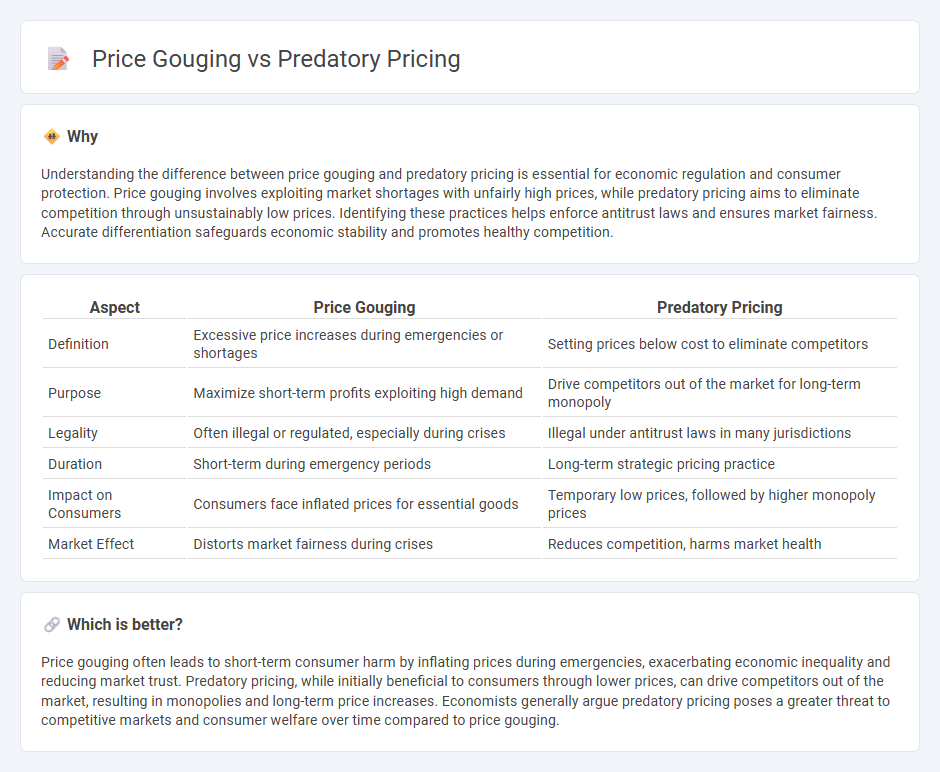
Understanding the difference between price gouging and predatory pricing is essential for economic regulation and consumer protection. Price gouging involves exploiting market shortages with unfairly high prices, while predatory pricing aims to eliminate competition through unsustainably low prices. Identifying these practices helps enforce antitrust laws and ensures market fairness. Accurate differentiation safeguards economic stability and promotes healthy competition.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Price Gouging | Predatory Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Excessive price increases during emergencies or shortages | Setting prices below cost to eliminate competitors |
| Purpose | Maximize short-term profits exploiting high demand | Drive competitors out of the market for long-term monopoly |
| Legality | Often illegal or regulated, especially during crises | Illegal under antitrust laws in many jurisdictions |
| Duration | Short-term during emergency periods | Long-term strategic pricing practice |
| Impact on Consumers | Consumers face inflated prices for essential goods | Temporary low prices, followed by higher monopoly prices |
| Market Effect | Distorts market fairness during crises | Reduces competition, harms market health |
Which is better?
Price gouging often leads to short-term consumer harm by inflating prices during emergencies, exacerbating economic inequality and reducing market trust. Predatory pricing, while initially beneficial to consumers through lower prices, can drive competitors out of the market, resulting in monopolies and long-term price increases. Economists generally argue predatory pricing poses a greater threat to competitive markets and consumer welfare over time compared to price gouging.
Connection
Price gouging and predatory pricing are connected through their impact on market pricing strategies that distort economic equilibrium. Both practices manipulate prices--price gouging inflates costs during high demand or shortages, while predatory pricing involves setting prices extremely low to eliminate competition. These tactics undermine fair competition, disrupt supply and demand balance, and can lead to long-term market inefficiencies.
Key Terms
Market Power
Predatory pricing involves setting prices below cost to eliminate competitors and establish market dominance, reflecting significant market power. Price gouging occurs when sellers exploit a lack of competition or emergency conditions to charge excessively high prices, also indicative of market power but under different circumstances. Explore the distinctions between predatory pricing and price gouging to understand their impact on consumer welfare and market competition.
Consumer Harm
Predatory pricing involves setting prices extremely low to eliminate competitors, risking future higher prices and reduced market competition, which ultimately harms consumers by limiting choice. Price gouging occurs when sellers drastically increase prices during emergencies, exploiting consumer vulnerability and leading to immediate financial strain. Explore the distinctions between these harmful pricing strategies and their impact on consumer welfare.
Regulatory Intervention
Regulatory intervention in predatory pricing targets anti-competitive behavior where firms set prices below cost to eliminate rivals, violating antitrust laws enforced by agencies like the Federal Trade Commission (FTC). Price gouging regulations focus on preventing unfairly high prices during emergencies or supply shortages, with statutes varying by state and often activated during declared disasters. Explore detailed differences in enforcement mechanisms and legal standards for a comprehensive understanding.
Source and External Links
How Predatory Pricing Works to Reduce Competition (2025) - Predatory pricing is a strategy where a company sets unsustainably low prices, often below cost, to drive competitors out, then later raises prices to gain monopoly power.
Business Guide to Predatory Pricing - Predatory pricing involves two phases: an initial below-cost pricing to weaken competitors, followed by a recoupment phase where prices increase to recover losses and gain dominance, distinguishing it from competitive pricing.
Predatory Pricing - Definition, Legalities, Examples - This strategy targets driving competitors out by sustained low pricing, requiring firms to absorb short-term losses for long-term market control and profits.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com