Gigification transforms the economy by promoting flexible, short-term contracts over traditional permanent employment, impacting job security and labor market dynamics. Studies show gig workers face income volatility and limited benefits compared to permanent employees, influencing consumer spending and social welfare systems. Explore the economic implications and future trends of gigification versus permanent contracts to understand their role in shaping modern labor markets.
Why it is important
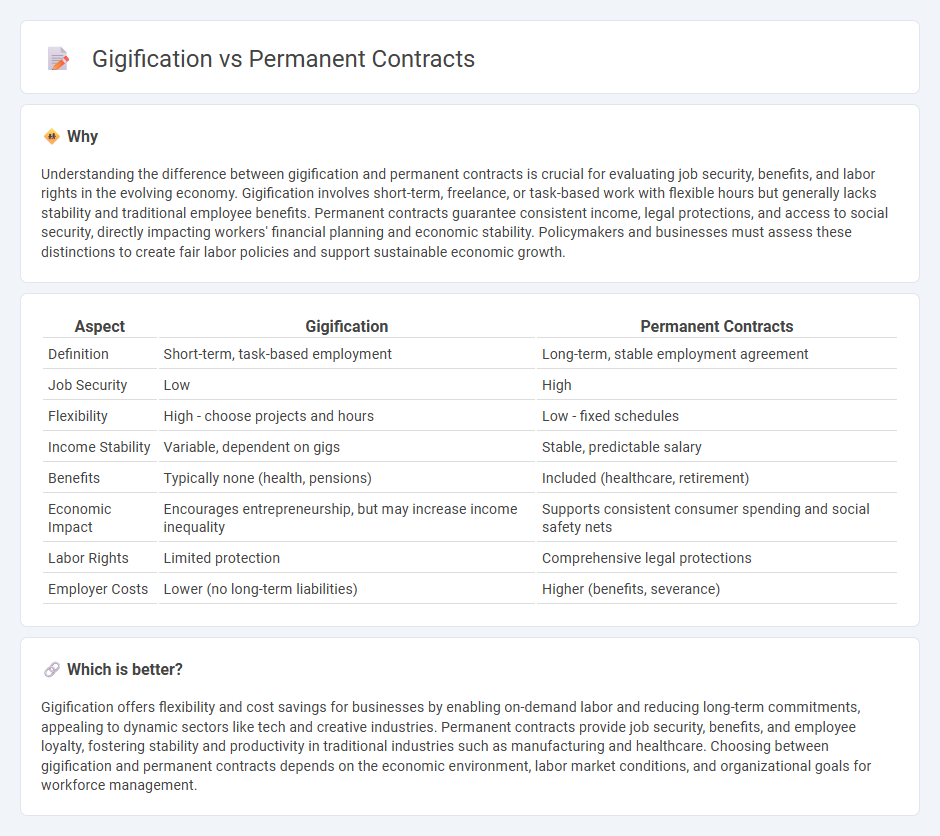
Understanding the difference between gigification and permanent contracts is crucial for evaluating job security, benefits, and labor rights in the evolving economy. Gigification involves short-term, freelance, or task-based work with flexible hours but generally lacks stability and traditional employee benefits. Permanent contracts guarantee consistent income, legal protections, and access to social security, directly impacting workers' financial planning and economic stability. Policymakers and businesses must assess these distinctions to create fair labor policies and support sustainable economic growth.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gigification | Permanent Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, task-based employment | Long-term, stable employment agreement |
| Job Security | Low | High |
| Flexibility | High - choose projects and hours | Low - fixed schedules |
| Income Stability | Variable, dependent on gigs | Stable, predictable salary |
| Benefits | Typically none (health, pensions) | Included (healthcare, retirement) |
| Economic Impact | Encourages entrepreneurship, but may increase income inequality | Supports consistent consumer spending and social safety nets |
| Labor Rights | Limited protection | Comprehensive legal protections |
| Employer Costs | Lower (no long-term liabilities) | Higher (benefits, severance) |
Which is better?
Gigification offers flexibility and cost savings for businesses by enabling on-demand labor and reducing long-term commitments, appealing to dynamic sectors like tech and creative industries. Permanent contracts provide job security, benefits, and employee loyalty, fostering stability and productivity in traditional industries such as manufacturing and healthcare. Choosing between gigification and permanent contracts depends on the economic environment, labor market conditions, and organizational goals for workforce management.
Connection
Gigification reshapes labor markets by increasing short-term, freelance opportunities, which challenges the prevalence of permanent contracts that traditionally offer job security and benefits. The rise of gig work pressures companies to balance flexible workforce needs with the stability provided by permanent employment, influencing employment policies and economic stability. This dynamic affects labor market trends, wage structures, and social protection frameworks globally.
Key Terms
Job Security
Permanent contracts offer employees job security through stable income, legal protections, and benefits such as health insurance and paid leave. The rise of gigification has shifted many workers into flexible, short-term roles with unpredictable earnings and limited employment rights, increasing job insecurity. Explore the implications of these employment trends on workforce stability and worker well-being.
Flexibility
Permanent contracts provide employees with job security, benefits, and predictable income, but often lack the flexibility gig work offers. Gigification enables workers to choose projects, set their schedules, and balance multiple income streams, appealing to those prioritizing autonomy. Explore how businesses and professionals navigate this shift toward flexible employment models.
Employee Benefits
Permanent contracts often provide comprehensive employee benefits such as health insurance, retirement plans, paid leave, and job security, which contribute to long-term financial stability and employee well-being. In contrast, gigification typically leads to fragmented benefits or none at all, as independent contractors or freelancers assume responsibility for their own insurance, retirement savings, and work-life balance. Explore the evolving landscape of employment benefits to understand how companies and workers are adapting to these contrasting models.
Source and External Links
Permanent Contract - Links International - A permanent contract is an employment agreement without a specified end date, providing long-term job security and access to benefits like health insurance and paid leave, unless either party terminates the contract with proper notice or for valid reasons.
What Is Permanent Contracts? - Sloneek(r) - A permanent contract is a legally binding agreement between employer and employee that details roles, remuneration, working hours, holidays, and termination notice periods, and may include benefits like healthcare, pension, or bonuses, along with post-termination restrictions.
Understanding the Permanent Contract for Employers - A permanent contract is an indefinite, legally binding agreement outlining job responsibilities, salary, working hours, benefits, and termination conditions, governed by employment laws such as the UK's Employment Rights Act 1996, which provides statutory rights and protections for employees.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com