Soft saving emphasizes gradual accumulation and flexible financial goals, allowing for adaptable spending habits and emergency funds. Hard budgeting enforces strict, predetermined spending limits to maximize savings and control expenses rigorously. Explore how each approach impacts financial stability and long-term wealth building.
Why it is important
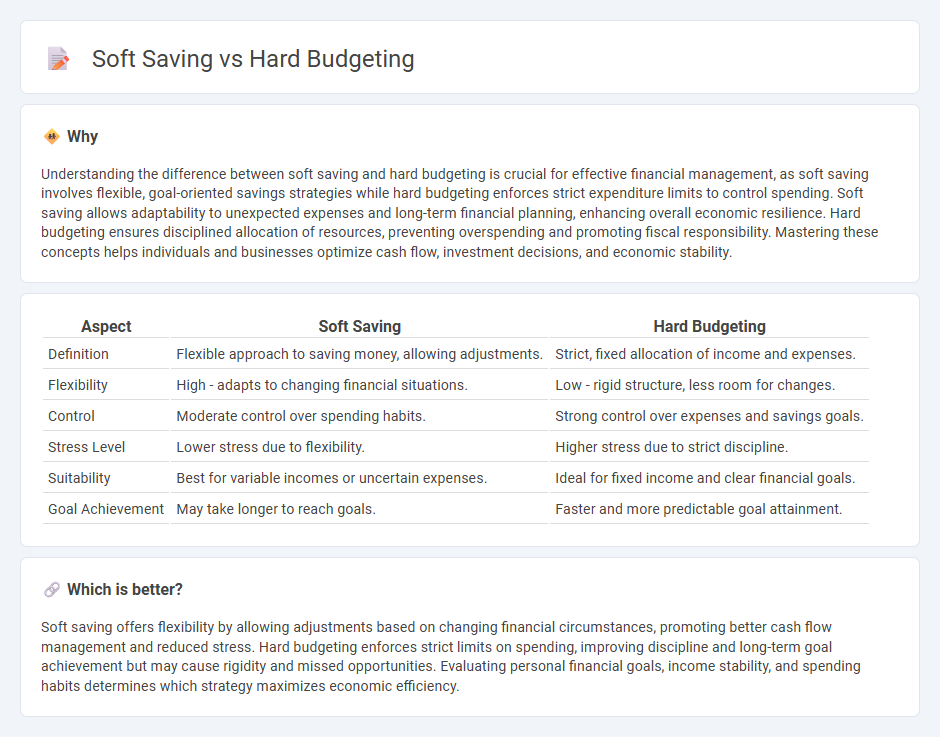
Understanding the difference between soft saving and hard budgeting is crucial for effective financial management, as soft saving involves flexible, goal-oriented savings strategies while hard budgeting enforces strict expenditure limits to control spending. Soft saving allows adaptability to unexpected expenses and long-term financial planning, enhancing overall economic resilience. Hard budgeting ensures disciplined allocation of resources, preventing overspending and promoting fiscal responsibility. Mastering these concepts helps individuals and businesses optimize cash flow, investment decisions, and economic stability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Soft Saving | Hard Budgeting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Flexible approach to saving money, allowing adjustments. | Strict, fixed allocation of income and expenses. |
| Flexibility | High - adapts to changing financial situations. | Low - rigid structure, less room for changes. |
| Control | Moderate control over spending habits. | Strong control over expenses and savings goals. |
| Stress Level | Lower stress due to flexibility. | Higher stress due to strict discipline. |
| Suitability | Best for variable incomes or uncertain expenses. | Ideal for fixed income and clear financial goals. |
| Goal Achievement | May take longer to reach goals. | Faster and more predictable goal attainment. |
Which is better?
Soft saving offers flexibility by allowing adjustments based on changing financial circumstances, promoting better cash flow management and reduced stress. Hard budgeting enforces strict limits on spending, improving discipline and long-term goal achievement but may cause rigidity and missed opportunities. Evaluating personal financial goals, income stability, and spending habits determines which strategy maximizes economic efficiency.
Connection
Soft saving enhances financial flexibility by allowing incremental, adaptive savings strategies that align with fluctuating income and expenses, while hard budgeting enforces strict expenditure limits to ensure disciplined fund allocation. This connection optimizes economic stability by balancing flexible saving habits with rigid spending controls, promoting efficient capital accumulation and risk management. Integrating both approaches supports sustainable personal finance management and broader economic resilience.
Key Terms
Fiscal Discipline
Hard budgeting enforces strict adherence to predefined spending limits, reducing the risk of overspending and ensuring robust fiscal discipline. Soft saving encourages flexible saving habits, promoting gradual accumulation of reserves while allowing adaptive financial management. Explore effective strategies to balance hard budgeting and soft saving for optimized fiscal discipline.
Expenditure Control
Hard budgeting enforces strict expenditure limits to ensure spending does not exceed set thresholds, promoting disciplined financial management. Soft saving emphasizes gradual adjustments in spending habits, allowing flexibility while encouraging incremental savings growth. Explore effective strategies to balance hard budgeting and soft saving for optimal expenditure control.
Financial Flexibility
Hard budgeting enforces strict spending limits, ensuring rigid control over finances but potentially reducing adaptability for unexpected expenses. Soft saving promotes gradual accumulation of funds with flexible spending allowances, enhancing financial flexibility and responsiveness to changing needs. Discover how balancing these strategies can optimize your financial resilience.
Source and External Links
How to Budget Money: A Step-By-Step Guide - NerdWallet - Hard budgeting involves setting strict priorities like building an emergency fund first, then maximizing 401(k) matching, and paying off high-interest debt to effectively control spending and debt repayment.
Cutting Back and Keeping Up When Money is Tight - Hard budgeting requires realistic spending tracking, prioritizing essential bills, and preparing for unexpected expenses by maintaining an emergency fund to avoid debt.
11 Ways to Stick to Your Budget and Jump Start Your Savings - Hard budgeting can involve tactics like a spending freeze or no-spend challenge to strictly limit expenses to necessities, helping to reset spending habits and build savings.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com