The gig economy thrives on short-term, flexible jobs fueled by digital platforms, enabling workers to offer services like ride-sharing, freelance writing, or delivery on demand. The creative economy centers on industries focused on cultural, artistic, and design expertise, including sectors such as film, music, fashion, and digital media. Explore the distinctions between these dynamic economic models and their impact on labor markets and innovation.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between the gig economy and creative economy is crucial for policymakers and businesses to tailor labor regulations and investment strategies effectively. The gig economy primarily involves short-term, flexible jobs typically facilitated by digital platforms, while the creative economy centers on industries driven by individual creativity, cultural value, and intellectual property. Recognizing these distinctions helps optimize workforce development, resource allocation, and economic growth by addressing sector-specific needs and challenges. This knowledge supports informed decisions that foster innovation, job creation, and sustainable economic resilience.
Comparison Table
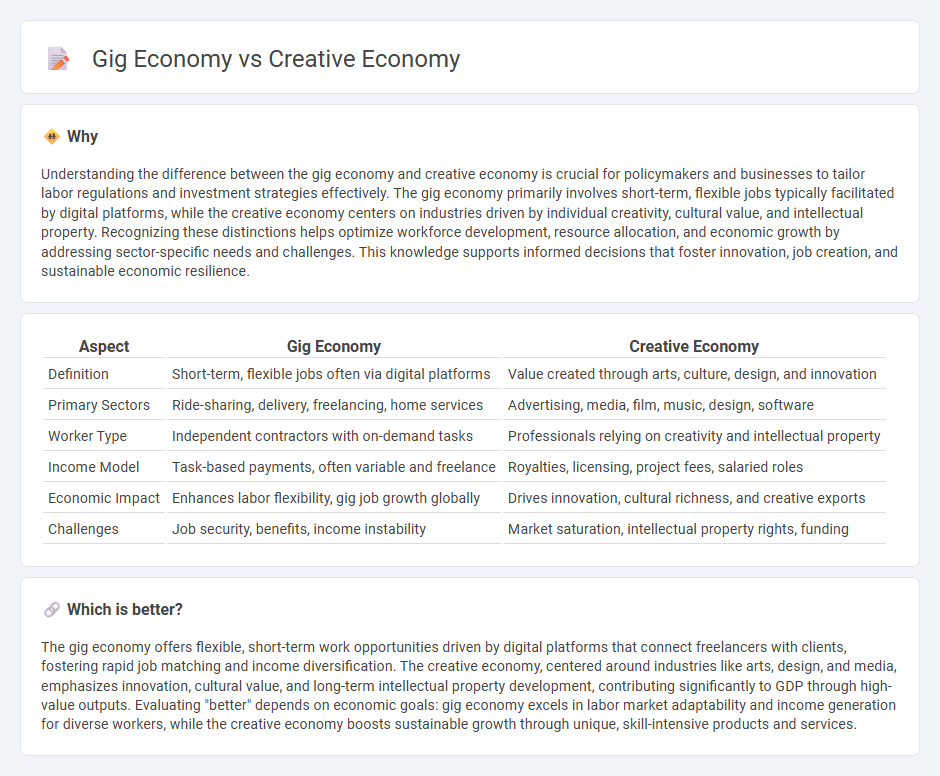
| Aspect | Gig Economy | Creative Economy |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Short-term, flexible jobs often via digital platforms | Value created through arts, culture, design, and innovation |
| Primary Sectors | Ride-sharing, delivery, freelancing, home services | Advertising, media, film, music, design, software |
| Worker Type | Independent contractors with on-demand tasks | Professionals relying on creativity and intellectual property |
| Income Model | Task-based payments, often variable and freelance | Royalties, licensing, project fees, salaried roles |
| Economic Impact | Enhances labor flexibility, gig job growth globally | Drives innovation, cultural richness, and creative exports |
| Challenges | Job security, benefits, income instability | Market saturation, intellectual property rights, funding |
Which is better?
The gig economy offers flexible, short-term work opportunities driven by digital platforms that connect freelancers with clients, fostering rapid job matching and income diversification. The creative economy, centered around industries like arts, design, and media, emphasizes innovation, cultural value, and long-term intellectual property development, contributing significantly to GDP through high-value outputs. Evaluating "better" depends on economic goals: gig economy excels in labor market adaptability and income generation for diverse workers, while the creative economy boosts sustainable growth through unique, skill-intensive products and services.
Connection
The gig economy and creative economy intersect through freelance and project-based work that fuels innovation and flexibility in markets. Platforms like Upwork and Fiverr enable creative professionals to monetize skills such as graphic design, writing, and digital marketing within the gig framework. This synergy drives economic growth by leveraging individual talents to meet diverse, on-demand consumer and business needs globally.
Key Terms
Creative economy:
The creative economy drives value through innovation, cultural expression, and intellectual property, encompassing industries like design, music, film, and advertising. It significantly contributes to GDP, employment, and urban development by fostering artistic talent and enabling creative entrepreneurship. Explore further insights to understand how the creative economy shapes modern business ecosystems.
Intellectual Property
The creative economy centers on generating value through intellectual property (IP) protection, including copyrights, trademarks, and patents that safeguard original works and innovations. In contrast, the gig economy prioritizes flexible, short-term contract work often lacking comprehensive IP rights, posing challenges for creators in protecting their contributions. Explore how intellectual property frameworks shape opportunities and challenges across these dynamic economic models.
Innovation
The creative economy thrives on innovation by leveraging unique artistic talents and intellectual property to generate economic value, while the gig economy centers on flexible, short-term tasks often enabled by digital platforms. Innovation in the creative economy drives new content, products, and cultural experiences, fueling sectors like design, media, and technology. Explore how these economic models shape the future of work and creativity in greater detail.
Source and External Links
Creative Economy - Washington innovation personified - The creative economy emphasizes the creation and commercialization of new products, services, and ideas through intellectual property, enabling diverse and inclusive growth without the need for traditional physical assets.
The Creative Economy - The Policy Circle - The creative economy, contributing over 6% to global GDP, drives job creation, innovation, and cultural promotion, with a strong focus on entrepreneurship, especially among artists and creative professionals.
Creative Economy Programme - UNCTAD - The creative economy is a dynamic, knowledge-based sector encompassing a wide range of industries--from arts to technology--that generate both commercial and cultural value through the trade of creative goods, services, and intellectual property.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com