Nearshoring involves relocating business processes to geographically closer countries to reduce costs and improve supply chain efficiency, while friendshoring focuses on shifting operations to politically allied nations to enhance security and stability. Both strategies aim to mitigate risks associated with global disruptions and evolving geopolitical tensions in the economy. Explore more to understand how nearshoring and friendshoring reshape global trade and economic resilience.
Why it is important
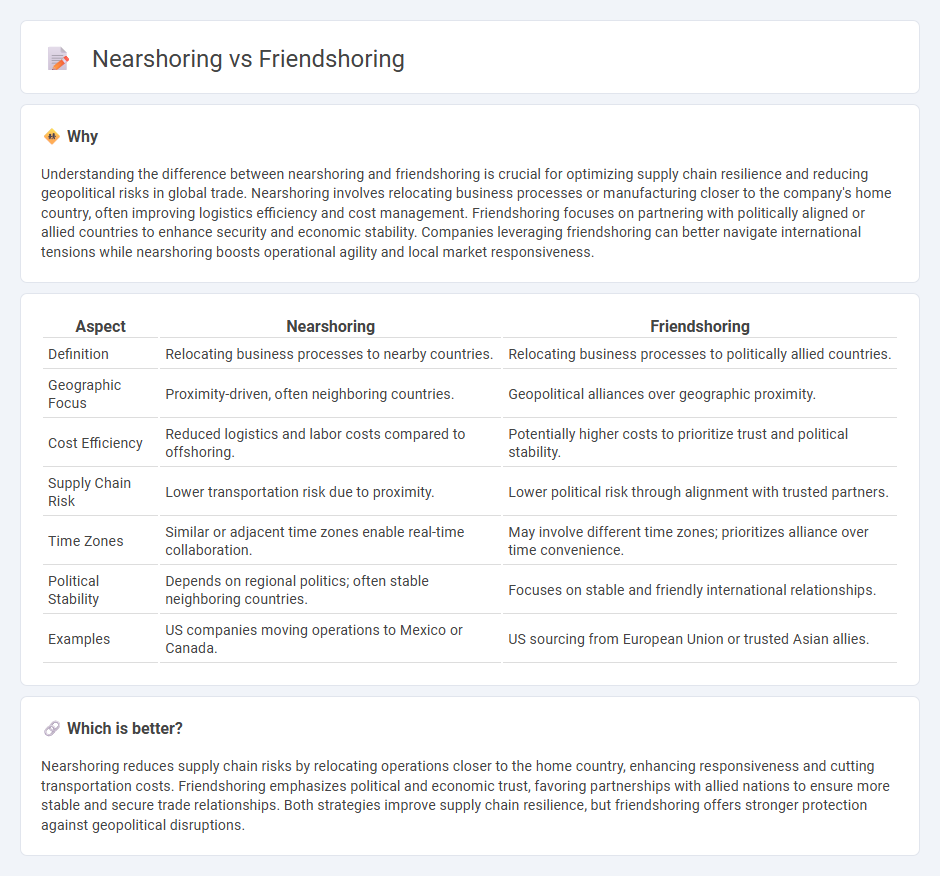
Understanding the difference between nearshoring and friendshoring is crucial for optimizing supply chain resilience and reducing geopolitical risks in global trade. Nearshoring involves relocating business processes or manufacturing closer to the company's home country, often improving logistics efficiency and cost management. Friendshoring focuses on partnering with politically aligned or allied countries to enhance security and economic stability. Companies leveraging friendshoring can better navigate international tensions while nearshoring boosts operational agility and local market responsiveness.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Nearshoring | Friendshoring |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Relocating business processes to nearby countries. | Relocating business processes to politically allied countries. |
| Geographic Focus | Proximity-driven, often neighboring countries. | Geopolitical alliances over geographic proximity. |
| Cost Efficiency | Reduced logistics and labor costs compared to offshoring. | Potentially higher costs to prioritize trust and political stability. |
| Supply Chain Risk | Lower transportation risk due to proximity. | Lower political risk through alignment with trusted partners. |
| Time Zones | Similar or adjacent time zones enable real-time collaboration. | May involve different time zones; prioritizes alliance over time convenience. |
| Political Stability | Depends on regional politics; often stable neighboring countries. | Focuses on stable and friendly international relationships. |
| Examples | US companies moving operations to Mexico or Canada. | US sourcing from European Union or trusted Asian allies. |
Which is better?
Nearshoring reduces supply chain risks by relocating operations closer to the home country, enhancing responsiveness and cutting transportation costs. Friendshoring emphasizes political and economic trust, favoring partnerships with allied nations to ensure more stable and secure trade relationships. Both strategies improve supply chain resilience, but friendshoring offers stronger protection against geopolitical disruptions.
Connection
Nearshoring and friendshoring are interconnected strategies reshaping global supply chains by relocating production closer to home or to politically allied countries, enhancing economic resilience and reducing dependency on distant or adversarial regions. Both approaches prioritize supply chain security, cost efficiency, and risk mitigation amid geopolitical tensions and trade disruptions. The combined implementation of nearshoring and friendshoring fosters regional economic integration and strengthens strategic partnerships.
Key Terms
Supply Chain Resilience
Friendshoring leverages trusted allies to establish supply chains, enhancing security and reducing geopolitical risks compared to nearshoring, which focuses on proximity to minimize transportation costs and lead times. Supply chain resilience improves with friendshoring by diversifying sources in politically stable regions, whereas nearshoring strengthens agility and responsiveness through closer geographic alignment. Explore detailed insights on how each strategy impacts supply chain resilience and operational efficiency.
Geopolitical Risk
Friendshoring minimizes geopolitical risk by relocating supply chains to allied countries with stable political relationships, reducing exposure to trade disputes and sanctions. Nearshoring shifts production closer to home but may not fully mitigate risks if the nearby country faces political instability or conflicting alliances. Explore how precise geopolitical risk assessments can guide strategic decisions between friendshoring and nearshoring.
Production Location
Friendshoring involves relocating production to politically stable, allied countries to reduce supply chain risks, while nearshoring focuses on moving manufacturing closer to the home country, often within neighboring regions, to cut transportation costs and improve lead times. Companies choosing friendshoring prioritize geopolitical alignment and security, whereas nearshoring emphasizes geographic proximity and regional economic integration. Explore how these strategies impact global supply chain resilience and operational efficiency.
Source and External Links
What is Friendshoring, Nearshoring, Reshoring and Offshoring - Friendshoring is a supply chain strategy where businesses source or produce goods in countries with shared values to build more stable and predictable logistics with trusted allies, focusing on security and shared standards rather than just cost savings.
What is 'friendshoring'? This and other global trade buzzwords - Friendshoring refers to rerouting supply chains to countries seen as politically and economically safe or low-risk allies, aiming to avoid disruptions caused by geopolitical tensions and to diversify critical material sourcing.
Friendshoring - Wikipedia - Friendshoring, also known as allyshoring, is the practice of manufacturing and sourcing from countries that are geopolitical allies, such as members of the same trade bloc or military alliance, to reduce geopolitical risks but with potential downsides like higher costs.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com